Abstract
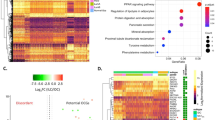
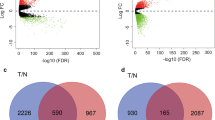
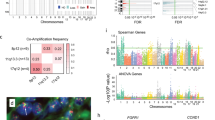
Breast cancer is a devastating malignancy, among which the luminal A (LumA) breast cancer is the most common subtype. In the present study, we used a comprehensive bioinformatics approach in the hope of identifying novel prognostic biomarkers for LumA breast cancer patients. Transcriptomic profiling of 611 LumA breast cancer patients was downloaded from TCGA database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between tumor samples and controls were first identified by differential expression analysis, before being used for the weighted gene co-expression network analysis. The subsequent univariate Cox regression and LASSO algorithm were used to uncover key prognostic genes for constructing multivariate Cox regression model. Patients were stratified into high-risk and low-risk groups according to the risk score, and subjected to multiple downstream analyses including survival analysis, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), inference on immune cell infiltration and analysis of mutation burden. Receiving operator curve analysis was also performed. A total of 7071 DEGs were first identified by edgeR package, pink module was found significantly associated with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC). 105 prognostic genes and 9 predictors were identified, allowing the identification of a 5-key prognostic genes (LRRC77P, CA3, BAMBI, CABP1, ATP8A2) after intersection. These 5 genes, and the resulting Cox model, displayed good prognostic performance. Furthermore, distinct differences existed between two risk-score stratified groups at various levels. The identified 5-gene prognostic model will help deepen the understanding of the molecular and immunological mechanisms that affect the survival of LumA-ILC patients and guide and proper monitoring of these patients.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysis are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- LumA:
-
Luminal A
- LumB:
-
Luminal B
- ER+:
-
Estrogen receptor
- HER2−:
-
Human epidermal growth receptor 2
- ILC:
-
Invasive lobular carcinoma
- IDC:
-
Invasive ductal carcinoma
- WGCNA:
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- ME:
-
Module eigengene
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein-interaction
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- GSEA:
-
Gene set enrichment analysis
- ES:
-
Enrichment score
- TIICs:
-
Tumor infiltrating immune cells
- CKM:
-
Creatine kinase, muscle
- MYH2:
-
Myosin heavy chain 2
- DHRS7C:
-
Dehydrogenase/Reductase 7C
- STRIT1:
-
Small transmembrane regulator of ion transport 1
- MIR1-1HG:
-
MIR1-1 host gene
- PPP1R3A:
-
Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3A
- MUC2:
-
Mucin 2
- CARTPT:
-
CART prepropeptide
- UCN3:
-
Urocortin 3
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
References
Astashchanka A, Shroka TM, Jacobsen BM (2019) Mucin 2 (MUC2) modulates the aggressiveness of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 173:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-4989-2
Banerjee A et al (2011) ARTEMIN synergizes with TWIST1 to promote metastasis and poor survival outcome in patients with ER negative mammary carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res 13:R112. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3054
Bar-Mashiah A, Soper ER, Cullina S, Belbin GM, Kenny EE, Lucas AL, Abul-Husn NS (2021) CDH1 pathogenic variants and cancer risk in an unselected patient population. Fam Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-021-00257-x
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, Banham AH (2006) Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol 24:5373–5380. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.05.9584
Bianchini G et al (2010) Molecular anatomy of breast cancer stroma and its prognostic value in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative cancers. J Clin Oncol 28:4316–4323. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.27.2419
Bieche I et al (2001) The CGA gene as new predictor of the response to endocrine therapy in ER alpha-positive postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Oncogene 20:6955–6959. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204739
Botia JA et al (2017) An additional k-means clustering step improves the biological features of WGCNA gene co-expression networks. BMC Syst Biol 11:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12918-017-0420-6
Burstein HJ, Polyak K, Wong JS, Lester SC, Kaelin CM (2004) Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. N Engl J Med 350:1430–1441. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra031301
Cheang MC et al (2009) Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:736–750. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djp082
Chu YH, Su CW, Hsieh YS, Chen PN, Lin CW, Yang SF (2020) Carbonic anhydrase III promotes cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030704
Ciriello G et al (2015) Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast. Cancer Cell 163:506–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.033
Desmedt C et al (2018) Immune infiltration in invasive lobular breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 110:768–776. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djx268
Dixon K et al (2021) Modelling hereditary diffuse gastric cancer initiation using transgenic mouse-derived gastric organoids and single-cell sequencing. J Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5675
Downing A, Harrison WJ, West RM, Forman D, Gilthorpe MS (2010) Latent class modelling of the association between socioeconomic background and breast cancer survival status at 5 years incorporating stage of disease. J Epidemiol Community Health 64:772–776. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2008.085852
Elkum N et al (2007) Being 40 or younger is an independent risk factor for relapse in operable breast cancer patients: the Saudi Arabia experience. BMC Cancer 7:222. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-7-222
Engstrom MJ, Opdahl S, Vatten LJ, Haugen OA, Bofin AM (2015) Invasive lobular breast cancer: the prognostic impact of histopathological grade E-cadherin and molecular subtypes. Histopathology 66:409–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12572
Esquivel-Velazquez M, Ostoa-Saloma P, Palacios-Arreola MI, Nava-Castro KE, Castro JI, Morales-Montor J (2015) The role of cytokines in breast cancer development and progression. J Interferon Cytokine Res 35:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2014.0026
Gao JJ, Swain SM (2018) Luminal A breast cancer and molecular assays: a review. Oncologist 23:556–565. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0535
Gobert M et al (2009) Regulatory T cells recruited through CCL22/CCR4 are selectively activated in lymphoid infiltrates surrounding primary breast tumors and lead to an adverse clinical outcome. Cancer Res 69:2000–2009. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2360
Graugaard-Jensen C, Hvistendahl GM, Frokiaer J, Bie P, Djurhuus JC (2008) The influence of high and low levels of estrogen on diurnal urine regulation in young women. BMC Urol 8:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2490-8-16
Guerrero-Zotano A, Mayer IA, Arteaga CL (2016) PI3K/AKT/mTOR: role in breast cancer progression, drug resistance, and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev 35:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-016-9637-x
Huan J, Wang L, Xing L, Qin X, Feng L, Pan X, Zhu L (2014) Insights into significant pathways and gene interaction networks underlying breast cancer cell line MCF-7 treated with 17beta-estradiol (E2). Gene 533:346–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.027
Jung SY, Sobel EM, Papp JC, Zhang ZF (2017) Effect of genetic variants and traits related to glucose metabolism and their interaction with obesity on breast and colorectal cancer risk among postmenopausal women. BMC Cancer 17:290. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3284-7
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Li B et al (2016) Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy. Genome Biol 17:174. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1028-7
Li J et al (2017a) Molecular differences between screen-detected and interval breast cancers are largely explained by PAM50 subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 23:2584–2592. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0967
Li T et al (2017b) TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res 77:e108–e110. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0307
Liu S, Zhang J, Zhu J, Jiao D, Liu Z (2020) Prognostic values of EDNRB in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Lett 20:149. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.12012
Mahmoud SM, Lee AH, Paish EC, Macmillan RD, Ellis IO, Green AR (2012) The prognostic significance of B lymphocytes in invasive carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1620-1
Martins IBS, Viegas TG, Dos Santos AD, de Souza BM, Palma MS, Ruggiero Neto J, de Araujo AS (2021) The effect of acidic pH on the adsorption and lytic activity of the peptides Polybia-MP1 and its histidine-containing analog in anionic lipid membrane: a biophysical study by molecular dynamics and spectroscopy. Amino Acids. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02982-0
Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C, Koeffler HP (2018) Maftools: efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res 28:1747–1756. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.239244.118
Mendez-Garcia LA et al (2019) Breast cancer metastasis: are cytokines important players during its development and progression? J Interferon Cytokine Res 39:39–55. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2018.0024
Mosele F et al (2020) Outcome and molecular landscape of patients with PIK3CA-mutated metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 31:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2019.11.006
Pandit P, Patil R, Palwe V, Gandhe S, Patil R, Nagarkar R (2020) Prevalence of molecular subtypes of breast cancer: a single institutional experience of 2062 patients. Eur J Breast Health 16:39–43. https://doi.org/10.5152/ejbh.2019.4997
Pink RC, Wicks K, Caley DP, Punch EK, Jacobs L, Carter DR (2011) Pseudogenes: pseudo-functional or key regulators in health and disease? RNA 17:792–798. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2658311
Poudel P, Nyamundanda G, Patil Y, Cheang MCU, Sadanandam A (2019) Heterocellular gene signatures reveal luminal-A breast cancer heterogeneity and differential therapeutic responses NPJ. Breast Cancer 5:21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-019-0116-8
Pratt SJP, Hernandez-Ochoa E, Martin SS (2020) Calcium signaling: breast cancer’s approach to manipulation of cellular circuitry. Biophys Rev 12:1343–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-020-00771-9
Russo J, Russo IH (2006) The role of estrogen in the initiation of breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 102:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.09.004
Shuwen H, Xi Y, Miao D, Jiamin X, Jing Z, Weili G (2020) Nine genes mediate the therapeutic effects of iodine-131 radiotherapy in thyroid carcinoma patients. Dis Markers 2020:9369341. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9369341
Sturm G et al (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of transcriptome-based cell-type quantification methods for immuno-oncology. Bioinformatics 35:i436–i445. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz363
Subramanian A et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Sun HW et al (2020) Glutamine deprivation promotes the generation and mobilization of MDSCs by enhancing expression of G-CSF and GM-CSF. Front Immunol 11:616367. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.616367
Taylor JM, Ankerst DP, Andridge RR (2008) Validation of biomarker-based risk prediction models. Clin Cancer Res 14:5977–5983. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-4534
Toi M et al (2017) Visualization of tumor-related blood vessels in human breast by photoacoustic imaging system with a hemispherical detector array. Sci Rep 7:41970. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41970
Vleminckx K, Vakaet L, Mareel M, Fiers W, Van Roy F (1991) Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell 66:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90143-m
Wang H, Cui Z (2015) The distribution and expression of BAMBI in breast cancer cell lines. Oalib 02:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1102147
Wen HY, Brogi E (2018) Lobular carcinoma in situ. Surg Pathol Clin 11:123–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.path.2017.09.009
West NR, Kost SE, Martin SD, Milne K, Deleeuw RJ, Nelson BH, Watson PH (2013) Tumour-infiltrating FOXP3(+) lymphocytes are associated with cytotoxic immune responses and good clinical outcome in oestrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Br J Cancer 108:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.524
Wind NS, Holen I (2011) Multidrug resistance in breast cancer: from in vitro models to clinical studies Int J. Breast Cancer 2011:967419. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/967419
Wu J, Zhang Y, Li M (2019) Identification of methylation markers and differentially expressed genes with prognostic value in breast cancer. J Comput Biol 26:1394–1408. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2019.0179
Xu H, Zhao Y, Gao X, Wang F, Gu Y (2021) An innovative fluorescent probe targeting IGF1R for breast cancer diagnosis. Eur J Med Chem 219:113440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113440
Yamashina S, Ikejima K, Rusyn I, Sato N (2007) Glycine as a potent anti-angiogenic nutrient for tumor growth. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(Suppl 1):S62-64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04655.x
Yang T et al (2018) Ca(2+)-binding protein 1 regulates hippocampal-dependent memory and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 380:90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.004
Yang L et al (2021) Diclofenac impairs the proliferation and glucose metabolism of triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting the c-Myc pathway. Exp Ther Med 21:584. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10016
Yu X, Guo J, Zhou Q, Huang W, Xu C, Long X (2021) A novel immune-related prognostic index for predicting breast cancer overall survival. Breast Cancer 28:434–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-020-01175-z
Zhao J, Wang B, Zhao J, Mao Y, Liu J, Yang Y (2020) Male breast cancer: a closer look at patient and tumor characteristics and factors associated with survival. Thorac Cancer 11:3107–3116. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13611
Zheng QX, Wang J, Gu XY, Huang CH, Chen C, Hong M, Chen Z (2021) TTN-AS1 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for multiple cancers. Biomed Pharmacother 135:111169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111169
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shantou Medical Science and Technology Planning Project [Grant Numbers 210521236491457, 210625106490696], the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China [grant numbers A2021432, B2021448], the Special Fund Project of Guangdong Science and Technology [Grant Numbers 210728156901524, 210728156901519] and the Undergraduate Innovation Training Project of Shantou University [Grant Number 31/38/47/54].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZYL and YHC designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data as well as wrote the manuscript. TZ, YL, JHZ, WL, YKC, JC and JZ contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data. ZYL designed the study and supervised the work. All the authors have read and approved the final version of the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10709_2022_157_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 (TIF 4449 kb). Supplementary Figure S1. Disease-free survival analysis of the the prognostic predictors
10709_2022_157_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 (TIF 4556 kb). Supplementary Figure S2. Progression specific survival analysis of the the prognostic predictors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YH., Zhang, TF., Liu, YY. et al. Identification of a 5-gene-risk score model for predicting luminal A-invasive lobular breast cancer survival. Genetica 150, 299–316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-022-00157-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-022-00157-7