Abstract
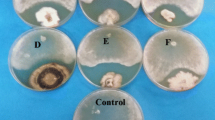
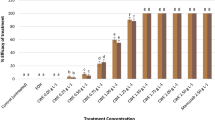
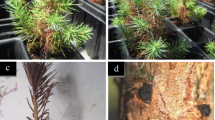
The inhibition of the fungus Moniliophthora perniciosa, which is the causal agent of witches’ broom disease in Theobroma cacao L., is the main focus of the present study. The use of phytoalexins has provided disease control that is as efficient as control with the use of fungicides, with the advantage of not harming humans and the environment. In this sense, the objective was to evaluate the action of 3-hydroxycoumarin compared with the standard defence activator acibenzolar-S-methyl (Bion® 500 WG) and systemic fungicide tebuconazole (Folicur® 200 CE), and study the possible mechanisms of action. Initially, basidiospore germination inhibition assays (in vitro) were performed using four different concentrations of 3-hydroxycoumarin. The result was 100% inhibition at the concentration of 1000 ppm. Thereafter, this substance was used in four different treatments (in vivo) of cacao seedlings of the SIC-23 genotype, with regard to the order of application. The data analysis showed greater inhibition when 3-hydroxycoumarin was applied after inoculation (TAI test), and suggested a curative effect on Theobroma cacao seedlings. In silico, it was used the enzyme chitin synthase because this action as key enzyme in chitin biosynthetic pathway. The in silico tests show that 3-hydroxycoumarin inhibited the production of chitin synthase by the fungus. Therefore, the present study identifies a potential inhibitor of M. perniciosa and suggests the best application methodology.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aime, M. C., & Phillips-Mora, W. (2005). The causal agents of witches’ broom and frosty pod rot of cacao (chocolate, Theobroma cacao) form a new lineage of Marasmiaceae. Mycologia, 97, 1012–1022.
Al-Amiery, A. A., Al-Bayati, R. I. H., Saour, K. Y., & Radi, M. F. (2011). Cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of novel 2-quinolone derivatives derived from coumarin. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 38, 559–569.
Al-Amiery, A. A., Kadhum, A. A. H., & Mohamad, A. B. (2012). Antifungal activities of new coumarins. Molecules, 17, 5713–5723.
Ampasala, D. R., Zheng, S., Zhang, D., Ladd, T., Doucet, D., Krell, P. J., Retnakaran, A., & Feng, Q. (2011). An epidermis-specific chitin synthase cdna in Choristoneura fumiferana: Cloning, characterization, developmental and hormonal-regulated expression. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 76(2), 83–96.
Atmaka, M., Bilgin, H. M., Obay, B. D., Diken, H., Kelle, M., & Kale, E. (2011). The hepatoprotective effect of coumarin and coumarin derivatives on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury by anti-oxidative activities in rats. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry, 67, 569–576.
Bansal, Y., Sethi, P., & Bansal, G. (2013). Coumarin: A potential nucleus for anti-inflammatory molecules. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 22, 3049–3060.
Behr, J. B. (2003). Chitin synthase as an antifungal target: Recent advances. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2, 173–189.
Carpinella, M. C., Ferrayoli, C. G., & Palacios, S. M. (2005). Antifungal synergistic effect of scopoletin, a hydroxycoumarin isolated from Melia azedarach L. fruits. Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53, 2922–2927.
Case, D. A., Darden, T. A., Cheatham III, T. E., Simmerling, C. L., Wang, J., Duke, R. E., Luo, R., Walker, R. C., Zhang, W., Merz, K. M., Roberts, B., Hayik, S., Roitberg, A., Seabra, G., Swails, J., Goets, A. W., Kolossváry, I., Wong, K. F., Paesani, F., Vanicek, J., Wolf, R. M., Liu, J., Wu, X., Brozell, S. R., Steinbrecher, T., Gohlke, H., Cai, Q., Ye, X., Wang, J., Hsieh, M. J., Cui, G., Roe, D. R., Mathews, D. H., Seetin, M. G., Salomon-Ferrer, R., Sagui, C., Babin, V., Luchko, T., Gusarov, S., Kovalenko, A., Kollman, P. A. (2012), AMBER 12, University of California, San Francisco.
Dhanavade, M. J., Jalkute, C. B., Ghosh, J. S., & Sonawane, K. D. (2011). Study antimicrobial activity of lemon (Citrus Lemon L.) peel extract. British Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2, 119–122.
Duo-Chuan, L. (2006). Review of fungal chitinases. Mycopathologia, 161, 345–360.
Ferreira, S. Z., Carneiro, H. C., Lara, H. A., Alves, R. B., Resende, J. M., Oliveira, H. M., & Freitas, R. P. (2015). Synthesis of a new peptide–coumarin conjugate: A potential agent against Cryptococcosis. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 6, 271–275.
Frias, G. A., Purdy, L. H., & Schmidt, R. A. (1995). An inoculation method for evaluate resistance of cocoa to Crinipellis perniciosa. Plant Disease, 79, 787–791.
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., Scuseria, G. E., Robb, M. A., Cheeseman, J. R., Scalmani, G., Barone, V., Petersson, G. A., Nakatsuji, H., Li, X., Caricato, M., Marenich, A., Bloino, J., Janesko, B. G., Gomperts, R., Mennucci, B., Hratchian, H. P., Ortiz, J. V., Izmaylov, A. F., Sonnenberg, J. L., Williams-Young, D., Ding, F., Lipparini, F., Egidi, F., Goings, J., Peng, B., Petrone, A., Henderson, T., Ranasinghe, D., Zakrzewski, V. G., Gao, J., Rega, N., Zheng, G., Liang, W., Hada, M., Ehara, M., Toyota, K., Fukuda, R., Hasegawa, J., Ishida, M., Nakajima, T., Honda, Y., Kitao, O., Nakai, H., Vreven, T., Throssell, K., Montgomery, Jr., J. A., Peralta, J. E., Ogliaro, F., Bearpark, M., Heyd, J. J., Brothers, E., Kudin, K. N., Staroverov, V. N., Keith, T., Kobayashi, R., Normand, J., Raghavachari, K., Rendell, A., Burant, J. C., Iyengar, S. S., Tomasi, J., Cossi, M., Millam, J. M., Klene, M., Adamo, C., Cammi, R., Ochterski, J. W., Martin, R. L., Morokuma, K., Farkas, O., Foresman, J. B., and Fox, D. J., Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016.
Godoy, M. F. P., Victor, S. R., Bellini, A. M., Guerreiro, G., Rocha, W. C., Bueno, O. C., Hebling, M. J. A., Bacci Jr., M., Silva, M. F. G. F., Vieira, P. C., Fernandes, J. B., & Pagnocca, F. C. (2005). Inhibition of the symbiotic fungus of leaf-cutting ants by coumarins. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 16, 669–672.
Gramacho, K. P., Luz, E. D. M. N., Silva, F. S., Lopes, U. V., Pires, J. L., & Pereira, L. (2016). Pathogenic variability of Moniliophthora perniciosa in three agroecological zones of the cacao region of Bahia, Brazil. Crop Breeding and Applied Biotechnology, 16, 7–13.
Johann, S., Mendes, B. G., Missau, F. C., Resende, M. A., & Pizzolatti, M. G. (2011). Antifungal activity of five species of Polygala. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 42, 1065–1075.
Karatas, M. O., Olgundeniz, B., Günal, S., Özdemir, I., Alici, B., & Çetinkaya, E. (2016). Synthesis, characterisation and antimicrobial activities of novel silver(I) complexes with coumarin substituted N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 24, 643–650.
Kasumbwe, K., Venugopala, K. N., Mohanlall, V., & Odhav, B. (2014). Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of substituted halogenated coumarins. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 5, 274–281.
Kerrigan, J. E. (2009). Amber 9.0 Drug/DNA complex. Piscataway, New Jersey, p. 17.
Krumrine, J., Raubacher, F., Brooijmans, N., & Kuntz, I. (2003). Principles and methods of docking and ligand design. In P. E. Bourne & W. Helge (Eds.), Structural Bioinformatics (pp. 443–476). New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Lagorce, A., Le Berre-Anton, V., Aguilar-Uscanga, B., Martin-Yken, H., Dagkessamanskaia, A., & François, J. (2002). Activation of the chitin synthesis pathway in response to cell-wall defects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. European Journal of Biochemistry, 269, 1697–1707.
Leal, L. K. A. M., Ferreira, A. A. G., Bezerra, G. A., Matos, F. J. A., & Viana, G. S. B. (2000). Anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator activities of Brazilian medicinal plants containing coumarin: A comparative study. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 70, 151–150.
Liu, X., Li, F., Li, D., Ma, E., Zhang, W., Zhu, K. Y., & Zhang, J. (2013). Molecular and functional analysis of UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases from the migratory locust, locusta migratoria. PLoS One, 8(8), e71970. Published online 2013 Aug 19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071970.
Meinhardt, L. W., Rincones, J., Bailey, B. A., Aime, M. C., Griffith, G. W., & Zhang, D. (2008). Moniliophthora perniciosa, the causal agent of witches’ broom disease of cacao: what’s new from this old foe? Molecular Plant Pathology, 9, 577–588.
Miyano, D. M., Lima, T., Simões, F. R., La-Scalea, M. A., Oliveira, h. P. M., & Codognoto, L. (2014). Electrochemical study of simple coumarin and its determination in aqueous infusion of Mikania glomerata. Journal of Brazilian Chemical Society, 25, 602–609.
Mouri, T., Yano, T., Kochi, S., Ando, T., & Hori, M. (2005). Synthesis and antifungal activity of new 3,4,7-tri-substituted coumarins. Journal of Pesticide Science, 30, 209–213.
Rehman, S. U., Chohan, Z. H., Gulnaz, F., & Supuran, C. T. (2005). In-vitro antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activities of some coumarins and their metal complexes. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 20, 333–340.
Rino, J. P., & Studart, N. (2001). Um potencial de interação para o estudo de materiais e simulações por dinâmica molecular. Química Nova, 24, 838–845.
Roncero, C. (2002). The genetic complexity of chitin synthesis in fungi. Current Genetics, 41, 367–378.
Scarpari, l. M., Meinhardt, l. W., Mazzafera, P., Pomella, A. W. V., Schiavinato, M. A., Cascardo, J. C. M., & Pereira, G. A. G. (2005). Biochemical changes during the development of witches’ broom: The most important disease of cocoa in Brazil caused by Crinipellis perniciosa. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 856–877.
Shi, Y., Zhou, C. H., Zhou, X. D., Geng, R. X., & Ji, Q. G. (2011). Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of coumarin-based benzotriazoles and their synergistic effects with chloromycin and fluconazole. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 46, 798–810.
Singh, L. K., Priyanka, Singh, V., & Katiyar, D. (2015). Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of some new coumarin derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents. Medicinal Chemistry, 11, 128–134.
Souza, C. S., Oliveira, B. M., Costa, G. G. L., Schriefer, A., Schnadelbach, A. S., Uetanabaro, A. P. T., Pirovani, C. P., Pereira, G. A., Taranto, A. G., Cascardo, J. C. M., & Goes-Neto, A. (2009). Identification and characterization of a class III chitin synthase gene of Monilliophthora perniciosa, the fungus that causes witches' broom disease of cacao. Journal of Microbiology, 47, 431–440.
Stein, A. C., Alvarez, S., Avancini, C., Zacchino, S., & von Poser, G. (2006). Antifungal activity of some coumarins obtained from species of Pterocaulon (Asteraceae). Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 107, 95–98.
Stewart, J. J. P. (2007). Optimization of parameters for semi-empirical methods V: Modification of NDDO approximations and application to 70 elements. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 13, 1173–1213.
Sulimov, A. V., Kutov, D. C., Katkova, E. V., Ilin, I. S., & Sulimov, V. B. (2017). New generation of docking programs: Supercomputer validation of force fields and quantum-chemical methods for docking. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 78, 139–147.
Trott, O., & Olson, A. J. (2010). AutoDockVina: Improvising the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimisation and multithreading. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 31, 455–461.
Venugopala, K. N., Rashmi, V., & Odhav, B. (2013). Review on natural coumarin lead compounds for their pharmacological activity. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/963248.
Yadav, I. S., Nandekar, P. P., Shrivastava, S., Sangamwar, A., Chaudhury, A., & Agarwal, S. M. (2014). Ensemble docking and molecular dynamics identify knoevenagel curcumin derivatives with potent anti-EGFR activity. Gene, 539(1), 82–90.
Yeager, A. R., & Finney, N. S. (2004). The first direct evaluation of the two-active site mechanism for chitin synthase. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 69(3), 613–618.
Young, D. C. (2009). Computational drug design: a guide for computational and medicinal chemists. John Wiley & Sons.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Andrade Gonçalves, P., dos Santos Junior, M.C., do Sacramento Sousa, C. et al. Study of sodium 3-hydroxycoumarin as inhibitors in vitro, in vivo and in silico of Moniliophthora perniciosa fungus. Eur J Plant Pathol 153, 15–27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1536-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1536-2