Abstract
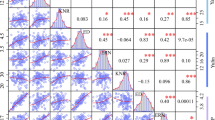
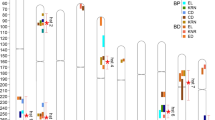
Cell-wall invertases (CWINVs), responsible for the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose, play important roles in plant development. Maize (Zea mays L.) ear-related traits were suggested to be important components of kernel yield. However, the association and nucleotide polymorphisms of maize CWINV genes with ear-related traits remain largely unclear. Herein, the maize ZmCWINV3 gene was re-sequenced in 301 inbred lines, 71 landraces and 31 teosintes to mine excellent variations associated with ear-related traits. A total of 594 variants, including 498 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 96 insertions and deletions (InDels), were identified in maize ZmCWINV3 locus. Five polymorphism sites in ZmCWINV3 were found to be significantly associated with six ear-related traits. Among them, a non-synonymous mutation SNP3694 was found to be significantly associated with ear weight (EW), ear grain weight (EGW), ear length (EL) and kernel length (KL). Further evidence revealed that the excellent allele T of SNP3694 was not exist in teosintes, while its frequencies raised to 9.86% and 69.44% in landraces and inbred lines, respectively. These observations suggested that the excellent allelic variations in ZmCWINV3 might possess potential application values in the genetic improvement of ear-related traits in maize.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the findings of this study are available in Supplementary Table S1 and Supplementary Dataset S1.
References
Bates D, Machler M, Bolker BM, Walker SC (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67(1):1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Chen L, Li YX, Li C, Shi Y, Song Y, Zhang D, Wang H, Li Y, Wang T (2020) The retromer protein ZmVPS29 regulates maize kernel morphology likely through an auxin-dependent process(es). Plant Biotechnol J 18(4):1004–1014. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13267
Cho JI, Lee SK, Ko SH, Kim HK, Jun SH, Lee YH, Bhoo SH, Lee KW, An GH, Hahn TR, Jeon JS (2005) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the cell-wall invertase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 24(4):225–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-004-0910-z
Choi M, Scholl UI, Ji W, Liu T, Tikhonova IR, Zumbo P, Nayir A, Bakkaloğlu A, Ozen S, Sanjad S, Nelson-Williams C, Farhi A, Mane S, Lifton RP (2009) Genetic diagnosis by whole exome capture and massively parallel DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(45):19096–19101. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910672106
Chourey PS, Jain M, Li QB, Carlson SJ (2006) Genetic control of cell wall invertases in developing endosperm of maize. Planta 223(2):159–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0039-5
Estruch JJ, Beltrán JP (1991) Gibberellic acid stimulates acid invertase secretion in pea ovary protoplasts. FEBS Lett 279(2):303–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(91)80173-z
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54(1):357–374. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134907
French SR, Abu-Zaitoon Y, Uddin MM, Bennett K, Nonhebel HM (2014) Auxin and cell wall invertase related signaling during rice grain development. Plants (basel) 3(1):95–112. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants3010095
Jia H, Li M, Li W, Liu L, Jian Y, Yang Z, Shen X, Ning Q, Du Y, Zhao R, Jackson D, Yang X, Zhang Z (2020) A serine/threonine protein kinase encoding gene KERNEL NUMBER PER ROW6 regulates maize grain yield. Nat Commun 11(1):988. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14746-7
Jiao Y, Zhao H, Ren L, Song W, Zeng B, Guo J, Wang B, Liu Z, Chen J, Li W, Zhang M, Xie S, Lai J (2012) Genome-wide genetic changes during modern breeding of maize. Nat Genet 44(7):812-U124. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2312
Juarez-Colunga S, Lopez-Gonzalez C, Cecilia Morales-Elias N, Armando Massange-Sanchez J, Trachsel S, Tiessen A (2018) Genome-wide analysis of the invertase gene family from maize. Plant Mol Biol 97(4–5):385–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0746-5
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Li Y, Ma X, Wang T, Li Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Sun B, Shi Y, Song Y, Carlone M, Bubeck D, Bhardwaj H, Whitaker D, Wilson W, Jones E, Wright K, Sun S, Niebur W, Smith S (2011a) Increasing maize productivity in china by planting hybrids with germplasm that responds favorably to higher planting densities. Crop Sci 51(6):2391–2400. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2011.03.0148
Li C, Li Q-G, Dunwell JM, Zhang Y-M (2012) Divergent evolutionary pattern of starch biosynthetic pathway genes in grasses and dicots. Mol Biol Evol 29(10):3227–3236. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss131
Li P, Pan T, Wang H, Wei J, Chen M, Hu X, Zhao Y, Yang X, Yin S, Xu Y, Fang H, Liu J, Xu C, Yang Z (2019a) Natural variation of ZmHKT1 affects root morphology in maize at the seedling stage. Planta 249(3):879–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-3043-2
Li P, Wei J, Wang H, Fang Y, Yin S, Xu Y, Liu J, Yang Z, Xu C (2019b) Natural variation and domestication selection of ZmPGP1 affects plant architecture and yield-related traits in maize. Genes (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090664
Li P, Ge Z, Wang H, Wei J, Wang Y, Xu Y, Yang Z, Xu C (2020) Nucleotide diversity and association analysis of ZmMADS60 with root length in the maize seedling stage. Agronomy (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030342
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25(11):1451–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Liu R, Jia H, Cao X, Huang J, Li F, Tao Y, Qiu F, Zheng Y, Zhang Z (2012) Fine mapping and candidate gene prediction of a pleiotropic quantitative trait locus for yield-related trait in zea mays. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049836
Paradis E (2010) pegas: an R package for population genetics with an integrated-modular approach. Bioinformatics 26(3):419–420. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp696
Pfeifer B, Wittelsbuerger U, Ramos-Onsins SE, Lercher MJ (2014) PopGenome: an efficient swiss army knife for population genomic analyses in R. Mol Biol Evol 31(7):1929–1936. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu136
Qin G, Zhu Z, Wang W, Cai J, Chen Y, Li L, Tian S (2016) A tomato vacuolar invertase inhibitor mediates sucrose metabolism and influences fruit ripening. Plant Physiol 172(3):1596–1611. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01269
Shen S, Ma S, Liu Y, Liao S, Li J, Wu L, Kartika D, Mock HP, Ruan YL (2019) Cell wall invertase and sugar transporters are differentially activated in tomato styles and ovaries during pollination and fertilization. Front Plant Sci 10:506. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00506
Slewinski TL (2011) Diverse functional roles of monosaccharide transporters and their homologs in vascular plants: a physiological perspective. Mol Plant 4:641–662. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr051
Sturm A (1999) Invertases. Primary structures, functions, and roles in plant development and sucrose partitioning. Plant Physiol 121(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.121.1.1
Thornsberry JM, Goodman MM, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Nielsen D, Buckler ES (2001) Dwarf8 polymorphisms associate with variation in flowering time. Nat Genet 28(3):286–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/90135
Vens M, Ziegler A (2017) Estimating disequilibrium coefficients. In: Elston RC (ed) Statistical human genetics: methods and protocols. Springer, NY, pp 117–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7274-6_7
Wang J, Caballero A, Hill WG (1998) The effect of linkage disequilibrium and deviation from Hardy-Weinberg proportions on the changes in genetic variance with bottlenecking. Heredity 81(2):174–186. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.1998.00390.x
Whitt SR, Wilson LM, Tenaillon MI, Gaut BS, Buckler ESt, (2002) Genetic diversity and selection in the maize starch pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(20):12959–12962. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.202476999
Xu S, Yang Z, Zhang E, Jiang Y, Pan L, Chen Q, Xie Z, Xu C (2014) Nucleotide diversity of Maize ZmBT1 gene and association with starch physicochemical properties. PLoS ONE 9(8):e103627. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103627
Yan W, Wu X, Li Y, Liu G, Cui Z, Jiang T, Ma Q, Luo L, Zhang P (2019) Cell wall invertase 3 affects cassava productivity via regulating sugar allocation from source to sink. Front Plant Sci 10:541. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00541
Yang Z, Zhang E, Jiang Y, Xu S, Pan L, Chen Q, Xu C (2014) Sequence polymorphisms in Zmisa2 gene are significantly associated with starch pasting and gelatinization properties in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Breeding 34(4):1833–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0142-z
Yang ZF, Ma SJ, Hu YY, Zhang EY, Xie ZW, Xu SH, Liu L, Deng LL, Xu CW, Huang JL (2015) Association analysis of the maize gene ZmYS1 with kernel mineral concentrations. Plant Mol Biol Rep 33(5):1327–1335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0836-8
Zhang J, Wu Z, Hu F, Liu L, Huang X, Zhao J, Wang H (2018) Aberrant seed development in Litchi chinensis is associated with the impaired expression of cell wall invertase genes. Hortic Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-018-0042-1
Zhou Z, Li G, Tan S, Li D, Weiss TM, Wang X, Chen S, Wuerschum T, Liu W (2020) A QTL atlas for grain yield and its component traits in maize (Zea mays). Plant Breeding 139(3):562–574. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12809
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070558, 32061143030, 31801028, 31972487, 32100448), a project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20210799).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.Z., C.X. and Z.Y. conceived and designed the research. Y.L., R.C., M.Z., Z.Z. and Y.Z. performed the association analyses and relative analyses. T.T., Y.J., Z.Z., E.Z., D.H., P.L. and Y.X. collected and analyzed the phenotypic data. M.Z., C.X. and Z.Y. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Lu, Y., Chen, R. et al. Nucleotide polymorphisms of the maize ZmCWINV3 gene and their association with ear-related traits. Genet Resour Crop Evol 69, 2115–2124 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01360-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01360-3