Abstract
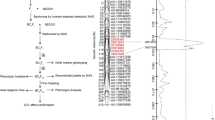
Ear traits play a vital role in maize (Zea mays) yield. The ear angle (EA) has an obvious impact on corn yield and planting density as well as other maize ear traits. However, the genetic control of EA is still unclear. In this study, we identified quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for EA from four recombinant inbred line populations, BY815/DE3, BY815/K22, CI7/K22 and Mo17/X26-4, which were grown in three environments, and the genetic architecture of EA in maize was subsequently dissected. The results indicated that maize EA was highly heritable and was affected by both genotype and environment. Based on the genetic linkage map constructed using 56,110 bins as markers, nine effective QTLs for maize EA were detected locating on chromosomes 2, 3, 4, 6 and 7. These QTLs accounted for different EA variations ranging from 5.5% (qCIKEA6) to 7.6% (qBYKEA3). Moreover, 14 candidate genes were identified from the reduced QTLs using a bin-map method, which mainly encoded enzymes in signal transduction, transcriptional regulation and metabolism. Conclusively, our results can benefit further study of the genetic basis of EA and improve the maize EA quality through molecular breeding.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB, Typeset IL (2005) Windows QTL cartographer v.2.5
Blösch R, Plaza WS, Barbier RP et al (2020) Panicle angle is an important factor in Tef lodging tolerance. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00061.eCollection
Chen GX, Liu JB, Hong DL (2006) Genetic analysis on panicle angle and number of spikelets per panicle by using six generations of three crosses derived from erect × curve panicles in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). ACTA Agron Sin 32(2):1143–1150 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen ZL, Wang BB, Dong XM et al (2014) An ultra-high density bin-map for rapid QTL mapping for tassel and ear architecture in a large F2 maize population. BMC Genom 15:433. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-433
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138(3):963–971
de Givry S, Bouchez M, Chabrier P et al (2005) CARHT A GENE: multipopulation integrated genetic and randiation hybrid mapping. Bioinformatics 21:1703–1704
Ding J, Zhang L, Chen J et al (2015) Genomic dissection of leaf angle in maize (Zea mays L.) using a four-way cross mapping population. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0141619. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141619
Falconer D, Mackay T (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics. Longman, Burnt Mill
Ganal MW, Durstewitz G, Polley A et al (2011) A large maize (Zea mays L.) SNP genotyping array: development and germplasm genotyping, and genetic mapping to compare with the B73 reference genome. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28334. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028334
Goldman IL, Rocheford TR, Dudley JW (1993) Quantitative loci influencing protein and starch concentration in the Illinois long term selection maize strains. Theor Appl Genet 87(1–2):217–224
Guo J, Su G, Zhang J et al (2008) Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of maize yield and associate agronomic traits under semi-arid land condition. Afr J Biotechnol 7(12):1829–1838
Guo TT, Yang N, Tong H et al (2014) Genetic basis of grain yield heterosis in an “immortalized F2” maize population. Theor Appl Genet 127(10):2149–2158
Guo Z, Zou C, Liu X et al (2020) Complex genetic system involved in fusarium ear rot resistance in maize as revealed by GWAS, bulked sample analysis, and genomic prediction. Plant Dis. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-07-19-1552-re
He J, Li J, Huang Z et al (2015) Composite interval mapping based on lattice design for error control may increase power of quantitative trait locus detection. PLoS ONE 10:e0130125. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130125
Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Myers MA (2013) Seed genomics. Springer, New York
Huang BQ, Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Myers AM et al (2014) Functions of multiple genes encoding ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase subunits in maize endosperm, embryo, and leaf. Plant Physiol 164(2):596–611
Huang C, Chen QY, Xu GH et al (2016) Identification and fine mapping of quantitative trait loci for the number of vascular bundle in maize stem. J Integr Plant Biol 58(1):81–90
James M, Myers A (2009) Handbook of maize: its biology. Springer, New York
Jiang JH, Guo Y, Chen XG et al (2007) The correlation between panicle angle and rice quality and genetic analysis on rice quality in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Yi Chuan 29(6):714–724
Kao CH, Zeng ZB, Teasdale RD (1999) Multiple interval mapping for quantitative trait loci. Genetics 152:1203–1216
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence-intervals for heritability on a progeny mean sasis. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Koch K (2004) Sucrose metabolism: regulatory mechanisms and pivotal roles in sugar sensing and plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7(3):235–246
Kramer EM, Ackelsberg EM (2015) Auxin metabolism rates and implications for plant development. Front Plant Sci 6:150
Ku LX, Zhao WM, Zhang J et al (2010) Quantitative trait loci mapping of leaf angle and leaf orientation value in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 121(5):951–959
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121(1):185–199
Li X, Cheng MJ, Wang Y et al (2010) Study on maize yield and its ear characters under water-limited conditions. J China Agric Univ 15(4):8–12 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Q, Yang X, Xu S et al (2012) Genome-wide association studies identified three independent polymorphisms associated with alpha-tocopherol content in maize kernels. PLoS ONE 7(5):e36807. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036807
Li C, Li Y, Shi Y et al (2015) Genetic control of the leaf angle and leaf orientation value as revealed by ultra-high density maps in three connected maize populations. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0121624. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121624
Li PC, Zhuang ZJ, Cai HG et al (2016a) Use of genotype-environment interactions to elucidate the pattern of maize root plasticity to nitrogen deficiency. J Integr Plant Biol 58(3):242–253
Li XN, Chen JX, Su WY et al (2016b) Correlation and path analysis of ear characters and yield in different maize combinations. Bull Agric Sci Technol 4:37–40 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Z, Liu P, Zhang X et al (2020) Genome-wide association studies and QTL mapping uncover the genetic architecture of ear tip-barrenness in maize. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13087
Liu JB, Hong DL (2005) Genetic analysis on panicle angle and number of spikelets per panicle in japonica rice (Oryza sativa). Chin J Rice Sci 19(3):223–230. https://doi.org/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2005.03.005(in Chinese with English abstract)
Mendes-Moreira P, Alves ML, Satovic Z et al (2015) Genetic architecture of ear fasciation in maize (Zea mays) under QTL scrutiny. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0124543. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124543
Mickelson SM, Stuber CS, Senior L et al (2002) Quantitative trait loci controlling leaf and tassel traits in a B73 × Mo17 population of maize. Crop Sci 42:1902–1909
Mitchell JW, Mandava N, Worley JF et al (1970) Brassins; a new family of plant hormonca from rape pollen. Nature 225(5237):1065–1068
Niu FA, Liu J, Guo Y et al (2013) New stably expressed loci responsible for panicle angle trait in Japonica rice in four environments. Rice Sci 20(2):111–119
Orawan J, Fu XY, Xu J et al (2017) Genetic dissection of carotenoids in maize kernels using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism markers in a recombinant inbred line population. Crop J 5(1):63–72
Ostheimer GJ, Rojas M, Hadjivassiliou H, Barkan A (2006) Formation of the CRS2-CAF2 group II intron splicing complex is mediated by a 22-amino acid motif in the COOH-terminal region of CAF2. J Biol Chem 281:4732–4738
Pan Q, Li L, Yang X et al (2016) Genome-wide recombination dynamics are associated with phenotypic variation in maize. New Phytol 210(3):1083–1094
Pautler M, Eveland AL, LaRue T et al (2015) FASCIATED EAR4 encodes a bZIP transcription factor that regulates shoot meristem size in maize. Plant Cell 27(1):104–120
Ren D, Rao Y, Wu L et al (2016) The pleiotropic ABNORMAL FlOWER AND DWARF1 affects plant height, floral development and grain yield in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 58:529–539
Robinson HF, Comstock RE, Harvey PH (1951) Genotupic and phenotypic correlations in corn and their implications in selection. Agron J 43(34):282–287
Song JJ, Liu JL, Zhou BM et al (2006) Study on the relationship between ear characters and yield in Maize. J Jilin Agric Sci 31(4):11–13 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song WB, Wang BB, Hauck AL et al (2016) Genetic dissection of maize seedling root system architecture traits using an ultra-high density bin-map and a recombinant inbred line population. J Integr Plant Biol 58(3):266–279
Sun SC (2019) Effect of plant density towards maize yield and traits in Shandong province. Agric Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.16815/j.cnki.11-5436/s.2019.11.013(in Chinese with English abstract)
Tai HH, Xin L, Nina O et al (2016) Transcriptomic and anatomical complexity of primary, seminal, and crown roots highlight root type-specific functional diversity in maize (Zea mays L.). J Exp Bot 67(4):1123–1135
Tang BJ, Ding Y (2008) Impact of plant density on maize yield and main agronomic traits. Chin Seed Ind 10:35–37. https://doi.org/10.19462/j.cnki.1671-895x.2008.10.014(in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang J, Yan J, Ma X et al (2010) Dissection of the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite maize hybrid by QTL mapping in an immortalized F2 population. Theor Appl Genet 120(2):333–340
Teppeman JM, Hwang YS, Quail PH (2006) HhyA dominates in transduction of red-light signals to rapidly-responding genes at the initiation of A rabidops is seeding de-etiolation. Plant J 48:728–742
Tong H (2015) Linkage analysis of ear characters in Maize. Dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University
Van OH, Stam P, Visser RG, Van Eck HJ (2015) RECORD: a novel method for ordering loci on a genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 112(1):30–40
Veldboom LR, Lee M (1994) Molecular-marker-facilitated studies of morphological traits in maize: II Determination of QTLs for grain yield and yield components. Theor Appl Genet 89(23):451–458
Wang T, Min W, Hu S et al (2015) Genetic basis of maize kernel starch content revealed by high-density single nucleotide polymorphism markers in a recombinant inbred line population. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):1–12
Wang B, Zhang ZH, Fu ZY et al (2016) Comparative QTL analysis of maize seed artificial aging between an immortalized F2 population and its corresponding RILs. Crop J 4(1):30–39
Wen WW, Li K, Alseekh S et al (2015) Genetic determinants of the network of primary metabolism and their relationships to plant performance in a maize recombinant inbred line population. Plant Cell 27(7):1839–1856
Xiao Y, Tong H, Yang X et al (2016) Genome-wide dissection of the maize ear genetic architecture using multiple populations. New Phytol 210(3):1095–1106
Xie WB, Feng Q, Yu HH et al (2010) Parent-independent genotyping for constructing an ultrahigh-density linkage map based on population sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(23):10578–10583
Yang X, Yan J, Shan T et al (2010) Genetic analysis and characterization of a new maize association mapping panel for quantitative trait loci dissection. Theor Appl Genet 121(3):417–431
Yu HH, Xie WB, Wang J et al (2011) Gains in QTL detection using an ultra-high density SNP map based on population sequencing relative to traditional RFLP/SSR markers. PLoS ONE 6(3):e17595. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017595
Zhang LG, Fan QJ, Chen XC et al (2012) Correlation analyisis between kernel dry-down rate and main agronomic traits after maize physiological mature. J Heilongjiang Agric Sci 3:1–5 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang J, Ku LX, Han ZP et al (2014) The ZmCLA4 gene in the qLA4-1 QTL controls leaf angle in maize (Zea mays L.). Exp Bot 65(17):5063–5076
Zou GH, Zhai GW, Feng Q et al (2012) Identification of QTLs for eight agronomically important traits using ultra-high-density map based on SNPs generated from high-throughput sequencing in sorghum under contrasting photoperiods. Exp Bot 63(15):5451–5462
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Professor Yang (China Agricultural University) for providing the seeds and genotypes of the four maize RIL populations. This work was supported by grants from the Technology Pillar Program of Liaoning Province, China (2015103001) and General Program of National Nature Science Foundation of China (31771880), and a grant from the Cultivation Plan for Youth Agricultural Science and Technology Innovative Talents of Liaoning Province (2015043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Li, S., Liang, G. et al. Genetic basis of maize ear angle revealed by high-density single nucleotide polymorphism markers in four recombinant inbred line populations. Euphytica 216, 132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02662-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02662-2