Abstract
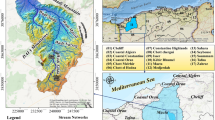
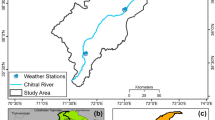
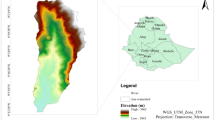
Soil erosion is a significant problem in the agriculture sector and the environment globally. Susceptible soil erosion zones must be identified and erosion rates evaluated to decrease land degradation problems and increase crop productivity by protecting soil fertility. Therefore, a research study has been carried out in the Ponnaniyar River basin, an ungauged tributary of the Cauvery basin in India, primarily used for agriculture. The main purpose of this study is to assess soil erosion (SE) and sediment yield (SY) for the future in an ungauged basin by utilizing the projected land use/land cover (LULC) map of the study area. Additionally, Landsat 8 satellite dataset was only used for the classification and prediction of LULC to eliminate the variation between the resolution, bands and its wavelength of different satellites datasets. To achieve the goals of this study, three phases were followed. First, the LULC of the study area was classified using a Random Trees Classifier (RTC), a machine learning technique, followed by the projection of land cover using a Cellular Automata-based Artificial Neural Network (CA-ANN) model. The driving factors for this model include digital elevation model (DEM), slope, distance to roads, settlements, and water bodies. The accuracy level of the projected LULC map was determined by comparing it with the classified LULC map of the study area, and the results showed an overall accuracy (OA) of 85.35 percentage and a kappa coefficient (K) of 0.74, respectively. Second, the projected LULC map was used in the land management factor (C) and conversation practice factor (P) of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model to assess soil erosion. The model was integrated with the sediment delivery ratio (SDR) to estimate sediment yield within the study area. The accuracy of the generated erosion map based on the classified and projected LULC for the year 2022 was determined using the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) curve, and it was found to be in satisfactory agreement. Finally, for effective soil and water conservation measures, the basin was divided into 13 sub-watersheds (SWs) using terrain analysis in geographical information system (GIS). The SWs were prioritized based on the mean soil loss in the 4-year interval from 2014 to 2030 and integrated using the weighted average method to determine the final prioritization. From these findings, SW 11, SW 9, SW 12, and SW 1 are extremely affected by soil erosion, and immediate implementation of water harvesting structures is required for soil conservation. Also, this research might be useful for decision-makers and policymakers in land management.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Depending on valid requests, research data and information will be provided.
Abbreviations
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural networks
- CA:
-
Cellular automata
- CHIRPS:
-
Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data
- K:
-
Kappa coefficient
- LULC:
-
Land use/land cover
- MOLUSCE:
-
Modules of land use and land change evaluation
- OA:
-
Overall accuracy
- PA:
-
Producer accuracy
- QGIS:
-
Quantum Geographical Information System
- RTC:
-
Random Trees Classifier
- RUSLE:
-
Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation
- SE:
-
Soil erosion
- SW:
-
Sub – watershed
- SY:
-
Sediment yield
- UA:
-
User accuracy
References
Abbas, Z., Yang, G., Zhong, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Spatiotemporal change analysis and future scenario of LULC using the CA-ANN approach: A case study of the greater bay area, china. Land, 10(6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060584
Abijith, D., & Saravanan, S. (2022). Assessment of land use and land cover change detection and prediction using remote sensing and CA Markov in the northern coastal districts of Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(57), 86055–86067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15782-6
Abijith, D., Saravanan, S., Singh, L., Jennifer, J. J., Saranya, T., & Parthasarathy, K. S. S. (2020). GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for identification of potential groundwater recharge zones-A case study from Ponnaniyaru watershed, Tamil Nadu, India. HydroResearch, 3, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2020.02.002
Ahire, J. H., Wang, Q., Coxon, P. R., Malhotra, G., Brydson, R., Chen, R., & Chao, Y. (2012). Highly luminescent and nontoxic amine-capped nanoparticles from porous silicon: Synthesis and their use in biomedical imaging. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4(6), 3285–3292. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300642m
Ahmad, F., Goparaju, L., & Qayum, A. (2017). LULC analysis of urban spaces using Markov chain predictive model at Ranchi in India. Spatial Information Research, 25(3), 351–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-017-0102-x
Ahmad, H., Abdallah, M., Jose, F., Elzain, H. E., Bhuyan, M. S., Shoemaker, D. J., & Selvam, S. (2023). Evaluation and mapping of predicted future land use changes using hybrid models in a coastal area. Ecological Informatics, 78, 102324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2023.102324
Akdeniz, H. B., Sag, N. S., & Inam, S. (2023). Analysis of land use/land cover changes and prediction of future changes with land change modeler: Case of Belek, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10746-w
Aksoy, H., & Kaptan, S. (2021). Monitoring of land use/land cover changes using GIS and CA-Markov modeling techniques: A study in Northern Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(8), 507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09281-x
Alam, S., Hasan, F., Debnath, M., & Rahman, A. (2023). Morphology and land use change analysis of lower Padma River floodplain of Bangladesh. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(7), 886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11461-w
Aliabad, F. A., Zare, M., Solgi, R., & Shojaei, S. (2023). Comparison of neural network methods (fuzzy ARTMAP, Kohonen and Perceptron) and maximum likelihood efficiency in preparation of land use map. GeoJournal, 88(2), 2199–2214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-022-10744-y
Arabi Aliabad, F., Shojaei, S., Zare, M., & Ekhtesasi, M. R. (2019). Assessment of the fuzzy ARTMAP neural network method performance in geological mapping using satellite images and Boolean logic. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16, 3829–3838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1795-7
Arsanjani, J. J., & Vaz, E. (2015). An assessment of a collaborative mapping approach for exploring land use patterns for several European metropolises. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 35, 329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2014.09.009
Aswathi, J., Sajinkumar, K. S., Rajaneesh, A., Oommen, T., Bouali, E. H., Binoj Kumar, R. B., et al. (2022). Furthering the precision of RUSLE soil erosion with PSInSAR data: An innovative model. Geocarto International, 37(27), 16108–16131. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2105407
Avand, M., & Moradi, H. (2021). Using machine learning models, remote sensing, and GIS to investigate the effects of changing climates and land uses on flood probability. Journal of Hydrology, 595, 125663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125663
Bag, R., Mondal, I., Dehbozorgi, M., Bank, S. P., Das, D. N., Bandyopadhyay, J., et al. (2022). Modelling and mapping of soil erosion susceptibility using machine learning in a tropical hot sub-humid environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 364, 132428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132428
Behera, M., Sena, D. R., Mandal, U., Kashyap, P. S., & Dash, S. S. (2020). Integrated GIS-based RUSLE approach for quantification of potential soil erosion under future climate change scenarios. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08688-2
Bhandari, S., Twayana, R., Shrestha, R., & Sharma, K. (2021). Future land use land cover scenario simulation using open-source GIS for the City of Banepa and Dhulikhel municipality, Nepal. FOSS 4G-ASIA
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45, 5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Chakrabortty, R., Pradhan, B., Mondal, P., & Pal, S. C. (2020). The use of RUSLE and GCMs to predict potential soil erosion associated with climate change in a monsoon-dominated region of eastern India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06033-y
Chandramohan, T., & Durbude, D. G. (2002). Estimation of soil erosion potential using universal soil loss equation. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 30, 181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000361
Dabral, P. P., Baithuri, N., & Pandey, A. (2008). Soil erosion assessment in a hilly catchment of North Eastern India using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resources Management, 22, 1783–1798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9253-9
Değermenci, A. S. (2023). Spatio-temporal change analysis and prediction of land use and land cover changes using CA-ANN model. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(10), 1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11848-9
Di Gregorio, A., & Jansen, L. (2000). Land cover classification system (LCCS): Classification concepts and user. FAO Corporate Document Repository. https://www.fao.org/3/x0596e/x0596e00.htm
Dunn, M., & Hickey, R. (1998). The effect of slope algorithms on slope estimates within a GIS. Cartography, 27(1), 9–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/00690805.1998.9714086
Erdogan, E. H., Erpul, G., & Bayramin, İ. (2007). Use of USLE/GIS methodology for predicting soil loss in a semiarid agricultural watershed. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 131, 153–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9464-6
Eslami, Z., Shojaei, S., & Hakimzadeh, M. A. (2017). Exploring prioritized sub-basins in terms of flooding risk using HEC_HMS model in Eskandari catchment, Iran. Spatial Information Research, 25, 677–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-017-0135-1
Feng, Y., & Liu, Y. (2016). Scenario prediction of emerging coastal city using CA modeling under different environmental conditions: A case study of Lingang New City, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5558-y
Fetene, D. T., Lohani, T. K., & Mohammed, A. K. (2023). LULC change detection using support vector machines and cellular automata-based ANN models in Guna Tana watershed of Abay basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(11), 1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11968-2
Floreano, I. X., & de Moraes, L. A. F. (2021). Land use/land cover (LULC) analysis (2009–2019) with Google Earth Engine and 2030 prediction using Markov-CA in the Rondônia State, Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(4), 239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09016-y
Forozan, G., Elmi, M. R., Talebi, A., Mokhtari, M. H., & Shojaei, S. (2020). Temporal-spatial simulation of landscape variations using combined model of Markov chain and automated cell. KN-Journal of Cartography and Geographic Information, 70, 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42489-020-00037-0
Funk, C., Peterson, P., Landsfeld, M., Pedreros, D., Verdin, J., Shukla, S., et al. (2015). The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Scientific Data, 2(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.66
Ganasri, B. P., & Ramesh, H. (2016). Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(6), 953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007
Gayen, A., Saha, S., & Pourghasemi, H. R. (2020). Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and its validation by FR probability model. Geocarto International, 35(15), 1750–1768. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1581272
Gobakis, K., Kolokotsa, D., Synnefa, A., Saliari, M., Giannopoulou, K., & Santamouris, M. (2011). Development of a model for urban heat island prediction using neural network techniques. Sustainable Cities and Society, 1(2), 104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2011.05.001
Halder, S., Das, S., & Basu, S. (2023). Use of support vector machine and cellular automata methods to evaluate impact of irrigation project on LULC. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10588-6
Ismail, J., & Ravichandran, S. (2008). RUSLE2 model application for soil erosion assessment using remote sensing and GIS. Water Resources Management, 22, 83–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9145-9
Jayabaskaran, M., & Das, B. (2023). Land Use Land Cover (LULC) dynamics by CA-ANN and CA-Markov model approaches: A case study of Ranipet Town, India. Nature, Environment and Pollution Technology, 22(3). https://doi.org/10.46488/NEPT.2023.v22i03.013
Jena, R. K., Padua, S., Ray, P., Ramachandran, S., Bandyopadhyay, S., Deb Roy, P., ... & Ray, S. K. (2018). Assessment of soil erosion in sub tropical ecosystem of Meghalaya, India using remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE. Indian Journal of Soil Conservation, 26(03),273–282. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330511894
Joorabian Shooshtari, S., & Aazami, J. (2023). Prediction of the dynamics of land use land cover using a hybrid spatiotemporal model in Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(7), 813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11425-0
Jusoff, K., & Hassan, H. M. (1998). An overview of satellite remote sensing for landuse planning with special emphasis in Malaysia. Remote Sensing Reviews, 16(3), 209–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757259809532352
Kafy, A. A., Al Rakib, A., Fattah, M. A., Rahaman, Z. A., & Sattar, G. S. (2022). Impact of vegetation cover loss on surface temperature and carbon emission in a fastest-growing city, Cumilla, Bangladesh. Building and Environment, 208, 108573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.108573
Kamaraj, M., & Rangarajan, S. (2022). Predicting the future land use and land cover changes for Bhavani basin, Tamil Nadu, India, using QGIS MOLUSCE plugin. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(57), 86337–86348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17904-6
Karimi, H., Jafarnezhad, J., Khaledi, J., & Ahmadi, P. (2018). Monitoring and prediction of land use/land cover changes using CA-Markov model: A case study of Ravansar County in Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3940-5
Kolli, M. K., Opp, C., & Groll, M. (2021). Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield concentration across the Kolleru Lake catchment using GIS. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09443-7
Kulithalai Shiyam Sundar, P., & Deka, P. C. (2022). Spatio-temporal classification and prediction of land use and land cover change for the Vembanad Lake system, Kerala: A machine learning approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(57), 86220–86236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17257-0
Kumar, A., Devi, M., & Deshmukh, B. (2014). Integrated remote sensing and geographic information system based RUSLE modelling for estimation of soil loss in western Himalaya, India. Water Resources Management, 28, 3307–3317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0680-5
Kumar, S., & Hole, R. M. (2021). Geospatial modelling of soil erosion and risk assessment in Indian Himalayan region—A study of Uttarakhand state. Environmental Advances, 4, 100039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100039
Kumar, V., & Agrawal, S. (2023). A multi-layer perceptron–Markov chain based LULC change analysis and prediction using remote sensing data in Prayagraj district, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(5), 619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11205-w
Lambin, E. F., Geist, H. J., & Lepers, E. (2003). Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 28(1), 205–241. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.energy.28.050302.105459
Lu, Y., Wu, P., Ma, X., & Li, X. (2019). Detection and prediction of land use/land cover change using spatiotemporal data fusion and the Cellular Automata–Markov model. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7200-2
Mandrekar, J. N. (2010). Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 5(9), 1315–1316. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ec173d
Matta, G., Nayak, A., Kumar, A., & Kumar, P. (2020). Water quality assessment using NSFWQI, OIP and multivariate techniques of Ganga River system, Uttarakhand, India. Applied Water Science, 10, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01288-y
Mawasha, T. S., & Britz, W. (2020). Simulating change in surface runoff depth due to LULC change using Soil and Water Assessment Tool for flash floods prediction. South African Journal of Geomatics, 9(2), 282–301. https://doi.org/10.4314/sajg.v9i2.19
Merritt, W. S., Letcher, R. A., & Jakeman, A. J. (2003). A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environmental Modelling & Software, 18(8-9), 761–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(03)00078-1
Mirakhorlo, M. S., & Rahimzadegan, M. (2021). Analysing the land-use change effects on soil erosion and sediment in the North of Iran; a case study: Talar watershed. Geocarto International, 36(8), 936–956. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1624985
Mondal, A., Khare, D., Kundu, S., Meena, P. K., Mishra, P. K., & Shukla, R. (2015). Impact of climate change on future soil erosion in different slope, land use, and soil-type conditions in a part of the Narmada River Basin, India. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 20(6), C5014003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001065
Monserud, R. A., & Leemans, R. (1992). Comparing global vegetation maps with the Kappa statistic. Ecological Modelling, 62(4), 275–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(92)90003-W
Moore, I. D., & Burch, G. J. (1986). Physical basis of the length-slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 50(5), 1294–1298. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000050042x
Moore, I. D., & Wilson, J. P. (1992). Length-slope factors for the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation: Simplified method of estimation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 47(5), 423–428.
Motlagh, Z. K., Lotfi, A., Pourmanafi, S., Ahmadizadeh, S., & Soffianian, A. (2020). Spatial modeling of land-use change in a rapidly urbanizing landscape in central Iran: Integration of remote sensing, CA-Markov, and landscape metrics. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08647-x
Mouat, D. A., Mahin, G. G., & Lancaster, J. (1993). Remote sensing techniques in the analysis of change detection. Geocarto International, 8(2), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049309354407
Mozaffaree Pour, N., Karasov, O., Burdun, I., & Oja, T. (2022). Simulation of land use/land cover changes and urban expansion in Estonia by a hybrid ANN-CA-MCA model and utilizing spectral-textural indices. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(8), 584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10266-7
Nasidi, N. M., Wayayok, A., Abdullah, A. F., & Kassim, M. S. M. (2021). Spatio-temporal dynamics of rainfall erosivity due to climate change in Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 7, 1847–1861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00917-4
Nasiri, A., Shirokova, V., Zareie, S., & Shojaei, S. (2017). Assessment of the status and intensity of water erosion in the river basin Delichai (Iranian territory) using GIS model. International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM, 17, 89–96.
Pandey, S., & Kumari, N. (2023). Prediction and monitoring of LULC shift using cellular automata-artificial neural network in Jumar watershed of Ranchi District, Jharkhand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10623-6
Pascale, S., Parisi, S., Mancini, A., Schiattarella, M., Conforti, M., Sole, A., et al. (2013). Landslide susceptibility mapping using artificial neural network in the urban area of Senise and San Costantino Albanese (Basilicata, Southern Italy). In Computational Science and Its Applications–ICCSA 2013: 13th International Conference, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, June 24-27, 2013, Proceedings, Part IV 13 (pp. 473–488). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39649-6_34
Patil, R. J., Sharma, S. K., Tignath, S., & Sharma, A. P. M. (2017). Use of remote sensing, GIS and C++ for soil erosion assessment in the Shakkar River basin, India. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 62(2), 217–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2016.1217413
Paul, A., & Bhattacharji, M. (2023). Prediction of landuse/landcover using CA-ANN approach and its association with river-bank erosion on a stretch of Bhagirathi River of Lower Ganga Plain. GeoJournal, 88(3), 3323–3346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-022-10814-1
Ragini, H. R., Debnath, M. K., Gupta, D. S., Deb, S., & Ajith, S. (2023). Modelling and monitoring land use: Land cover change dynamics of Cooch Behar District of West Bengal using Multi-Temporal Satellite Data. Agricultural Research, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-023-00657-8
Rahman, M. T. U., Tabassum, F., Rasheduzzaman, M., Saba, H., Sarkar, L., Ferdous, J., et al. (2017). Temporal dynamics of land use/land cover change and its prediction using CA-ANN model for southwestern coastal Bangladesh. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6272-0
Rajbanshi, J., & Bhattacharya, S. (2021). Modelling the impact of climate change on soil erosion and sediment yield: A case study in a sub-tropical catchment, India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01117-4
Reddy, N. M., & Saravanan, S. (2023). Evaluation of the accuracy of seven gridded satellite precipitation products over the Godavari River basin, India. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 20(9), 10179–10204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04524-x
Renard, K. G. (1997). Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service.
Rizeei, H. M., Saharkhiz, M. A., Pradhan, B., & Ahmad, N. (2016). Soil erosion prediction based on land cover dynamics at the Semenyih watershed in Malaysia using LTM and USLE models. Geocarto International, 31(10), 1158–1177. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2015.1120354
Rodriguez-Galiano, V. F., Ghimire, B., Rogan, J., Chica-Olmo, M., & Rigol-Sanchez, J. P. (2012). An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 67, 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2011.11.002
Roose, M., & Hietala, R. (2018). A methodological Markov-CA projection of the greening agricultural landscape—A case study from 2005 to 2017 in southwestern Finland. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6796-y
Roy, S., & Chintalacheruvu, M. R. (2023, February). LULC dynamics study and modeling of urban land expansion using CA-ANN. In International Conference on Science, Technology and Engineering (pp. 79–90). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-4665-5_9
Rwanga, S. S., & Ndambuki, J. M. (2017). Accuracy assessment of land use/land cover classification using remote sensing and GIS. International Journal of Geosciences, 8(04), 611. 2. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2017.84033
Saha, P., Mitra, R., Chakraborty, K., & Roy, M. (2022). Application of multi layer perceptron neural network Markov Chain model for LULC change detection in the Sub-Himalayan North Bengal. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 26, 100730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2022.100730
Şahin, M. (2021). A comprehensive analysis of weighting and multicriteria methods in the context of sustainable energy. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 18(6), 1591–1616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02922-7
Sajan, B., Mishra, V. N., Kanga, S., Meraj, G., Singh, S. K., & Kumar, P. (2022). Cellular automata-based artificial neural network model for assessing past, present, and future land use/land cover dynamics. Agronomy, 12(11), 2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112772
Sathiyamurthi, S., Ramya, M., Saravanan, S., & Subramani, T. (2023). Estimation of soil erosion for a semi-urban watershed in Tamil Nadu, India using RUSLE and geospatial techniques. Urban Climate, 48, 101424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2023.101424
Senanayake, S., & Pradhan, B. (2022). Predicting soil erosion susceptibility associated with climate change scenarios in the Central Highlands of Sri Lanka. Journal of Environmental Management, 308, 114589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114589
Shafie, B., Javid, A. H., Behbahani, H. I., Darabi, H., & Lotfi, F. H. (2023). Modeling land use/cover change based on LCM model for a semi-arid area in the Latian Dam Watershed (Iran). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(3), 363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10876-1
Shahbazian, Z., Faramarzi, M., Rostami, N., & Mahdizadeh, H. (2019). Integrating logistic regression and cellular automata–Markov models with the experts’ perceptions for detecting and simulating land use changes and their driving forces. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7555-4
Shekar, P. R., & Mathew, A. (2022). Morphometric analysis for prioritizing sub-watersheds of Murredu River basin, Telangana State, India, using a geographical information system. Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, 69(1), 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s44147-022-00094-4
Shekar, P. R., & Mathew, A. (2023a). Assessing groundwater potential zones and artificial recharge sites in the monsoon-fed Murredu river basin, India: An integrated approach using GIS, AHP, and Fuzzy-AHP. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 23, 100994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2023.100994
Shekar, P. R., & Mathew, A. (2023b). Integrated assessment of groundwater potential zones and artificial recharge sites using GIS and Fuzzy-AHP: A case study in Peddavagu watershed, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(7), 906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11474-5
Shojaei, S., Kalantari, Z., & Rodrigo-Comino, J. (2020). Prediction of factors affecting activation of soil erosion by mathematical modeling at pedon scale under laboratory conditions. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 20163. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76926-1
Singh, G., Babu, R., Narain, P., Bhushan, L. S., & Abrol, I. P. (1992). Soil erosion rates in India. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 47(1), 97–99.
Singh, L., & Saravanan, S. (2020). Impact of climate change on hydrology components using CORDEX South Asia climate model in Wunna, Bharathpuzha, and Mahanadi, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(11), 678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08637-z
Sinha, D., & Joshi, V. U. (2012). Application of universal soil loss equation (USLE) to recently reclaimed badlands along the Adula and Mahalungi Rivers, Pravara Basin, Maharashtra. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 80, 341–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-012-0152-6
Sujatha, E. R., & Sridhar, V. (2018). Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a small mountainous watershed using RUSLE: A case-study of the Palar sub-watershed in Kodaikanal, South India. Water, 10(11), 1608.
Sun, L., & Schulz, K. (2015). The improvement of land cover classification by thermal remote sensing. Remote Sensing, 7(7), 8368–8390. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70708368
Talukdar, S., Singha, P., Mahato, S., Pal, S., Liou, Y. A., & Rahman, A. (2020). Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—A review. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071135
Tariq, A., Mumtaz, F., Majeed, M., & Zeng, X. (2023). Spatio-temporal assessment of land use land cover based on trajectories and cellular automata Markov modelling and its impact on land surface temperature of Lahore district Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10738-w
Tehrany, M. S., Pradhan, B., & Jebur, M. N. (2013). Spatial prediction of flood susceptible areas using rule based decision tree (DT) and a novel ensemble bivariate and multivariate statistical models in GIS. Journal of Hydrology, 504, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.034
Theres, B. L., & Selvakumar, R. (2022). Comparison of landuse/landcover classifier for monitoring urban dynamics using spatially enhanced landsat dataset. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(5), 142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10242-x
Tilahun, A., Asmare, T., Nega, W., & Gashaw, T. (2023). The nexus between land use, land cover dynamics, and soil erosion: A case study of the Temecha watershed, upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(1), 1023–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22213-7
Vanoni, V. A. (1975). Sedimentation engineering: American society of civil engineers, manuals and reports on engineering practice. No. 54, p. 745.
Wang, S. J., Liu, Q. M., & Zhang, D. F. (2004). Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: Geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degradation & Development, 15(2), 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.592
Wang, R., Zhang, S., Yang, J., Pu, L., Yang, C., Yu, L., & Bu, K. (2016). Integrated use of GCM, RS, and GIS for the assessment of hillslope and gully erosion in the Mushi River Sub-Catchment. Northeast China. Sustainability, 8(4), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8040317
Weifeng, Z. H. O. U., & Bingfang, W. U. (2008). Assessment of soil erosion and sediment delivery ratio using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of upstream Chaobaihe River catchment, north China. International Journal of Sediment Research, 23(2), 167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6279(08)60016-5
Weslati, O., Bouaziz, S., & Sarbeji, M. M. (2023). Modelling and assessing the spatiotemporal changes to future land use change scenarios using remote sensing and CA-Markov model in the Mellegue catchment. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 51(1), 9–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01618-4
Wischmeier, W. H., & Smith, D. D. (1978). Predicting rainfall erosion losses: A guide to conservation planning (No. 537). Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration.
Yu, W., Zang, S., Wu, C., Liu, W., & Na, X. (2011). Analyzing and modeling land use land cover change (LUCC) in the Daqing City, China. Applied Geography, 31(2), 600–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2010.11.019
Zadbagher, E., Becek, K., & Berberoglu, S. (2018). Modeling land use/land cover change using remote sensing and geographic information systems: Case study of the Seyhan Basin, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6877-y
Zarris, D., Vlastara, M., & Panagoulia, D. (2011). Sediment delivery assessment for a transboundary Mediterranean catchment: The example of Nestos River catchment. Water Resources Management, 25, 3785–3803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9889-8
Zweig, M. H., & Campbell, G. (1993). Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: A fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clinical Chemistry, 39(4), 561–577. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/39.4.561
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Bhuvan India, USGS, FAO and Climate Hazard center for free download of Cartosat, Landsat, Soil layers and rainfall data which were used in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Vinoth Kumar Sampath: Conception, Methodology Formulation, Investigation, Data Preservation, Original Manuscript Writing. Nisha Radhakrishnan: Guidance, Monitoring, Evaluating, Formatting, Approval of the final Manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sampath, V.K., Radhakrishnan, N. Prediction of soil erosion and sediment yield in an ungauged basin based on land use land cover changes. Environ Monit Assess 196, 56 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12166-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12166-w