Abstract
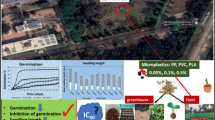
Microplastics (MPs) and copper (Cu) pollution coexist widely in cultivation environment. In this paper, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) were used to simulate the MPs exposure environment, and the combined effects of MPs + Cu on the germination of perilla seeds were analyzed. The results showed that low concentrations of Cu promoted seed germination, while medium to high concentrations exhibited inhibition and deteriorated the morphology of germinated seeds. The germination potential, germination index and vitality index of 8 mg • L−1 Cu treatment group with were 23.08%, 76.32% and 65.65%, respectively, of the control group. The addition of low concentration PVC increased the above indicators by 1.27, 1.15, and 1.35 times, respectively, while high concentration addition led to a decrease of 65.38%, 82.5%, and 66.44%, respectively. The addition of low concentration PVC reduced the amount of PVC attached to radicle. There was no significant change in germination rate. PVC treatment alone had no significant effect on germination. MPs + Cu inhibited seed germination, which was mainly reflected in the deterioration of seed morphology. Cu significantly enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and MDA content. The addition of low concentration PVC enhanced SOD activity, reduced MDA and H2O2 content. The SOD activity of the Cu2+8 + PVC10 group was 4.05 and 1.35 times higher than that of the control group and Cu treatment group at their peak, respectively. At this time, the CAT activity of the Cu2+8 + PVC5000 group increased by 2.66 and 1.42 times, and the H2O2 content was 2.02 times higher than the control. Most of the above indicators reached their peak at 24 h. The activity of α-amylase was inhibited by different treatments, but β-amylase activity, starch and soluble sugar content did not change regularly. The research results can provide new ideas for evaluating the impact of MPs + Cu combined pollution on perilla and its potential ecological risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, S., Moore, F., Keshavarzi, B., Hopke, P. K., Naidu, R., Rahman, M. M., Oleszczuk, P., & Karimi, J. (2020). PET-microplastics as a vector for heavy metals in a simulated plant rhizosphere zone. Science of the Total Environment, 744, 140984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140984
Bosker, T., Bouwman, L. J., Brun, N. R., Behrens, P., & Vijver, M. G. (2019). Microplastics accumulate on pores in seed capsule and delay germination and root growth of the terrestrial vascular plant lepidium sativum. Chemosphere, 226, 774–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.163
Bu, R., Xiao, X., Liao, W., Hu, Y., Li, J., Lv, J., Wang, R., & Xie, J. (2018). Exogenous Si alleviation of autotoxicity in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seed germination is correlated with changes in carbohydrate metabolism. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 37, 784–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9773-8
Cai, H., Liu, X., Zou, J., Xiao, J., Yuan, B., Li, F., & Cheng, Q. (2018). Multi-wavelength spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen peroxide in water with peroxidase catalyzed oxidation of ABTS. Chemosphere, 193, 833–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.091
Cao, Q., Li, G., Cui, Z., Yang, F., Jiang, X., Diallo, L., & Kong, F. (2019). Seed priming with melatonin improves the seed germination of waxy maize under chilling stress via promoting the antioxidant system and starch metabolism. Science and Reports, 9(1), 15044. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51122-y
Costa, H., Gallego, S. M., & Tomaro, M. L. (2002). Effect of UV-B radiation on antioxidant defense system in sunflower cotyledons. Plant Science, 162(6), 939–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00051-1
de Silva, Y., Rajagopalan, U. M., Kadono, H., & Li, D. (2023). The synergy of microplastics with the heavy metal zinc has resulted in reducing the toxic effects of zinc on lentil (lens culinaris) seed germination and seedling growth. Heliyon, 9(11), e21464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21464
Gill, S. S., & Tuteja, N. (2010). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12), 909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Gong, Q., Wang, L., Dai, T., Zhou, J., Kang, Q., Chen, H., Li, K., & Li, Z. (2019). Effects of copper on the growth, antioxidant enzymes and photosynthesis of spinach seedlings. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171, 771–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.016
Guo, M., Zhao, F., Tian, L., Ni, K., Lu, Y., & Borah, P. (2022). Effects of polystyrene microplastics on the seed germination of herbaceous ornamental plants. Science of the Total Environment, 809, 151100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151100
Han, Z., Osman, R., Liu, Y., Wei, Z., Wang, L., & Xu, M. (2023). Analyzing the impacts of cadmium alone and in co-existence with polypropylene microplastics on wheat growth. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14, 1240472. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1240472
Hartmann, N. B., Rist, S., Bodin, J., Jensen, L. H., Schmidt, S. N., Mayer, P., Meibom, A., & Baun, A. (2017). Microplastics as vectors for environmental contaminants: Exploring sorption, desorption, and transfer to biota. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 13(3), 488–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1904
Hasanuzzaman, M., Hossain, M.A., da Silva, J.A.T., Fujita, M., (2012). Plant response and tolerance to abiotic oxidative stress: antioxidant defense is a key factor. In: Venkateswarlu, B., Shanker, A., Shanker, C., Maheswari, M. (eds) Crop Stress and its Management: Perspectives and Strategies. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2220-0_8.
Horton, A. A., Walton, A., Spurgeon, D. J., Lahive, E., & Svendsen, C. (2017). Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Science of the Total Environment, 586, 127–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.163
Hou, T., Netala, V. R., Zhang, H., Xing, Y., Li, H., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Perilla frutescens: A rich source of pharmacological active compounds. Molecules, 27(11), 3578. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113578
Kalcikova, G., Zgajnar, G. A., Kladnik, A., & Jemec, A. (2017). Impact of polyethylene microbeads on the floating freshwater plant duckweed lemna minor. Environmental Pollution, 230, 1108–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.050
Kono, Y. (2022). Reprint of: Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 726, 109247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2022.109247
Kudzin, M. H., Piwowarska, D., Festinger, N., & Chruściel, J. J. (2023). Risks associated with the presence of polyvinyl chloride in the environment and methods for its disposal and utilization. Materials, 17(1), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010173
Kumar, R., Ivy, N., Bhattacharya, S., Dey, A., & Sharma, P. (2022). Coupled effects of microplastics and heavy metals on plants: Uptake, bioaccumulation, and environmental health perspectives. Science of the Total Environment, 836, 155619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155619
Kumar, V., Pandita, S., Singh, S. G., Sharma, A., Khanna, K., Kaur, P., Bali, A. S., & Setia, R. (2021). Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere, 262, 127810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127810
Laurentin, A., & Edwards, C. A. (2003). A microtiter modification of the anthrone-sulfuric acid colorimetric assay for glucose-based carbohydrates. Analytical Biochemistry, 315(1), 143–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-2697(02)00704-2
Li, R., Wu, L., Shao, Y., Hu, Q., & Zhang, H. (2022). Melatonin alleviates copper stress to promote rice seed germination and seedling growth via crosstalk among various defensive response pathways. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 179, 65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.03.016
Li, Z., Zeng, X., Sun, F., Feng, T., Xu, Y., Li, Z., Wu, J., Wang-Pruski, G., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Physiological analysis and transcriptome profiling reveals the impact of microplastic on melon (Cucumis melo L.) seed germination and seedling growth. Journal of Plant Physiology, 287, 154039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2023.154039
Lian, J., Wu, J., Xiong, H., Zeb, A., Yang, T., Su, X., Su, L., & Liu, W. (2020). Impact of polystyrene nanoplastics (psnps) on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385, 121620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121620
Liu, B., Lin, R., Jiang, Y., Jiang, S., Xiong, Y., Lian, H., Zeng, Q., Liu, X., Liu, Z. J., & Chen, S. (2020). Transcriptome analysis and identification of genes associated with starch metabolism in Castanea henryi seed (Fagaceae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(4), 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041431
Liu, T. F., Wang, T., Sun, C., & Wang, Y. M. (2009). Single and joint toxicity of cypermethrin and copper on Chinese cabbage (pakchoi) seeds. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(1), 344–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.099
Mcglade, J., Fahim, I., Green, D., Landrigan, P., Andrady, A., Costa, M., Geyer, R., Gomes, R., Hwai, A., Jambeck, J., Li, D., Rochman, C., Ryan, P., Thiel, M., Thompson, R., Townsend, K., Turra, A., Maes, T., (2021). From pollution to solution: a global assessment of marine litter and plastic pollution. United Nations Environment Programme Report. https://nottingham-repository.worktribe.com/output/8047115.
Moravcova, S., Tuma, J., Ducaiova, Z. K., Waligorski, P., Kula, M., Saja, D., Slomka, A., Baba, W., & Libik-Konieczny, M. (2018). Influence of salicylic acid pretreatment on seeds germination and some defence mechanisms of zea mays plants under copper stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 122, 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.11.007
Nizzetto, L., Futter, M., & Langaas, S. (2016). Are agricultural soils dumps for microplastics of urban origin? Environmental Science and Technology, 50(20), 10777–10779. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04140
Peñalver, R., Arroyo-Manzanares, N., López-García, I., & Hernández-Córdoba, M. (2020). An overview of microplastics characterization by thermal analysis. Chemosphere, 242, 125170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125170
Rady, M. M., & Hemida, K. A. (2016). Sequenced application of ascorbate-proline-glutathione improves salt tolerance in maize seedlings. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 133, 252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.07.028
Rao, M. V., Paliyath, G., Ormrod, D. P., Murr, D. P., & Watkins, C. B. (1997). Influence of salicylic acid on H2O2 production, oxidative stress, and H2O2-metabolizing enzymes (salicylic acid-mediated oxidative damage requires H2O2). Plant Physiology, 115, 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.115.1.137
Real, L. E. P. (2022). Plastics statistics: production, recycling, and market data. in recycled materials for construction applications: plastic products and composites. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Roy, T., Dey, T. K., & Jamal, M. (2023). Microplastic/nanoplastic toxicity in plants: An imminent concern. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10654-z
Sfaxi-Bousbih, A., Chaoui, A., & El, F. E. (2010). Copper affects the cotyledonary carbohydrate status during the germination of bean seed. Biological Trace Element Research, 137(1), 110–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8556-x
Shabbir, Z., Sardar, A., Shabbir, A., Abbas, G., Shamshad, S., Khalid, S., Natasha, M., Dumat, C., & Shahid, M. (2020). Copper uptake, essentiality, toxicity, detoxification and risk assessment in soil-plant environment. Chemosphere, 259, 127436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127436
Sharma, S., Arunachalam, K., & Arunachalam, A. (2022). Morphology and physiology of Perilla frutescens (Linn) Britt in relation to micro-climate and edaphic characteristics. Tropical Ecology, 63(3), 375–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-021-00195-w
Song, X., Zhuang, W., Cui, H., Liu, M., Gao, T., Li, A., & Gao, Z. (2022). Interactions of microplastics with organic, inorganic and bio-pollutants and the ecotoxicological effects on terrestrial and aquatic organisms. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 156068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156068
Stapleton, M. J., & Hai, F. I. (2023). Microplastics as an emerging contaminant of concern to our environment: A brief overview of the sources and implications. Bioengineered, 14(1), 2244754. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2023.2244754
Tsikas, D. (2017). Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Analytical Biochemistry, 524, 13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.021
Wang, F., Feng, X., Liu, Y., Adams, C. A., Sun, Y., & Zhang, S. (2022). Micro (nano) plastics and terrestrial plants: Up-to-date knowledge on uptake, translocation, and phytotoxicity. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 185, 106503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106503
Wang, X., Sun, J., Dang, G. F., Gao, Y., Duan, L., & Wu, X. Y. (2015). Antioxidant content and cytological examination of aqueous fluid from patients with age-related cataracts at different stages. Genetics and Molecular Research, 14(2), 6251–6255. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.June.9.11
Wei, H., Wu, L., Liu, Z., Saleem, M., Chen, X., Xie, J., & Zhang, J. (2022). Meta-analysis reveals differential impacts of microplastics on soil biota. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 230, 113150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113150
Xiao, Q., Wang, Y., Lü, Q., Wen, H., Han, B., Chen, S., Zheng, X., & Lin, R. (2020). Responses of glutathione and phytochelatins biosysthesis in a cadmium accumulator of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. under cadmium contaminated conditions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 201, 110805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110805
Xin, X., Zhao, F., Rho, J. Y., Goodrich, S. L., Sumerlin, B. S., & He, Z. (2020). Use of polymeric nanoparticles to improve seed germination and plant growth under copper stress. Science of the Total Environment, 745, 141055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141055
Ya, H., Jiang, B., Xing, Y., Zhang, T., Lv, M., & Wang, X. (2021). Recent advances on ecological effects of microplastics on soil environment. Science of the Total Environment, 798, 149338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149338
Yaldagard, M., Mortazavi, S. A., & Tabatabaie, F. (2008). The effect of ultrasound in combination with thermal treatment on the germinated barley’s alpha-amylase activity. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 25, 517–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-008-0087-1
Zhang, Y., Cai, C., Gu, Y., Shi, Y., & Gao, X. (2022). Microplastics in plant-soil ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Environmental Pollution, 308, 119718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119718
Zhou, Y., Liu, X., & Wang, J. (2019). Characterization of microplastics and the association of heavy metals with microplastics in suburban soil of central china. Science of the Total Environment, 694, 133798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133798
Zong, X., Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Zhang, L., Jiang, L., Yin, Y., & Guo, H. (2021). Effects of polystyrene microplastic on uptake and toxicity of copper and cadmium in hydroponic wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 217, 112217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112217
Funding
This work was supported by the MinJiang Scholar fund from Fujian Province and Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (FAFU) (116-114120019); Training Program of innovation and entrepreneurship for undergraduate in FAFU (X202310389211), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JHWu, FHS, and ZZZ designed and performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. TJF, YXX, and XLZ analyzed the data and contributed reagents and materials. GWP polished the language of manuscript. ZZZ and JHW provided financial support and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable.
Consent to participate
The authors declare that they consent to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they consent to the publication of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Feng, T., Xu, Y. et al. Combined effects of micron-sized polyvinyl chloride particles and copper on seed germination of perilla. Environ Geochem Health 46, 193 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01976-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01976-7