Abstract
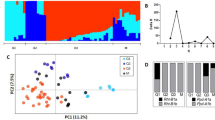
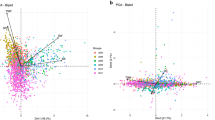
Field pea (Pisum sativum) is an important pulse crop globally for human consumption and livestock feed. A panel of 92 diverse pea cultivars was evaluated across nine environments and genotyped using 1536 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) arranged in a GoldenGate array. Population structure analysis revealed three subpopulations roughly consistent with the cultivar origin. Phenotyping included days to flowering (DTF), duration of flowering (DOF), number of reproductive nodes, number of pods on the main stem, percentage of pods set, percentage of pods retained with seed and pollen germination reduction due to heat stress. Association analyses identified a total of 60 SNPs significantly associated (−log10 p ≥ 4.3) with these seven reproductive development-related traits. Among these 60 marker-trait associations, 33 SNPs were associated with the onset of flowering, 8 SNPs with pod development and 19 SNPs with the number of reproductive nodes. No SNP marker was significantly associated with in vitro pollen germination reduction caused by high temperature stress. We found that 12 SNPs associated with DTF and 2 SNPs associated with DOF overlapped with the SNP markers associated with the number of reproductive nodes. Genomic regions associated with variation for reproductive development-related traits identified in this study provide grounds for future genetic improvement in pea.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrama H, Eizenga A, Yan G (2007) Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol Breed 19:341–356
Ahmad S, Kaur S, Lamb-Palmer ND, Lefsrud M, Singh J (2015) Genetic diversity and population structure of Pisum sativum accessions for marker-trait association of lipid content. Crop J 3:238–245
Ahmed FE, Hall AE, DeMason DA (1992) Heat injury during floral development in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata, Fabaceae). Am J Bot 79:784–791
Alcade JA, Wheeler TR, Summerfield RJ, Norero AL (1999) Quantitative effects of the genes Lf, Sn, E, and Hr on time to flowering in pea (Pisum sativum L.). J Exp Bot 50:1691–1700
Alcalde JA, Larrain MF (2006) Timing of photoperiod sensitivity in relation to floral initiation in contrasting genotypes of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Field Crops Res 96:348–354
Annicchiarico P, Nazzicari N, Pecetti L, Romani M, Ferrari B, Wei Y, Brummer EC (2017) GBS-based genomic selection for pea grain yield under severe terminal drought. Plant Genome 10:1–13
Benlloch R, Berbel A, Ali L, Gohari G, Millán T, Madueño F (2015) Genetic control of inflorescence architecture in legumes. Front Plant Sci 6:543
Berger JD, Ali M, Basu PS, Chaudhary BD, Chaturvedi SK, Deshmukh PS, Yadav SS (2006) Genotype by environment studies demonstrate the critical role of phenology in adaptation of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to high and low yielding environments of India. Field Crop Res 98:230–244
Bordat A, Savois V, Nicolas M, Salse J, Chauveau A, Bourgeois M, Potier J, Houtin H, Rond C, Murat F, Marget P, Aubert G, Burstin J (2011) Translational genomics in legumes allowed placing in Silico 5460 unigenes on the pea functional map and identified candidate genes in Pisum sativum L. G3 1:93–103
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Brazauskas G, Lenk I, Pedersen MG, Studer B, Lübberstedt T (2011) Genetic variation, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in European elite germplasm of perennial ryegrass. Plant Sci 181:412–420
Bueckert RA, Wagenhoffer S, Hnatowich G, Warkentin TD (2015) Effect of heat and precipitation on pea yield and reproductive performance in the field. Can J Plant Sci 95:629–639
Cheng P, Holdsworth W, Ma Y, Coyne CJ, Mazourek M, Grusak MA, Fuchs S, McGee RJ (2015) Association mapping of agronomic and quality traits in USDA pea single-plant collection. Mol Breed 35:75
Desclaux D, Roumet P (1996) Impact of drought stress on the phenology of two soybean (Glycine max L. Merr) cultivars. Field Crop Res 46:61–70
Desgroux A, L’Anthoëne V, Roux-Duparque M, Rivière J, Aubert G, Tayeh N, Moussart A, Mangin P, Vetel P, Piriou C, McGee RJ, Coyne CJ, Burstin J, Baranger A, Manzanares-Dauleux M, Bourion V, Pilet-Nayel M (2016) Genome-wide association mapping of partial resistance to Aphanomyces euteiches in pea. BMC Genom 17:124
Devasirvatham V, Gaur PM, Mallikarjuna N, Tokachichu RN, Trethowan RM, Tan DKY (2012) Effect of high temperature on the reproductive development of chickpea genotypes under controlled environments. Funct Plant Biol 39:1009–1018
Diapari M, Sindhu A, Bett K, Deokar A, Warkentin TD, Tar’an B (2014) Genetic diversity and association mapping of iron and zinc concentrations in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genome 57:459–468
Diapari M, Sindhu A, Warkentin TD, Bett K, Tar’an B (2015) Population structure and marker-trait association studies of iron, zinc and selenium concentrations in seed of field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Mol Breed 35:30
Dolezel J, Greilhuber J (2010) Nuclear genome size: are we getting closer? Cytometry Part A 77:635–642
Earl DA, VonHoldt BM (2012) Structure Harvester: a website and program for visualizing structure output and implementing the evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
FAOSTAT (2016) Taken from http://faostat3.fao.org/browse/Q/QC/E 8 Oct 2016
Ferrari B, Romani M, Aubert G, Boucherot K, Burstin J, Pecetti L, Huart-Naudet M, Klein A, Annicchiarico P (2016) Association of SNP markers with agronomic and quality traits of field pea in Italy. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 52:83–93
Frova C, Sari-Gorla M (1994) Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for pollen thermotolerance detected in maize. Mol Gen Genet 245:424–430
Hall AE (2004) Breeding for adaptation to drought and heat in cowpea. Eur J Agron 21:447–454
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1938) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. University of California, Berkeley, pp 35–39
Holland JB (2007) Genetic architecture of complex traits in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:156–161
Holmes MG, Smith H (1975) Function of phytochrome in plants growing in natural-environment. Nature 254:512–514
Huang S, Gali KK, Tar’an B, Warkentin TD, Bueckert RA (2017) Pea phenology: crop potential in a warming environment. Crop Sci 57:1540–1551
Jiang Y (2016) Effect of heat stress on pollen development and seed set in field pea. University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Jiang Y, Lahlali R, Karunakaran C, Kumar S, Davis AR, Bueckert RA (2015) Seed set, pollen morphology and pollen surface composition response to heat stress in field pea. Plant Cell Environ 38:2387–2397
Jombart T (2008) Adegenet: a R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 24:1403–1405
Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F (2010) Discriminant analysis of principal components: a new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet 11:94
Kakani VG, Prasad PVV, Craufurd PQ, Wheeler TR (2002) Response of in vitro pollen germination and pollen tube growth of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes to temperature. Plant Cell Environ 25:1651–1661
Kang MS, Balzarini MG, Guerra JLL (2004) Genotype-by-environment interaction. In: Saxton AM (ed) Genetic analysis of complex traits using SAS. SAS Institute, Cary
Konsens I, Ofir M, Kigel J (1991) The effect of temperature on the production and abscission of flowers and pods in snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Ann Bot 67:391–399
Krajewski P, Bocianowski J, Gawłowska M, Kaczmarek Z, Pniewski T, Święcicki W, Wolko B (2012) QTL for yield components and protein content: a multienvironment study of two pea (Pisum sativum L.) populations. Euphytica 183:323–336
Kwon S, Brown AF, Hu J, McGee R, Watt C, Kisha T, Timmerman-Vaughan G, Grusak M, McPhee KE, Coyne CJ (2012) Genetic diversity, population structure and genome-wide marker-trait association analysis emphasizing seed nutrients of the USDA pea (Pisum sativum L.) core collection. Genes Genom 34:305–320
Lahlali R, Jiang Y, Kumar S, Karunakaran C, Liu X, Borondics F, Hallin E, Bueckert R (2014) ATR-FTIR spectroscopy reveals involvement of lipids and proteins of intact pea pollen grains to heat stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci 5:747
Li Y, Smulders M, Chang J, Qiu M (2011) Genetic diversity and association mapping in a collection of selected Chinese soybean accessions based on SSR marker analysis. Conserv Genet 12:1145–1157
Liew LC, Hecht V, Sussmilch FC, Weller JL (2014) The pea photoperiod response gene STERILE NODES is an ortholog of LUX ARRHYTHMO. Plant Physiol 165:648–657
Marjanović-Jeromela A, Nagl N, Gvozdanović-Varga J, Hristov N, Kondić-Špika A, Vasić M, Marinković R (2011) Genotype by environment interaction for seed yield per plant in rapeseed using AMMI model. Pesq agropec bras 46:174–181
Mobini SH, Lulsdorf M, Warkentin T, Vandenberg A (2016) Low red:far-red light ratio causes faster in vitro flowering in lentil. Can J Plant Sci 96:908–918
Morrell P, Buckler E, Ross-Ibarra J (2012) Crop genomics: advances and applications. Nature Rev Genet 13:85–96
Murfet IC (1985) Pisum sativum. In: Halevy AH (ed) CRC handbook of flowering, vol IV. CRC Press. Boca Raton, FL, pp 97–126
Myles S, Peiffer J, Brown PJ, Ersoz ES, Zhang Z, Costich DE, Buckler ES (2009) Association mapping: critical considerations shift from genotyping to experimental design. Plant Cell 21:2194–2202
Nemli S, Asciogul TK, Kaya HB, Kahraman A, Eşiyok D, Tanyolac B (2014) Association mapping for five agronomic traits in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Sci Food Agric 94:3141–3151
Petkova V, Nikolova V, Kalapchieva SH, Stoeva V, Topalova E, Angelova S (2009) Physiological response and pollen viability of Pisum sativum genotypes under high temperature influence. Acta Hortic 830:665–671
Pierre J, Huguet T, Barre P, Huyghe C, Julier B (2008) Detection of QTLs for flowering date in three mapping populations of the model legume species Medicago truncatula. Theor Appl Genet 117:609–620
Pillen K, Zacharias A, Léon J (2003) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:340–352
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Reid JB, Murfet IC, Singer SR, Weller JL, Taylor SA (1996) Physiological-genetics of flowering in Pisum. Semin Cell Dev Biol 7:455–463
Roche R, Jeuffroy M, Ney B (1998) A model to simulate the final number of reproductive nodes in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Ann Bot 81:545–555
Sabaghnia N, Sabaghpour SH, Dehghani H (2008) The use of an AMMI model and its parameters to analyse yield stability in multi-environment trials. J Agric Sci 146:571–581
Sakiroglu M, Sherman-Broyles S, Story A, Moore K, Doyle JJ, Charles BE (2012) Patterns of linkage disequilibrium and association mapping in diploid alfalfa (M. sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:577–590
Salem MA, Kakani VG, Koti S, Reddy KR (2007) Pollen-based screening of soybean genotypes for high temperatures. Crop Sci 47:219–231
Salvi S, Tuberosa R (2005) To clone or not to clone plant QTLs: present and future challenges. Trends Plant Sci 10:297–304
Shi C, Navabi A, Yu K (2011) Association mapping of common bacterial blight resistance QTL in Ontario bean breeding populations. BMC Plant Biol 11:52
Sindhu A, Ramsay L, Sanderson LA, Stonehouse R, Li R, Condie J, Shunmugam ASK, Liu Y, Jha AB, Diapari M, Burstin J, Aubert G, Tar’an B, Bett KE, Warkentin TD, Sharpe AG (2014) Gene-based SNP discovery and genetic mapping in pea. Theor Appl Genet 127:2225–2241
Tar’an B, Warkentin T, Somers DJ, Miranda D, Vandenberg A, Blade S, Bing D (2004) Identification of quantitative trait loci for grain yield, seed protein concentration and maturity in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 136:297–306
Thudi M, Upadhyaya HD, Rathore A, Gaur PM, Krishnamurthy L, Roorkiwal M, Nayak SN, Chaturvedi SK, Basu PS, Gangarao N, Fikre A, Kimurto P, Sharma PC, Sheshashavee MS, Tobita S, Kashiwagi J, Ito O, Killian A, Varshney RK (2014) Genetic dissection of drought and heat tolerance in chickpea through genome-wide and candidate gene-based association mapping approaches. PLOS One 9:e96758
Timmerman-Vaughan GM, Mills A, Whitfield C, Frew T, Butler R, Murray S, Lakeman M, McCallum J, Russell A, Wilson D (2005) Linkage mapping of QTL for seed yield, yield components, and developmental traits in pea. Crop Sci 45:1336–1344
Truong H, Duthion C (1993) Time of flowering of pea (Pisum sativum L.) as a function of leaf appearance rate and node of first flower. Ann Bot 72:133–142
Vanhala T, Normann KR, Lundstrom M, Weller JL, Leino MW, Hagenblad J (2016) Flowering time adaption in Swedish landrace pea (Pisum sativum L.). BMC Genet 17:117
Varshney RK, Ribaut J, Buckler ES, Tuberosa R, Rafalski JA, Langridge P (2012) Can genomics boost productivity of orphan crops? Nat Biotechnol 30:1172–1176
Wang H, Smith KP, Combs E, Blake T, Horsley RD, Muehlbauer GJ (2012) Effect of population size and unbalanced data sets on QTL detection using genome-wide association mapping in barley breeding germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 124:111–124
Wang N, Chen B, Xu K, Gao G, Li F, Qiao J, Yan G, Li J, Li H, Wu X (2016) Association mapping of flowering time QTLs and insight into their contributions to rapeseed growth habits. Front Plant Sci 7:338
Weller J, Ortega R (2015) Genetic control of flowering time in legumes. Front Plant Sci 6:207
Weller JL, Reid JB, Taylor SA, Murfet IC (1997) The genetic control of flowering in pea. Trends Plant Sci 2:412–418
Weller JL, Hecht V, Liew LC, Sussmilch FC, Wenden B, Knowles CL, Vander SJK (2009) Update on the genetic control of flowering in garden pea. J Exp Bot 60:2493–2499
Xiao YH, Pan Y, Luo LH, Deng HB, Zhang GL, Tang WB, Chen LY (2011) Quantitative trait loci associated with pollen fertility under high temperature stress at flowering stage in rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Sci 18:204–209
Yu J, Holland JB, McMullen MD, Buckler ES (2008) Genetic design and statistical power of nested association mapping in maize. Genetics 178:539–551
Zhu C, Gore M, Buckler ES, Yu J (2008) Status and prospects of association mapping in plants. Plant Genome 1:5–20
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Saskatchewan Agriculture Development Fund [Grant Number 20100033], Saskatchewan Pulse Growers Association [Grant Number AGR1116], Western Grains Research Fund [Grant Number 411939], and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada—Collaborative Research and Development (CRD) Program [Grant Number CRDPJ 439277]. We acknowledge the kind help from the staff at the Pulse Crop Breeding Program of the Crop Science Field Laboratory and the staff at the Crop Physiology Lab at University of Saskatchewan. We thank Amidou N’Diaye and Kirstin Bett for helpful discussions. We are grateful for the helpful comments from two anonymous referees that improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Jiang and M. Diapari are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Diapari, M., Bueckert, R.A. et al. Population structure and association mapping of traits related to reproductive development in field pea. Euphytica 213, 215 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-2006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-2006-1