Abstract
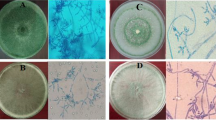
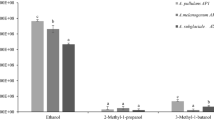
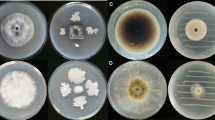
Production of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is one of the modes of actions of Trichoderma spp. They inhibit pathogenic fungi/bacteria, promote plant growth, and also affect interactions of plants with pathogens. However, the study of VOCs emitted by Trichoderma species associated with olive roots and its benefits are still limited. In the present study, two strains of Trichoderma collected from olive grove soil were evaluated for their antagonistic activity against five strains of Verticillium dahliae named (Vd1 to Vd5) by indirect confrontation assay. In addition, identification and quantification of volatile compounds produced by each strain were assessed through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS). The extraction of metabolites was performed from filtrates using liquid–liquid extraction. Extracts obtained were taken for analysis through GC–MS. Results of indirect confrontation assay showed a high inhibitory activity against V.dahliae. Trichoderma asperellum (T4) and Trichoderma harzianum (T12) exhibited an average inhibition rate of 64.49% and 61.59% respectively. Besides, 98 volatile compounds were detected through GC–MS analysis, including important volatile compounds with antifungal activities, such as D-limonene, octadecanoic acid methyl ester, hexadecanoic acid, toluene, phenylethyl alcohol, benzene derivatives, several phenolic isomers, citral, eicosane and 13-docosenamide. Other volatile compounds revealed antibacterial activity, providing growth promotion, or antioxidant activity, such as oleic acid. Importantly, 7-epi-nemorosone was detected for the first time as new molecule produced by Trichoderma harzianum (T12). This molecule provides anticancer and antioxidant activity. Overall, these strains with various activities are considered as excellent source for discovery of bioactive molecules with eventual application in different biological fields. However, they could be beneficial mainly for suppressing plant pathogens and stimulation of plant growth.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author,.please contact author for data requests.
References
Agoramoorthy, G., Chandrasekaran, M., Venkatesalu, V., & Hsu, M. (2007). Antibacterial and antifungal activities of fatty acid methyl esters of the blind-your-eye mangrove from India. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 38(4), 739–742. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822007000400028
Altieri, C., Cardillo, D., Bevilacqua, A., & Sinigaglia, M. (2007). Inhibition of Aspergillus spp. and Penicillium spp. by fatty acids and their monoglycerides. Journal of Food Protection, 70(5), 1206–1212. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-70.5.1206
Angel, L. P. L., Yusof, M. T., Ismail, I. S., Ping, B. T. Y., Azni, I. N. A. M., Kamarudin, N. H., & Sundram, S. (2016). An in vitro study of antifungal activity of Trichoderma virens 7b and profile of its non-polar antifungal components released against Ganoderma boninense. Journal of Microbiology, 54, 732–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-6304-4
Arlorio, M., Ludwig, A., Boller, T., & Bonfante, P. (1992). Inhibition of fungal growth by plant chitinases and â-1,3-glucanases. Protoplasma, 171, 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01379278
Audrain, B., Farag, M. A., Ryu, C. M., & Ghigo, J. M. (2015). Role of bacterial volatile compounds in bacterial biology. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 39, 222–233. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuu013
Avis, T., Boulanger, R., & Bélanger, R. (2000). Synthesis and biological characterization of (Z)-9-heptadecenoic and (Z)-6-methyl-9-heptadecenoic acids: Fatty acids with antibiotic activity produced by Pseudozyma focculosa. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 26(4), 987–1000. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005464326573
Banaras, S., Javaid, A., Shoaib, A., & Ahmed, E. (2017). Antifungal activity of Cirsium arvense extracts against phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina. Planta Daninha, 35, e0171. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582017350100014
Bao, L. J., Wei, Y. L., Yao, Y., Ruan, Q. Q., & Zeng, E. Y. (2015). Global trends of research on emerging contaminants in the environment and humans: A literature assimilation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 1635–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3404-8
Bitas, V., Kim, H. S., Bennett, J. W., & Kang, S. (2013). Sniffing on microbes: Diverse roles of microbial volatile organic compounds in plant health. Molecular Plant-Microbe Intractions, 26, 835–843. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-10-12-0249-CR
Burke, B. A., & Nair, M. G. (1989). Antimicrobial/antifungal compositions. United States Utility Patent, US4876277.
Carrero-Carrón, I., Trapero-Casas, J. L., Olivares-García, C., Monte, E., Hermosa, R., & Jiménez-Díaz, R. M. (2016). Trichoderma asperellum is effective for biocontrol of Verticillium wilt in olive caused by the defoliating pathotype of Verticillium dahliae. Crop Protection, 88, 45–52.
Crutcher, F. K., Parich, A., Schuhmacher, R., Mukherjee, P. K., Zeilinger, S., & Kenerley, C. M. (2013). Fungal Genetics and Biology, 56, 67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2013.05.003
Cuesta-Rubio, O., Frontana-Uribe, B. A., Ramirez-Apan, T., & Cárdenas, J. (2002). Polyisoprenylated benzophenones in Cuban propolis; biological activity of nemorosone. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C, 57, 372–378. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2002-3-429
Dandurishvili, N., Toklikishvili, N., Ovadis, M., Eliashvili, P., Giorgobiani, N., Keshelava, R., Tediashvili, M., Vainstein, A., Khmel, I., Szegedi, E., & Chernin, L. (2011). Broadrange antagonistic rhizobacteria Pseudomonas fluorescens and Serratia plymuthica suppress Agrobacterium crown gall tumours on tomato plants. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04891.x
Dennis, C., & Webster, J. (1971). Antagonistic properties of speciesgroups of Trichoderma. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 57, 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-1536(71)80078-5
Druzhinina, I. S., Seidl-Seiboth, V., Herrera-Estrella, A., Horwitz, B. A., Kenerley, C. M., Monte, E., Mukherjee, P. K., Zeilinger, S., Grigoriev, I. V., & Kubicek, C. P. (2011). Trichoderma: The genomics of opportunistic success. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 9(10), 749. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2637
Fincheira, P., Parada, M., & Quiroz, A. (2017). Volatile organic compounds stimulate plant growing and seed germination of Lactuca sativa. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 17, 853–867. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162017000400002
Gams, W., & Bissett, J. (1998). Morphology and Identification of Trichoderma In: C. P. Kubicek & G. E. Harman (Eds.), Trichoderma and Gliocladium: Basic Biology, Taxonomy and Genetics (1, pp. 3–34). Taylor & Francis Led.
Gams, W., & Bissett, J. (2002). Morphology and identification of Trichoderma. In C. P. Kubicek & G. E. Harman (Eds.), Trichoderma and Gliocladium: Basic biology, taxonomy and genetics (pp. 3–31). Taylor and Francis.
Gardes, M., & Bruns, T. D. (1993). ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Molecular Ecology, 2(2), 113–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.1993.tb00005.x
Ghisalberti, E. L., & Sivasithamparam, K. (2011). Antifungal antibiotics produced by Trichoderma spp. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 23, 1011–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(91)90036-J
Gibka, A. J., Styczynska, K., & Glinski, M. (2009). Antimicrobial activity of undecan-3-one, undecan-3-ol and undec-3-yl acetate. Central European Journal of Immunology, 2009(34), 154–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2009.10643763
Hung, R., Lee, S., & Bennett, J. W. (2015). Fungal volatile organic compounds and their role in ecosystems. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99, 3395–3405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6494-4
Hunziker, L., Bönisch, D., Groenhagen, U., Bailly, A., Schulz, S., & Weisskopf, L. (2015). Pseudomonas strains naturally associated with potato plants produce volatiles with high potential for inhibition of Phytophthora infestans. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 81, 821–830. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02999-14
Intana, W., Kheawleng, S., & Sunpapao, A. (2021). Trichoderma asperellum T76–14 released volatile organic compounds against postharvest fruit rot in muskmelons (Cucumis melo) caused by Fusarium incarnatum. Journal of Fungi, 7(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7010046
Iqbal, S., Ashfaq, M., Malik, A. H., Khan, K., & Mathew, P. (2017). Isolation, preservation and revival of Trichoderma viride in culture media. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 5(3), 1640–1646.
Jeleń, H., Błaszczyk, L., Chełkowski, J., Rogowicz, K., & Strakowska, J. (2014). Formation of 6-n-pentyl-2h-pyran-2-one (6-pap) and other volatiles by different Trichoderma species. Mycological Progress, 13(3), 589–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-013-0942-2
Jeong, M. H., Lee, Y. S., Cho, J. Y., Ahn, Y. S., Moon, J. H., Hyun, H. N., & Kim, K. Y. (2017). Isolation and characterization of metabolites from Bacillus licheniformis MH48 with antifungal activity against plant pathogens. Microbial Pathogenesis, 110, 645–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.07.027
Karanja, E., Boga, H., Muigai, A., Wamunyokoli, F., Kinyua, J., & Nonoh, J. (2012). Growth characteristics and production of secondary metabolites from selected novel Streptomyces species isolated from selected Kenyan national parks. In: Scientific conference proceeding
Khatri, D. K., Tiwari, D. N., & Bariya, H. S. (2017). Chitinolytic efficacy and secretion of cell wall-degrading enzymes from Trichoderma spp. In response to phytopathological fungi. Journal of Applied Biology and Biotechnology, 5(6), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2017.50601
Korpi, A., Järnberg, J., & Pasanen, A. L. (2009). Microbial volatile organic compounds. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 39, 139–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440802291497
Lambert, C. (2011). Etude du rôle des stilbènes dans les défenses de la vigne contre les maladies du bois. Thèse de Doctorat d’Université.
Lester, G. (1965). Inhibition of growth, synthesis, and permeability in Neurospora crassa by phenethyl alcohol. Journal of Bacteriology, 90, 29–37. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.90.1.29-37.1965
Li, R. Y., Wu, X. M., Yin, X. H., Liang, J. N., & Li, M. (2014). The natural product citral can cause significant damage to the hyphal cell walls of Magnaporthe grisea. Molecules, 19(7), 10279–10290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190710279
Liu, S., Ruan, W., Li, J., Xu, H., Wang, J., Gao, Y., & Wang, J. (2008). Biological control of phytopathogenic fungi by fatty acids. Mycopathologia, 166(2), 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-008-9124-1
Liu, T., Song, T., Zhang, X., Yuan, H., Su, L., Li, W., Xu, J., Liu, S., Chen, L., & Chen, T. (2014). Unconventionally secreted effectors of two filamentous pathogens target plant salicylate biosynthesis. Nature Communications, 5, 4686. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5686
Marrufo, T., Nazzaro, F., Mancini, E., Fratianni, F., Coppola, R., De Martino, L., Agostinho, A., & De Feo, V. (2013). Chemical composition and bioactivity of the essential oil from leaves of Moringa oleifera Lam. cultivated in Mozambique. Molecules, 18(9), 10989–11000. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules180910989
Mihailovi, V., Vukori, N., Niforovi, N., Soluji, S., Mladenovi, M., & Maskovi, P. (2011). Studies on the antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of the essential oils and alcoholic extracts of Gentiana asclepiadea L. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 5(7), 1164–1174.
Mo, E. K., & Sung, C. K. (2007). Phenylethyl alcohol (PEA) application slows fungal growth and maintains aroma in strawberry. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 45, 234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.02.005
Nandhini, S. U. (2015). Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of bioactive constituents from the marine Streptomyces. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 8, 244–246.
Pezet, R., & Pont, V. (1988). Identification of pteroslibene in grape berries of Vitis vinifera. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 26(5), 603–607.
Pohl, C. H., Kock, J. L., & Thibane, V. S. (2011). Antifungal free fatty acids: A review. Science Against Microbial Pathogens: Current Research and Technological Advances, 1, 61–71.
Raza, W., Yuan, J., Wu, Y. C., Rajer, F. U., Huang, Q., & Shen, Q. R. (2015). Biocontrol traits of two Paenibacillus polymyxa strains SQR-21 and WR-2 In response to fusaric acid, a phytotoxin produced by Fusarium species. Plant Pathology, 64, 1041–1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12354
Reghmit, A., Benzina-tihar, F., López Escudero, F. J., Halouane-Sahir, F., Oukali, Z., Bensmail, S., & Ghozali, N. (2021). Trichoderma spp. isolates from the rhizosphere of healthy olive trees in northern Algeria and their biocontrol potentials against the olive wilt pathogen, Verticillium Dahliae. Organic Agriculture, 11, 639–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-021-00371-1
Rodríguez-Meizoso, I., Jaime, L., Santoyo, S., Señoráns, F., Cifuentes, A., & Ibáñez, E. (2010). Subcritical water extraction and characterization of bioactive compounds from Haematococcus pluvialis. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 51, 456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2009.03.014
Rojas, N. M., Cuesta, O., Avilés, A., Lugo, D., & Avellaneda, S. (2001). Actividad antimicrobiana de nemorosona aislada de Clusia rosea. Rev Cub Farm, 35, 197–200.
Ruangwong, O. U., Wonglom, P., Suwannarach, N., Kumla, J., Thaochan, N., Chomnunti, P., & Sunpapao, A. (2021). Volatile organic compound from Trichoderma asperelloides TSU1: Impact on plant pathogenic fungi. Journal of Fungi, 7(3), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7030187
Ryu, C. M., Farag, M. A., Hu, C. H., Reddy, M. S., Wie, H. X., Pare, P. W., & Kloepper, J. W. (2003). Bacterial volatiles promote growth of Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100, 4927–4932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0199-0
Saba, H., Vibhash, D., Manisha, M., Prashant, K., Farhan, H., & Tauseef, A. (2012). Trichoderma–a promising plant growth stimulator and biocontrol agent. Mycosphere, 3(4), 524–531. https://doi.org/10.5943/mycosphere/3/4/14
Samuels, G. J., Dodd, S. L., Gams, W., Castlebury, L. A., & Petrini, O. (2002). Trichoderma species associated with the green mold epidemic of commercially grown Agaricus bisporus. Mycologia, 94, 146–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2003.11833257
Santos, S. S., Augusto, D. G., Alves, P. A. C., Pereira, J. S., Duarte, L. M., Melo, P. C., Gross, E., Kaneto, C. M., Silva, A., & Santos, J. L. (2018). Trichoderma asperelloides ethanolic extracts efficiently inhibit Staphylococcus growth and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE, 13(8), 0202828. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202828
Schnürer, J., Olsson, J., & Börjesson, T. (1999). Fungal volatiles as indicators of food and feeds spoilage. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 27, 209–217. https://doi.org/10.1006/fgbi.1999.1139
Sharma, D., Pramanik, A., & Agrawal, P. K. (2016). Evaluation of bioactive secondary metabolites from endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis neglecta BAB-5510 isolated from leaves of Cupressus torulosa D.Don. 3 Biotech. 6–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0518-3.
Siddiquee, S., Cheong, B. E., Taslima, K., Kausar, H., & Hasan, M. M. (2012). Separation and identification of volatile compounds from liquid cultures of Trichodermaharzianumby GC-MS using three different capillary columns. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 50, 358–367. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bms012
Sohrabi, M., Zhang, L., Zhang, K., Ahmetagic, A., & Wei, M. Q. (2014). Volatile organic compounds as novel markers for the detection of bacterial infections. Clinical Microbiology: Open Access, 3, 151. https://doi.org/10.4172/2327-5073.1000151
Srivastava, M., Singh, A., & Srivastava, D. K. (2014). Morphological and molecular characterization of Trichoderma isolates: An antagonist against soil borne pathogens. International Journal of Science and Research, 3(7), 2399–2404. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2020.903.122
Strobel, G., Singh, S. K., Riyaz-Ul-Hassan, S., Mitchell, A. M., Geary, B., & Sears, J. (2011). An endophytic/ pathogenic Phoma sp. fromcreosote bush producing biologically active volatile compounds having fuel potential. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 320, 87–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02297.x
Tirranen, L. S., & Gitelson, I. I. (2006). The role of volatile metabolites in microbial communities of the LSS higher plant link. Advances in Space Research., 38(6), 1227–1232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2006.02.038
Vinale, F., Manganiello, G., Nigro, M., Mazzei, P., Piccolo, A., Pascale, A., Ruocco, M., Marra, R., Lombardi, N., & Lanzuise, S. (2014). A novel fungal metabolite with beneficial properties for agricultural applications". Molecules, 19(7), 9760–9772. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19079760
Yogeswari, S., Ramalakshmi, S., Neelavathi, R., & Muthumary, J. (2012). Identification and comparative studies of different volatile fractions of Monochaetia kanesensis by GCMS. Global Journal of Pharmacy, 6(2), 65–71.
Zhang, X., Li, B., Wang, Y., Guo, Q., Lu, X., Li, S., & Ma, P. (2013). Lipopeptides, a novel protein, and volatile compounds contribute to the antifungal activity of the biocontrol agent Bacillus atrophaeus CAB-1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 9525–9534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5198-x
Zhao, L. J., Yang, X. N., Li, X. Y., Mu, W., & Liu, F. (2011). Antifungal, Insecticidal and Herbicidal Properties of Volatile Components from Paenibacillus polymyxa StrainBMP-11. Agricultural Sciences in China, 10, 728–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(11)60056-4
Zhu, Y. J., Zhou, H. T., Hu, Y. H., Tang, J. Y., Su, M. X., Guo, Y. J., Chen, Q. X., & Liu, B. (2011). Antityrosinase and antimicrobial activities of 2-phenylethanol, 2-phenylacetaldehyde and 2-phenylacetic acid. Food Chemistry, 124, 298–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.06.036
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to DGRST (General Delegation for Scientific and Technical Research in Algeria) for financial and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Reghmit Abdenaceur, Benzina-tihar Farida and Sahir-Halouane Fatma. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Reghmit Abdenaceur and all the authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdenaceur, R., Farida, Bt. & Fatma, SH. Volatile organic compounds activities of Trichoderma species isolated from olive grove soil against the wilt pathogen, Verticillium dahliae. Eur J Plant Pathol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-024-02839-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-024-02839-8