Abstract
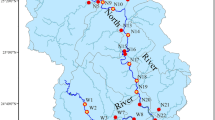
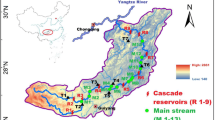
It is widely acknowledged that dams affect sediment transport and water quality. To support water management of reservoirs, it is useful to explore how the fractions of phosphorus (P) in sediments were changed after the dam was built. The aim of this study was to assess the spatial and temporal trends of the P fractions in sediments from the Miyun Reservoir, a pivotal drinking water supply for Beijing City, the capital of China. Nine surface sediment samples, together with a sediment core, were collected. The concentrations of total P (TP) and their fractions were then determined by using a sequential extraction method. The results showed that the reservoir was classified into three areas spatially based on the TP concentrations, i.e., high (Baihe area), medium (transitional area), and low (Chaohe area) concentrations. The concentrations of iron-bound P (BD-P) and metal oxide–bound P (NaOH-P) were higher in the Baihe and Chaohe regions than those in the transitional area and tended to increase with water depth. Dam construction can lead to the concentrations of P increased in sediments and further increase the potential of internal P loadings. This study revealed the effect of dam construction on sedimentary P accumulation. The results will be helpful in better understanding the mobility and bioavailability of P in the aquatic ecosystem, which aim to achieve a more highly targeted environmental management for this important region.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell, J. M., Hamilton, D. P., & Rutherford, J. C. (2013). Quantifying temporal and spatial variations in sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus transport in stream inflows to a large eutrophic lake. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 15(6), 1137–1152. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00083D.
Andreas, M., Tonya, D., Mcginnis, D. F., Helmut, F., Sabine, F., Mark, S., Peer, F., & Andreas, L. (2013). Sediment trapping by dams creates methane emission hot spots. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(15), 8130–8137. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4003907.
Aydin, I., Aydin, F., Saydut, A., & Hamamci, C. (2009). A sequential extraction to determine the distribution of phosphorus in the seawater and marine surface sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2), 664–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.095.
Bao, L., Li, X., & Cheng, P. (2018). Phosphorus retention along a typical urban landscape river with a series of rubber dams. Journal of Environmental Management, 228, 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.019.
Bayram, A., Kömürcü, M. İ., & Bulut, V. N. (2012). Effects of Torul dam on water quality in the stream Harşit, NE Turkey. Environmental Earth Sciences, 65(3), 713–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1118-5.
Bianchini, I., Fushita, Â. T., & Cunha-Santino, M. B. (2019). Evaluating the retention capacity of a new subtropical run-of-river reservoir. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(3), 161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7295-5.
Cai, Y., Guo, L., Douglas, T. A., & Whitledge, T. E. (2008). Seasonal variations in nutrient concentrations and speciation in the Chena River, Alaska. Journal of Geophysical Research – Biogeosciences, 113(G3). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008jg000733.
Chen, J. (2019). Dam construction alters function and community composition of diazotrophs in riparian soils across an environmental gradient. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 132, 14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.01.020.
Chowdhury, M., & Al Bakri, D. (2006). Diffusive nutrient flux at the sediment-water interface in Suma Park reservoir, Australia. Hydrological Sciences Journal-Journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques, 51(1), 144–156. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.51.1.144.
Christophoridis, C., & Fytianos, K. (2006). Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35(4), 1181–1192. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2005.0213.
Dai, S. B., Yang, S. L., & Li, M. (2009). The sharp decrease in suspended sediment supply from China's rivers to the sea: anthropogenic and natural causes. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 54(1), 135–146. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.54.1.135.
Di, Z., Zhang, H., & Shan, B. (2015). Using sedimentary phosphorus/nitrogen as indicators of shallow lake eutrophication: concentrations or accumulation fluxes. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(5), 3935–3944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4465-9.
Elledge, A., & Thornton, C. (2017). Effect of changing land use from virgin brigalow (Acacia harpophylla) woodland to a crop or pasture system on sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus in runoff over 25 years in subtropical Australia. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 239, 119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.12.031.
Fang, H. (2017). Impact of land use change and dam construction on soil erosion and sediment yield in the black soil region, northeastern China. Land Degradation & Development, 28(4), 1482–1492. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2677.
Fox, G. A., Sheshukov, A., Cruse, R., Kolar, R. L., Guertault, L., Gesch, K. R., & Dutnell, R. C. (2016). Reservoir sedimentation and upstream sediment sources: perspectives and future research needs on streambank and gully erosion. Environmental Management, 57(5), 945–955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-016-0671-9.
Gächter, R., Tessier, A., Szabo, E., & Carignan, R. (1992). Measurement of total dissolved phosphorus in small volumes of iron rich interstitial water. Aquatic Sciences, 54(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00877261.
Gao, L., Zhou, J. M., Yang, H., & Chen, J. (2005). Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environmental Geology, 48(7), 835–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-0005-3.
Ge, Y. W., Zhang, K., & Yang, X. D. (2019). A 110-year pollen record of land use and land cover changes in an anthropogenic watershed landscape, eastern China: understanding past human-environment interactions. Science of the Total Environment, 650, 2906–2918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.058.
Guan, Y., Zang, S., & Xiao, H. (2014). The vertical variation of nutrients in a sediment core of Delong Lake reveals the anthropogenic effect. Ecotoxicology, 23(4), 480–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1198-6.
Guo, W., Huo, S., & Ding, W. (2015). Historical record of human impact in a lake of northern China: magnetic susceptibility, nutrients, heavy metals and OCPs. Ecological Indicators, 57, 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.04.019.
Gupta, H., Kao, S. J., & Dai, M. (2012). The role of mega dams in reducing sediment fluxes: a case study of large Asian rivers. Journal of Hydrology, 464, 447–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.07.038.
Hou, D., He, J., Lü, C., Dong, S., Wang, J., Xie, Z., & Zhang, F. (2014). Spatial variations and distributions of phosphorus and nitrogen in bottom sediments from a typical north-temperate lake, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(7), 3063–3079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2683-6.
Humborg, C., Ittekkot, V., Cociasu, A., & VonBodungen, B. (1997). Effect of Danube River dam on Black Sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure. Nature, 386(6623), 385–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/386385a0.
Hunter, H. M., & Walton, R. S. (2008). Land-use effects on fluxes of suspended sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus from a river catchment of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Journal of Hydrology, 356(1–2), 131–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.04.003.
Hupfer, M., & Lewandowski, J. (2005). Retention and early diagenetic transformation of phosphorus in Lake Arendsee (Germany) - consequences for management strategies. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie, 164(2), 143–167. https://doi.org/10.1127/0003-9136/2005/0164-0143.
Hupfer, M., Gachter, R., & Giovanoli, R. (1995). Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquatic Sciences, 57(4), 305–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00878395.
Jia, B., Tang, Y., Yang, B., & Huang, J. H. (2017). Historical and seasonal dynamics of phosphorus mobility in Sancha Lake of Southwest China's Sichuan Province. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5727-z.
Jin, G., Onodera, S., Amano, A., Saito, M., Shimizu, Y., & Satou, T. (2013). Effects of dam construction on sediment phosphorus variation in a semi-enclosed bay of the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 135, 191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2013.10.009.
Kapanen, G. (2012). Pool of mobile and immobile phosphorus in sediments of the large, shallow Lake Peipsi over the last 100 years. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(11), 6749–6763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2455-2.
Keller, S., Zhang, T. Q., Webb, S., Brugam, R., Johnson, K., & Lin, Z. Q. (2008). Effects of suburban land use on phosphorus fractions and speciation in the upper Peruque Creek, eastern Missouri. Water Environment Research, 80(4), 316–323. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143007x221283.
Kurunc, A., Yurekli, K., & Okman, C. (2006). Effects of Kilickaya dam on concentration and load values of water quality constituents in Kelkit stream in Turkey. Journal of Hydrology, 317(1), 17–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.05.006.
Lai, X., Liang, Q., Jiang, J., & Huang, Q. (2014). Impoundment effects of the Three-Gorges-Dam on flow regimes in two China’s largest freshwater lakes. Water Resources Management, 28(14), 5111–5124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0797-6.
Lei, P., Zhang, H., & Shan, B. (2016). Vertical records of sedimentary PAHs and their freely dissolved fraction in porewater profiles from the northern bays of Taihu Lake, eastern China. RSC Advances, 6, 98835. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra11180g.
Lewis, G. N., Auer, M. T., Xiang, X., & Penn, M. R. (2007). Modeling phosphorus flux in the sediments of Onondaga Lake: insights on the timing of lake response and recovery. Ecological Modelling, 209(2), 121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2007.06.015.
Liu, X. (2001). Studying on eutrophication of Miyun Reservoir water body. In Thesis (p. 76). Beijing: Capital Normal University (in Chinese).
Liu, N. (2004). Issues related to safety management, abandonment and construction of dams in 21st century in China. China Water Resources, 23, 27–30 (in Chinese).
Liu, X. R., Xu, Q., Ge, X. L., & Wang, Y. H. (2003). Phosphorous species and their distribution characters in sediments of Miyun Reservoir. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 12(2), 5 (in Chinese).
Liu, X. R., Xu, Q., Liu, L., & Wu, D. W. (2004). The study on phosphorus geochemical effects of sediment-water Interface in Miyun Reservoir. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 23(4), 5 (in Chinese).
Liu, E., Shen, J., Yuan, H., Zhang, E., & Du, C. (2013). The spatio-temporal variations of sedimentary phosphorus in Taihu Lake and the implications for internal loading change and recent eutrophication. Hydrobiologia, 711(1), 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1465-1.
Liu, Q., Liu, S., Zhao, H., Deng, L., Wang, C., Zhao, Q., & Dong, S. (2015). The phosphorus speciations in the sediments up- and down-stream of cascade dams along the middle Lancang River. Chemosphere, 120, 653–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.10.012.
Lou, B., & Yin, S. (2016). Spatial and seasonal distribution of phosphorus in the mainstem within the Three Gorges Reservoir before and after impoundment. Water Science and Technology, 73(3), 636–642. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.516.
Luo, W., Lu, Y., Zhang, Y., Fu, W., Wang, B., Jiao, W., Wang, G., Tong, X., & Giesy, J. (2010). Watershed-scale assessment of arsenic and metal contamination in the surface soils surrounding Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 91(12), 2599–2607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.07.023.
Maavara, T., Parsons, C. T., Ridenour, C., Stojanovic, S., Duerr, H. H., Powley, H. R., & Van, C. P. (2015). Global phosphorus retention by river damming. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(51), 15603–15608. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511797112.
Martínez, C. M., Marcos, M. L. F., & Rodríguez, E. A. (1996). Factors influencing phosphorus adsorption in mine soils in Galicia, Spain. Science of the Total Environment, 180(2), 137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(95)04934-7.
Mayer, T., Simpson, S., Thorleifson, L., Lockhart, W., & Wilkinson, P. (2006). Phosphorus geochemistry of recent sediments in the South Basin of Lake Winnipeg. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 9(3), 307–318. https://doi.org/10.1080/14634980600876039.
Murphy, T., Dougall, C., Burger, P., & Carroll, C. (2013). Runoff water quality from dryland cropping on Vertisols in Central Queensland, Australia. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 180, 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.07.023.
Némery, J., Gratiot, N., Doan, P. T. K., Duvert, C., Alvarado-Villanueva, R., & Duwig, C. (2016). Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediment sources and retention in a small eutrophic tropical reservoir. Aquatic Sciences, 78(1), 171–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-015-0416-5.
Ouyang, W., Jiao, W., Li, X. M., Giubilato, E., & Critto, A. (2016). Long-term agricultural non-point source pollution loading dynamics and correlation with outlet sediment geochemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 540, 379–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.06.043.
Pan, L. B., Fang, G. L., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Su, B. Y., Li, D., & Xiang, B. (2018). Potentially toxic element pollution levels and risk assessment of soils and sediments in the upstream river, Miyun Reservoir, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(11), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112364.
Powers, S. M., Tank, J. L., & Robertson, D. M. (2015). Control of nitrogen and phosphorus transport by reservoirs in agricultural landscapes. Biogeochemistry, 124(1), 417–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-015-0106-3.
Qin, L., Zeng, Q., Zhang, W., Li, X., Steinman, A. D., & Du, X. (2016). Estimating internal P loading in a deep water reservoir of northern China using three different methods. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(18), 18512–18523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7035-0.
Ribeiro, D. C., Martins, G., Nogueira, R., Cruz, J. V., & Brito, A. G. (2008). Phosphorus fractionation in volcanic lake sediments (Azores - Portugal). Chemosphere, 70(7), 1256–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.07.064.
Ruttenberg, K. C. (1992). Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 37(7), 1460–1482. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1992.37.7.1460.
Rydin, E. (2000). Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Research, 34(7), 2037–2042. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00375-9.
Serieyssol, C. A., Edlund, M. B., & Kallemeyn, L. W. (2009). Impacts of settlement, damming, and hydromanagement in two boreal lakes: a comparative paleolimnological study. Journal of Paleolimnology, 42(4), 497–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-008-9300-9.
Shen, X., Du, X. Z., Jia, D. M., & Li, X. Y. (2015). The influence of upstream input on phosphorus retention in Miyun Reservoir. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(10), 3114–3120 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0010.
Stow, C. A., Borsuk, M. E., & Stanley, D. W. (2001). Long-term changes in watershed nutrient inputs and riverine exports in the Neuse river, North Carolina. Water Research, 35(6), 1489–1499. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00402-4.
Syvitski, J. P. M., Vörösmarty, C. J., Kettner, A. J., & Green, P. (2005). Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science, 308(5720), 376–380. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1109454.
Tylmann, W. (2005). Lithological and geochemical record of anthropogenic changes in recent sediments of a small and shallow lake (Lake Pusty Staw, northern Poland). Journal of Paleolimnology, 33(3), 313–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-004-5506-7.
Vo, N. X. Q. (2014). Impoundments increase potential for phosphorus retention and remobilization in an urban stream. Environmental Engineering Research, 19(2), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2014.19.2.175.
Vörösmarty, C. J., Meybeck, M., Fekete, B., Sharma, K., Green, P., & Syvitski, J. P. M. (2003). Anthropogenic sediment retention: major global impact from registered river impoundments. Global and Planetary Change, 39(1–2), 169–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8181(03)00023-7.
Wang, X. (2015). Study of forest ecohydrological characteristics in plot and watershed scales in mountainous regions of northern China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 178 p (in Chinese).
Wang, S. R., Zhao, H. C., Zhou, X. N., & Chu, J. Z. (2004). Study on the organic matter, Total nitrogen and phosphorus form distribution of different particle size fractions in the sediments from Wuli Lake and Gonghu Lake. Research of Environmental Sciences, 17(S1), 4 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13198/j.res.2004.s1.13.wangshr.003.
Wei, F., Qi, W., Sun, Z., Huang, Y., & Shen, Y. (2002). Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method (pp. 211–284). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese).
Wei, G., Yang, Z., Cui, B., Li, B., Chen, H., Bai, J., & Dong, S. (2009). Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resources Management, 23(9), 1763–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9351-8.
Xia, X., Wu, Q., Zhu, B., Zhao, P., Zhang, S., & Yang, L. (2015). Analyzing the contribution of climate change to long-term variations in sediment nitrogen sources for reservoirs/lakes. Science of the Total Environment, 523, 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.140.
Xin, X. K., Zhang, H., Lei, P., Tang, W. Z., Yin, W., Li, J., Zhong, H., & Li, K. F. (2020) Algal blooms in the middle and lower Han River: Characteristics, early warning and prevention. Science of The Total Environment, 706,135293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135293.
Zan, F., Huo, S., Xi, B., Zhu, C., Liao, H., Zhang, J., & Yeager, K. (2012). A 100-year sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic impacts on a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14(3), 804–816. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1em10760g.
Zhang, Y., Su, Y., Liu, Z., Chen, X., Yu, J., & Jin, M. (2016). A sediment record of environmental change in and around Lake Lugu, SW China, during the past two centuries. Journal of Paleolimnology, 55(3), 259–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-016-9878-2.
Zhou, J., Man, Z., & Lu, P. (2013). The effect of dams on phosphorus in the middle and lower Yangtze river. Water Resources Research, 49(6), 3659–3669. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrcr.20283.
Zhu, M., Zhu, G., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Zhao, L., & Gu, Z. (2013a). Estimation of the algal-available phosphorus pool in sediments of a large, shallow eutrophic lake (Taihu, China) using profiled SMT fractional analysis. Environmental Pollution, 173, 216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.016.
Zhu, X. F., Ji, H. B., Chen, Y., Qiao, M. M., & Tang, L. (2013b). Assessment and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments of Miyun reservoir, Beijing. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(7), 6049–6062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3005-2.
Zhu, Y., Zhang, R., Wu, F., Qu, X., Xie, F., & Fu, Z. (2013c). Phosphorus fractions and bioavailability in relation to particle size characteristics in sediments from Lake Hongfeng, Southwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 68(4), 1041–1052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2224-3.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural ScienceFoundation of China (41771531); the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0503007), the One-Three-Five Project (No. YSW2013B02-4) of the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment in China (No. 2014ZX07203010), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M622782).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 84 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, L., Lei, P., Lei, Q. et al. Evaluating the effect of dam construction on the phosphorus fractions in sediments in a reservoir of drinking water source, China. Environ Monit Assess 192, 99 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8053-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8053-4