Abstract
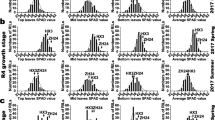
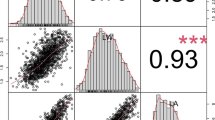
Leaf pigment content is a complicated quantitative trait which results from the cooperation of multiple related genes or quantitative trait loci (QTL) in rice. So far, more than 600 QTL for leaf pigment content has been reported. However, most QTL positions could not be directly compared with each other. In this study, our goal was to analyze consistent QTL regions affecting leaf pigment content by applying a genome wide QTL meta-analysis approach. 20 QTL related to leaf pigment content were detected at 5 different growth periods in 134 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) from a typical Indica-Japonica cross derived from PA64s and 9311 (two parents of super hybrid rice Liangyoupei 9). There was a candidate gene GLTP in the region of 3 QTL (qFS_Chla4, qFS_Chla+b4, and qFS_Car4), which related to component of chloroplast thylakoid membranes. After sequencing and qRT-PCR analysis, the gene showed significant difference in parents of the RILs. Meta-analysis was performed on 618 QTL collected from 38 previous studies. Consequently, a total of 64 MQTL (Meta-QTL) were obtained, of which 58.95% confidence intervals (CI) were smaller than the average Cl of the original QTL. In addition, 64 MQTL covered 6 of 20 QTL detected. Among them, four main QTL were included in 3 MQTL, and phenotypic variation of 21 MQTL was greater than 20%. The traits with higher number of QTL had higher number of MQTL, and candidate genes in overlapping MQTL include multiple effects. 7 candidate genes related to leaf pigment content were found in 4 MQTL spanning physical intervals < 0.5 Mb. These findings are not only anticipated to help molecular marker-assisted selection and pyramiding, but also contribute to determine candidate genes that regulate pigment content.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A-JIA LT, Zeng LJ, Xue DW et al (2008) QTL analysis for chlorophyll content in four grain-filling stage in rice. Acta Agron Sin 34:61–66
Alscher RG, Erturk N, Heath LS (2002) Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 53:1331–1341. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1331
Andersson B, Anderson JM (1980) Lateral heterogeneity in the distribution of chlorophyll protein complexes in the thylakoid membranes of spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 593:427–440
Andersson I, Backlund A (2008) Structure and function of Rubisco. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:275–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.01.001
Anne A, Aymeric L, Matthieu F et al (2004) Biomercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324–2326. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.02-1094
Beale SI (2005) Green genes gleaned. Trends Plant Sci 10:309–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.05.005
Betterle N, Ballottari M, Baginsky S et al (2015) High light-dependent phosphorylation of photosystem II inner antenna CP29 in monocots is STN7 independent and enhances nonphotochemical quenching. Plant Physiol 167:457–471. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.252379
Cao ZX (2017) Meta-analysis of rice sheath blight resistance QTL and identification of candidate genes. Dissertation, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou
Chen WF, Fan SX (2005) Changes of chlorophyll content of high-yielding rice. J Shenyang Agric Univ 35:14–17
Chetal S, Wagle DS et al (1981) Glycolipid changes in wheat and barley chloroplast under water stress. Plant Sci Lett 20:225–230
Deng JY (2007) QTL mapping associated with the traits of photosynthesis and yield components in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Dissertation, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou
Dong H, Fei GL, Wu CY et al (2013) A rice virescent-yellow leaf mutant reveals new insights into the role and assembly of plastid caseinolytic protease in higher plants. Plant physiol 162:1867–1880
Fan SX, Wang JX, Mao T (2010) Identification of QTLs for chlorophyll content at booting stage in rice. J Shenyang Agric Univ 25:69–72
Fukuda A, Terao T (2015) QTLs for shoot length and chlorophyll content of rice seedlings grown under low-temperature conditions, using a cross between indica and Japonica Cultivars. Plant Prod Sci 18:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.18.128
Goffinet B, Gerber S et al (2000) Quantitative trait loci: a meta-analysis. Genetics 155:463–473
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujioka S et al (2005) The rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell 17:2243–2254. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.030973
Jiang SK, Zhang XJ, Wang JY et al (2012) Dynamic QTL analysis on chlorophyll contents in rice. J Northeast Agric Univ 43:47–52
Jordan P, Fromme P, Witt HT et al (2001) Three-dimensional structure of cyanobacterial photosystem I at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 411:909–917
Jung KH, Hur J, Ryu C et al (2003) Characterization of a rice chlorophyll-deficient mutant using the T-DNA Gene-trap system. Plant Cell Physiol 44:463–472
Kelly AA, Dörmann P (2002) DGD2, an Arabidopsis gene encoding a UDP-galactose-dependent Digalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase is expressed during growth under phosphate-limiting conditions. J Biol Chem 277:1166–1173. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110066200
Khahani B, Tavakol E, Shariati V et al (2020) Genome wide screening and comparative genome analysis for Meta-QTL, ortho-MQTL and candidate genes controlling yield and yield-related traits in rice. BMC Genomics 21:294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-6702-1
Kobayashi K, Kondo M, Fukuda H et al (2007) Galactolipid synthesis in chloroplast inner envelope is essential for proper thylakoid biogenesis, photosynthesis, and embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:17216–17221
Kong WY, Yu XW, Chen HY et al (2016) The catalytic subunit of magnesium-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester cyclase forms a chloroplast complex to regulate chlorophyll biosynthesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol 92:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0513-4
Kourill R, Ilikl P, Naus J et al (1999) On the limits of applicability of spectrophotometric and spectrofluorime tricmethods for the determination of chlorophyll a /b ratio. Photosynth Res 62:107–1163
Li CM, Hu Y, Huang R et al (2015) Mutation of FdC2 gene encoding a ferredoxin-like protein with C-terminal extension causes yellow-green leaf phenotype in rice. Plant Sci 238:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.010
Li HH, Ribaut JM, Li ZL et al (2008) Inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) for digenic epistasis of quantitative traits in biparental populations. Theor Appl Genet 116:243–260
Li JM, Qi YQ, Wang JJ (2018a) Integration of QTL related to plant height of rice. Mol Plant Breed 16:159–166
Li Q, Zhu FY, Gao X et al (2014) Young Leaf Chlorosis 2 encodes the stroma-localized heme oxygenase 2 which is required for normal tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in rice. Planta 240:701–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2116-0
Li YH, Li CX, Liu CY et al (2018b) QTL analysis for chlorophyll content using recombinant inbred lines of Gang46B/A232. Southwest China J Agric Sci 31:10–15
Li ZY, Mo WP, Jia LQ et al (2019) Rice FLUORESCENT1 is involved in the regulation of chlorophyll. Plant Cell Physiol 60:2307–2318. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz129
Lichtenthaler HK, Kuhn G, Prenzel U et al (1982) Chlorophyll-protein levels and degree of thylakoid stacking in radish chloroplasts from high-light, low-light and bentazon-treated plants. Physiol Plant 56:183–188
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1985) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0110591
Liu DH (1983) The senescence of plant leaves. Plant Physiol Commun 2:14–19. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.1983.02.004
Liu H, Li Q, Yang F et al (2016) Differential regulation of protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase abundances by VIRESCENT 5A (OsV5A) and VIRESCENT 5B (OsV5B) in rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 57:2392–2402. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx019
Loll B, Kern J, Saenger W et al (2005) Towards complete cofactor arrangement in the 3.0 A resolution structure of photosystem II. Nature 438:1040–1044
Loll B, Kern J, Saenger W et al (2007) Lipids in photosystem II: interactions with protein and cofactors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:509–519
Malinina L, Malakhova ML, Teplov A et al (2004) Structural basis for glycosphingolipid transfer specificity. Nature 430:1048–1053
McCouch SR, Cho Y, Yano M et al (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13
Miles C, Wayne M (2008) Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis. Nature Edu 1(1):208. https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/quantitative-traitlocus-qtl-analysis-53904/
Morita R, Sato Y, Yu M et al (2010) Defect in non-yellow coloring 3, an alpha/beta hydrolase-fold family protein, causes a stay-green phenotype during leaf senescence in rice. Plant J 59:940–952. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03919.x
Muthuramalingam P, Krishnan SR, Pandian S et al (2018) Global analysis of threonine metabolism genes unravel key players in rice to improve the abiotic stress tolerance. Sci Rep 8:9270
Nagata N, Tanaka R, Satoh S et al (2005) Identification of a vinyl reductase gene for chlorophyll synthesis in Arabiopsis thalinana and implications for the evolution of prochlorococcus species. Plant Cell 17:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.027276
Ni J, Pujar A, Youens-Clark K et al (2009) Gramene QTL database: development, content and applications. Database J Biol Databases Curation 1:204–219
Ouyang YD, Huang XL, Lu ZH et al (2012) Genomic survey, expression profile and co-expression network analysis of OsWD40 family in rice. BMC Genomics 13:100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-100
Pan XW, LI YC, LI XX et al (2013) Differential regulatory mechanisms of CBF regulon between nipponbare (Japonica) and 93–11 (Indica) during cold acclimation. Chin J Rice Sci 20:165–172
Peter GF, Thornber JP (1991) Biochemical composition and organization of higher plant photosystem II light-harvesting pigment proteins. J Biol Chem 266:16745–16754
Piao W, Han SH, Sakuraba Y et al (2017) Rice 7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll a reductase is involved in the promotion of chlorophyll degradation and modulates cell death signaling. Mol Cells 40:773–786
Qian YQ, Sun ZY, Han L et al (2010) Response of reactive oxygen and its scavenging system in leaves of Buchloe dactyloides (Nutt.) engelm to water stress. Acta Ecol Sin 7:1920–1926
Raza Q, Riaz A, Sabar M et al (2019) Meta-analysis of grain iron and zinc associated QTL identified hotspot chromosomal regions and positional candidate genes for breeding biofortified rice. Plant Sci 288:110214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110214
Rikard F, Vener AV, Ivan B (2011) High light induced disassembly of Photosystem II supercomplexes in Arabidopsis requires STN7-dependent phosphorylation of CP29. PLoS ONE 6:e24565
Saito H, Okumoto Y, Yoshitake Y et al (2011) Complete loss of photoperiodic response in the rice mutant line X61 is caused by deficiency of phytochrome chromophore biosynthesis gene. Theor Appl Genet 122:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1426-2
Sakuraba Y, Rahman ML, Cho SH et al (2013) The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions. Plant J 74:122–133
Salas JJ, Ohlrogge JB (2002) Characterization of substrate specificity of plant FatA and FatB acyl-ACP thioesterases. Arch Biochem Biophys 403:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-9861(02)00017-6
Sosnowski O, Charcosset A, Joets J (2012) BioMercator V3: an upgrade of genetic map compilation and quantitative trait loci meta-analysis algorithms. Bioinformatics 28:2082–2083
Swamy BPM, Sarla N (2011) Meta-analysis of yield QTL derived from inter-specific crosses of rice reveals consensus regions and candidate genes. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:663–680
Takai T, Adachi S (2013) A natural variant of NAL1, selected in high-yield rice breeding programs, pleiotropically increases photosynthesis rate. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02149
Tinker NA, Mather DE, Rossnagel BG et al (1996) Regions of the genome that affect agronomic performance in two-row barley. Crop Sci 36:1053–1062
Tsukihara T, Aoyama H, Yamashita E et al (1996) The whole structure of the 13-subunit oxidized cytochrome c oxidase at 2.8 Å. Science 272:1136–1144. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5265.1136
Tu ZP (1997) Studies on the photosynthetic character is tics of rice and breeding for high use eficiency of solar energy. Sci Agric Sin 30:28–35
Wang FH, Wang GX, Li XY et al (2008) Heredity, physiology and mapping of a chlorophyll content gene of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Physiol 165:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2006.11.006
Wang JK (2009) Inclusive composite interval mapping of quantitative trait genes. Acta Agron Sin 35:239–245
Wang JX (2017) Study on the interactions and QTL mapping of physiological and yield related traits under irrigation and drought conditions in Japonica rice. Dissertation, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin
Wang PR, Wan CM, Xu ZJ et al (2013) One divinyl reductase reduces the 8-vinyl groups in various intermediates of chlorophyll biosynthesis in a given higher plant species, but the isozyme differs between species. Plant Physiol 161:521–534. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.208421
Wang XC, Min W, Zhi-Juan JL et al (2014) Functional characterization of the glycoside hydrolase encoding gene OsBE1 during chloroplast development in Oryza sativa. Acta Agron Sin 40:2090. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2014.02090
Wang YJ, Xu J, Deng DX et al (2016) A comprehensive meta-analysis of plant morphology, yield, stay-green, and virus disease resistance QTL in maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 243:459–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2419-9
Wu XL, Hu ZL (2012) Meta-analysis of QTL mapping experiments. Methods mol biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-785-9_8
Wu YH, Huang M, Tao XX et al (2016) Quantitative trait loci identification and meta-analysis for rice panicle-related traits. Mol Genet Genomics 291:1927–1940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1227-7
Yang SR (2003) A further discussion on the theories and methods of rice breeding for super high yield. J Shenyang Agric Univ 34:321–323
Yang YL, Xu J, Huang LC et al (2016) PGL, encoding chlorophyllide a oxygenase 1, impacts leaf senescence and indirectly affects grain yield and quality in rice. J Exp Bot 67:1297–1310. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv529
Yang YL, Xu J, Rao YC et al (2015) Cloning and functional analysis of pale-green leaf (PGL10) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Growth Regul 78:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0075-5
Ye WJ (2016) Fine mapping leaf chlorophyll content QTL qFCC7_L& cloning and function analysis of leaf color gene WSL12. Dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou
Yoo SC, Cho SH, Sugimoto H et al (2009) Rice virescent3 and stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Plant Physiol 150:388–401. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.136648
Sato Y, Morita R, Katsuma S et al (2009) Two short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases, NON-YELLOW COLORING 1 and NYC1-LIKE, are required for chlorophyll b and light-harvesting complex II degradation during senescence in rice. Plant J 57:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03670.x
Zhang FC, Zhu ZH (1990) Harvest index for various crops in China. Sci Agric Sin 23:83–87
Zhang GH, Li SY, Wang L et al (2014) LSCHL4 from Japonica Cultivar, which is allelic to NAL1, increases yield of indica super rice 93–11. Mol Plant 7:1350–1364. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu055
Zhang H, Li J, Yoo JH et al (2006) Rice Chlorina-1 and Chlorina-9 encode ChlD and ChlI subunits of Mg-chelatase, a key enzyme for chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development. Plant Mol Biol 62:325–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9024-z
Zhang SH (2019) QTL and Meta-QTL analysis of rice quality related to rice. Dissertation, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang
Zhang XL, Zhang ZQ, Li J et al (2011) Correlation of leaf senescence and gene expression/activities of chlorophyll degradation enzymes in harvested Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica rapa var. parachinensis). J Plant Physiol 168:2081–2087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.06.011
Zhang Z, Shang H, Shi Y et al (2016) Construction of a high-density genetic map by specific locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq) and its application to Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) analysis for boll weight in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). BMC Plant Biol 16:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0741-4
Zhou HL, Huang SM (2017) Effects of sink source relationship on chlorophyll content and photosynthetic characteristics of rice. J Green Sci Technol 24:147–149
Zhou KN, Ren YL, Lv J et al (2013) Young Leaf Chlorosis 1, a chloroplast-localized gene required for chlorophyll and lutein accumulation during early leaf development in rice. Planta 237:279–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1756-1
Zhou SX, Sawicki A, Willows RD et al (2012) C-terminal residues of Oryza sativa GUN4 are required for the activation of the ChlH subunit of magnesium chelatase in chlorophyll synthesis. FEBS Lett 586:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.12.026
Zhu XY, Guo S, Wang ZW et al (2016) Map-based cloning and functional analysis of YGL8, which controls leaf colour in rice (Oryza sativa). BMC Plant Biol 16:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0821-5
Zuo HL, Xiao K, Dong YJ et al (2007) Molecular detection of quantitative trait loci for leaf chlorophyll content at different growth-stages of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian J Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajps.2007.518.522
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Qian Qian who provide the RIL population in this research. We would also like to thank the reviewers who provided suggestions to improve this paper.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32001491), the Genetically Modified Organisms Breeding Major Projects of China (2016ZX08001-002), the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0100201), the Educational Commission of Sichuan Province, China (18ZA0507).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL, YP, and ST conducted the phenotypic experiment. ST, DY, FG, GY and LL measured the physiological traits and collected QTL information. LL, MT, YP, XW and YH performed the bioinformatics analysis and statistical analysis. LL and ST wrote the draft of manuscript, and YP revision of the manuscript. YP and YH were involved in designing the entire experiment and providing critical advices on the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
We declare that the experiments obey the ethical standards of the Rice Research Institute, Southwest University of Science and Technology.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Peng, Y., Tang, S. et al. Mapping QTL for leaf pigment content at dynamic development stage and analyzing Meta-QTL in rice. Euphytica 217, 90 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02820-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02820-0