Abstract
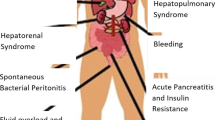
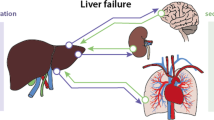
Patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension are at an increased risk of the development of circulatory dysfunction that may potentially result in multiple organ failure. Apart from the liver, this may involve the heart, lungs, kidneys, the immune system, the adrenal glands, and other organ systems. As the disease progresses, the circulation becomes hyperdynamic, and signs of cardiac, pulmonary, and renal dysfunction are observed, in addition to reduced survival. Infections and an altered cardiac function known as cirrhotic cardiomyopathy may be precipitators for the development of other complications such as hepatorenal syndrome. In patients with chronic organ dysfunction, various precipitating events may induce an acute-on-chronic renal failure and acute-on-chronic liver failure that negatively affect the prognosis. Future research on the pathophysiologic mechanisms of the complications and the precipitating factors is essential to understand the basics of the treatment of these challenging conditions. The aim of the present review is to focus on the development and precipitating factors of various organ failures in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACLF:
-
Acute-on-chronic liver failure
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- BRS:
-
Baroreflex sensitivity
- CCK:
-
Cholecystokinin
- CCM:
-
Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy
- CEE:
-
Contrast-enhanced echocardiography
- CGRP:
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- ET:
-
Endothelin
- GFR:
-
Glomerular filtration rate
- HPS:
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- HRS:
-
Hepatorenal syndrome
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- mIBG:
-
Metaiodobenzyl-guanidine
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- PAa,O2 :
-
Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PoPH:
-
Portopulmonary hypertension
- RAI:
-
Relative adrenal insufficiency
- SBP:
-
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- SIRS:
-
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- TIPS:
-
Transjugular portosystemic shunt
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VIP:
-
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide
References
D’amico G, Pasta L, Morabito A, et al. Competing risks and prognostic stages of cirrhosis: a 25-year inception cohort study of 494 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:1180–1193.
Zipprich A, Garcia-Tsao G, Rogowski S, Fleig WE, Seufferlein T, Dollinger MM. Prognostic indicators of survival in patients with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2012;32:1407–1414.
Bajaj JS, O’Leary JG, Reddy KR, et al. Survival in infection-related acute-on-chronic liver failure is defined by extra-hepatic organ failures. Hepatology. 2014;60:250–256.
Lee UE, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;25:195–206.
Buck M, Garcia-Tsao G, Groszmann RJ, et al. Novel inflammatory biomarkers of portal pressure in compensated cirrhosis patients. Hepatology. 2014;59:1052–1059.
Rockey DC. The cell and molecular biology of hepatic fibrogenesis. Clinical and therapeutic implications. Clin Liver Dis. 2000;4:319–355.
Matuchansky C. Bacterial translocation in liver cirrhosis: site and role in fibrogenesis. J Hepatol. 2014;3:709–710.
Tandon P, Garcia-Tsao G. Bacterial infections, sepsis, and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:26–42.
Gines P, Fernandez J, Durand F, Saliba F. Management of critically-ill cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol. 2012;56:S13–S24.
Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1426–1437.
Moreau R, Arroyo V. Acute on chronic liver failure: a new clinical entity. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:836–841.
Marra F, Parola M. Cells in the liver—functions in health and disease. In: Gines P, Kamath PS, Arroyo V, eds. Chronic liver failure. Mechanisms and management. New York: Springer; 2011:3–32.
Matsumura H, Shimizu Y, Ohsawa Y, Kawahara A, Uchiyama Y, Nagata S. Necrotic death pathway in Fas receptor signaling. J Cell Biol. 2000;151:1247–1256.
Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1655–1669.
Henriksen JH. Degradation of bioactive substances: physiology and pathophysiology. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1991.
Gerbes AL, Witthaut R, Gulberg V, Thibault G, Bilzer M, Jungst D. Role of the liver in splanchnic extraction of atrial natriuretic factor in the rat. Hepatology. 1992;16:790–793.
Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:125–172.
Sethasine S, Jain D, Groszmann RJ, Garcia-Tsao G. Quantitative histological-hemodynamic correlations in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2012;55:1146–1153.
Rockey DC. Hepatic fibrosis, stellate cells, and portal hypertension. Clin Liver Dis. 2006;10:459–479.
Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC. Complications of cirrhosis. I. Portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2000;32:141–156.
Albillos A, Banares R, Gonzalez M, et al. The extent of the collateral circulation influences the postprandial increase in portal pressure in cirrhotic patient. Gut. 2006;56:259–264.
Berzigotti A, De Gottardi A, Vukotic R, et al. Effect of meal ingestion on liver stiffness in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e58742.
Bendtsen F, Krag A, Møller S. Treatment of acute variceal bleeding. Dig Liver Dis. 2008;40:328–336.
Bendtsen F, Simonsen L, Henriksen JH. Effect on hemodynamics of a liquid meal alone and in combination with propranolol in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1992;102:1017–1023.
Møller S, Henriksen JH. The systemic circulation in cirrhosis. In: Gines P, Arroyo V, Rodes J, Schrier RW, eds. Ascites and renal dysfunction in liver disease. Malden: Blackwell; 2005:139–155.
Møller S, Bendtsen F, Henriksen JH. Vasoactive substances in the circulatory dysfunction of cirrhosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2001;61:421–429.
Møller S, Hobolth L, Winkler C, Bendtsen F, Christensen E. Determinants of the hyperdynamic circulation and central hypovolaemia in cirrhosis. Gut. 2011;60:1254–1259.
Shawcross DL, Austin MJ, Abeles RD, et al. The impact of organ dysfunction in cirrhosis: survival at a cost? J Hepatol. 2012;56:1054–1062.
Angeli P, Sanyal A, Møller S, et al. Current limits and future challenges in the management of renal dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis: report from the International Club of Ascites. Liver Int. 2013;33:16–23.
Arroyo V, Colmenero J. Ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis: pathophysiological basis of therapy and current management. J Hepatol. 2003;38:S69–S89.
Iwakiri Y. Endothelial dysfunction in the regulation of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2012;32:199–213.
Langer DA, Shah VH. Nitric oxide and portal hypertension: interface of vasoreactivity and angiogenesis. J Hepatol. 2006;44:209–216.
Iwakiri Y, Shah V, Rockey DC. Vascular pathobiology in chronic liver disease and cirrhosis—current status and future directions. J Hepatol. 2014;61:912–924.
Wiest R, Groszmann RJ. The paradox of nitric oxide in cirrhosis and portal hypertension: too much, not enough. Hepatology. 2002;35:478–491.
Møller S, Bendtsen F, Schifter S, Henriksen JH. Relation of calcitonin gene-related peptide to systemic vasodilatation and central hypovolaemia in cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1996;31:928–933.
Hori N, Okanoue T, Sawa Y, Kashima K. Role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the vascular system on the development of the hyperdynamic circulation in conscious cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol. 1997;26:1111–1119.
Guevara M, Gines P, Jimenez W, et al. Increased adrenomedullin levels in cirrhosis: relationship with hemodynamic abnormalities and vasoconstrictor systems. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:336–343.
Batkai S, Jarai Z, Wagner JA, et al. Endocannabinoids acting at vascular CB1 receptors mediate the vasodilated state in advanced liver cirrhosis. Nat Med. 2001;7:827–832.
Moezi L, Gaskari SA, Lee SS. Endocannabinoids and liver disease. v. Endocannabinoids as mediators of vascular and cardiac abnormalities in cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295:G649–G653.
Ros J, Claria J, To-Figueras J, et al. Endogenous cannabinoids: a new system involved in the homeostasis of arterial pressure in experimental cirrhosis in the rat. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:85–93.
Fernandez M, Mejias M, Angermayr B, Garcia-Pagan JC, Rodes J, Bosch J. Inhibition of VEGF receptor-2 decreases the development of hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation and portal-systemic collateral vessels in portal hypertensive rats. J Hepatol. 2005;43:98–103.
Huang HC, Haq O, Utsumi T, et al. Intestinal and plasma VEGF levels in cirrhosis: the role of portal pressure. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:1125–1133.
Baldassarre M, Giannone FA, Napoli L, et al. The endocannabinoid system in advanced liver cirrhosis: pathophysiological implication and future perspectives. Liver Int. 2013;33:1298–1308.
Wiese S, Mortensen C, Gotze JP, et al. Cardiac and proinflammatory markers predict prognosis in cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2014;34:e19–e30.
Møller S, Henriksen JH. Cardiovascular complications of cirrhosis. Gut. 2008;57:268–278.
Iwakiri Y. Endothelial dysfunction in the regulation of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2011;32:199–213.
Møller S, Iversen JS, Krag A, Bie P, Kjaer A, Bendtsen F. Reduced baroreflex sensitivity and pulmonary dysfunction in alcoholic cirrhosis: effect of hyperoxia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299:G784–G790.
Bolognesi M, Di Pascoli M, Verardo A, Gatta A. Splanchnic vasodilation and hyperdynamic circulatory syndrome in cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:2555–2563.
Tage-Jensen U, Henriksen JH, Christensen E, Widding A, Ring-Larsen H, Christensen NJ. Plasma catecholamine level and portal venous pressure as guides to prognosis in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1988;6:350–358.
Iwakiri Y, Groszmann RJ. The hyperdynamic circulation of chronic liver diseases: from the patient to the molecule. Hepatology. 2006;43:S121–S131.
Kiszka-Kanowitz M, Henriksen JH, Møller S, Bendtsen F. Blood volume distribution in patients with cirrhosis: aspects of the dual-head gamma-camera technique. J Hepatol. 2001;35:605–612.
Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F, Gerbes AL, Christensen NJ, Ring-Larsen H, Sørensen TIA. Estimated central blood volume in cirrhosis—relationship to sympathetic nervous activity, beta-adrenergic blockade and atrial natriuretic factor. Hepatology. 1992;16:1163–1170.
Brinch K, Møller S, Bendtsen F, Becker U, Henriksen JH. Plasma volume expansion by albumin in cirrhosis. Relation to blood volume distribution, arterial compliance and severity of disease. J Hepatol. 2003;39:24–31.
Schrier RW. Water and sodium retention in edematous disorders: role of vasopressin and aldosterone. Am J Med. 2006;119:S47–S53.
Møller S, Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F. Central- and non-central blood volumes in cirrhosis. Relation to anthropometrics and gender. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;284:G970–G979.
Ruiz-Del-Arbol L, Monescillo A, Arocena C, et al. Circulatory function and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2005;42:439–447.
Krag A, Bendtsen F, Henriksen JH, Møller S. Low cardiac output predicts development of hepatorenal syndrome and survival in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Gut. 2010;59:105–110.
Braillon A, Cales P, Valla D, Gaudy D, Geoffroy P, Lebrec D. Influence of the degree of liver failure on systemic and splanchnic haemodynamics and on response to propranolol in patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 1986;27:1204–1209.
Bendtsen F, Henriksen JH, Sørensen TIA. Long-term effects of oral propranolol on splanchnic and systemic haemodynamics in patients with cirrhosis and oesophageal varices. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991;26:933–939.
Krag A, Møller S, Burroughs AK, Bendtsen F. Betablockers induce cardiac chronotropic incompetence. J Hepatol. 2012;56:298–299.
Ge PS, Runyon BA. The changing role of beta-blocker therapy in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2013;60:643–653.
Tripathi D, Hayes P. Beta blockers in portal hypertension: new developments and controversies. Liver Int. 2013;34:655–667.
Llach J, Ginés P, Arroyo V, et al. Prognostic value of arterial pressure, endogenous vasoactive systems, and renal function in cirrhotic patients admitted to the hospital for the treatment of ascites. Gastroenterology. 1988;94:482–487.
Vilar GE, Torres GA, Calzadilla BL, Yasells GA, Sanchez RY, Perez YM. Arterial blood pressure is closely related to ascites development in compensated HCV-related cirrhosis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e95736.
Fasolato S, Angeli P, Dallagnese L, et al. Renal failure and bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis: Epidemiology and clinical features. Hepatology. 2007;45:223–229.
Bajaj JS, O’Leary JG, Wong F, Reddy KR, Kamath PS. Bacterial infections in end-stage liver disease: current challenges and future directions. Gut. 2012;61:1219–1225.
Fernandez J, Gustot T. Management of bacterial infections in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2012;56:S1–12.
Reiberger T, Ferlitsch A, Payer BA, et al. Non-selective betablocker therapy decreases intestinal permeability and serum levels of LBP and IL-6 in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2013;58:911–921.
Wiest R, Lawson M, Geuking M. Pathological bacterial translocation in liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2014;60:197–209.
Wiest R, Krag A, Gerbes A. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: recent guidelines and beyond. Gut. 2012;61:297–310.
Wiest R, Garcia-Tsao G. Bacterial translocation (BT) in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2005;41:422–433.
Gustot T, Durand F, Lebrec D, Vincent JL, Moreau R. Severe sepsis in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2009;50:2022–2033.
Mehta G, Gustot T, Mookerjee RP, et al. Inflammation and portal hypertension - The undiscovered country. J Hepatol. 2014;61:155–163.
Leithead JA, Ferguson JW, Bates CM, et al. The systemic inflammatory response syndrome is predictive of renal dysfunction in patients with non-paracetamol-induced acute liver failure. Gut. 2009;58:443–449.
Follo A, Llovet JM, Navasa M, et al. Renal impairment after spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: incidence, clinical course, predictive factors and prognosis. Hepatology. 1994;20:1495–1501.
Fagundes C, Gines P. Hepatorenal syndrome: a severe, but treatable, cause of kidney failure in cirrhosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59:874–885.
Mehta G, Mookerjee RP, Sharma V, Jalan R. Systemic inflammation is associated with increased intrahepatic resistance and mortality in alcohol-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver Int. 2015;35:724–734.
Møller S, Hove JD, Dixen U, Bendtsen F. New insights into cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167:1101–1108.
Zambruni A, Trevisani F, Caraceni P, Bernardi M. Cardiac electrophysiological abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2006;2006:994–1002.
Møller S, Henriksen JH. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. J Hepatol. 2010;53:179–190.
Rabie RN, Cazzaniga M, Salerno F, Wong F. The use of E/A ratio as a predictor of outcome in cirrhotic patients treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2458–2466.
Saner FH, Neumann T, Canbay A, et al. High brain-natriuretic peptide level predicts cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in liver transplant patients. Transpl Int. 2011;24:425–432.
Wong F, Girgrah N, Graba J, Allidina Y, Liu P, Blendis L. The cardiac response to exercise in cirrhosis. Gut. 2001;49:268–275.
Krag A, Bendtsen F, Mortensen C, Henriksen JH, Møller S. Effects of a single terlipressin administration on cardiac function and perfusion in cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22:1085–1092.
Kazankov K, Holland-Fischer P, Andersen NH, et al. Resting myocardial dysfunction in cirrhosis quantified by tissue Doppler imaging. Liver Int. 2011;31:534–540.
Sampaio F, Pimenta J, Bettencourt N, et al. Systolic and diastolic dysfunction in cirrhosis: a tissue-Doppler and speckle tracking echocardiography study. Liver Int. 2013;33:1158–1165.
Pozzi M, Redaelli E, Ratti L, et al. Time-course of diastolic dysfunction in different stages of chronic HCV related liver diseases. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2005;51:179–186.
Gaskari SA, Honar H, Lee SS. Therapy insight: cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;3:329–337.
Møller S, Henriksen JH. Cardiovascular dysfunction in cirrhosis. Pathophysiological evidence of a cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001;36:785–794.
Torregrosa M, Aguade S, Dos L, et al. Cardiac alterations in cirrhosis: reversibility after liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2005;42:68–74.
Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F, Hansen EF, Møller S. Acute non-selective beta-adrenergic blockade reduces prolonged frequency-adjusted Q-T interval (QTc) in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2004;40:239–246.
Henriksen JH, Gøetze JP, Fuglsang S, Christensen E, Bendtsen F, Møller S. Increased circulating pro-brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in patients with cirrhosis: relation to cardiovascular dysfunction and severity of disease. Gut. 2003;52:1511–1517.
Genovesi S, Prata Pizzala DM, Pozzi M, et al. QT interval prolongation and decreased heart rate variability in cirrhotic patients: relevance of hepatic venous pressure gradient and serum calcium. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009;116:851–859.
Bernardi M, Maggioli C, Dibra V, Zaccherini G. QT interval prolongation in liver cirrhosis: innocent bystander or serious threat? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;6:57–66.
Cavasi A, Cavasi E, Grigorescu M, Sitar-Taut A. Relationship between NT-proBNP and cardio-renal dysfunction in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2014;23:51–56.
Mohamed R, Forsey PR, Davies MK, Neuberger JM. Effect of liver transplantation on QT interval prolongation and autonomic dysfunction in end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 1996;23:1128–1134.
Møller S, Bernardi M. Interactions of the heart and the liver. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2804–2811.
Pellicori P, Torromeo C, Calicchia A, et al. Does cirrhotic cardiomyopathy exist? 50 years of uncertainty. Clin Res Cardiol. 2013;102:859–864.
Dumcke CW, Møller S. Autonomic dysfunction in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2008;68:437–447.
Dahl EK, Møller S, Kjaer A, Petersen CL, Bendtsen F, Krag A. Diastolic and autonomic dysfunction in early cirrhosis: a dobutamine stress study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:362–372.
Ates F, Topal E, Kosar F, et al. The relationship of heart rate variability with severity and prognosis of cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:1614–1618.
Wiese S, Hove JD, Bendtsen F, Møller S. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy: pathogenesis and clinical relevance. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11:177–186.
Møller S, Iversen JS, Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F. Reduced baroreflex sensitivity in alcoholic cirrhosis:relations to hemodynamics and humoral systems. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292:H2966–H2972.
Song JG, Kim YK, Shin WJ, Hwang GS. Changes in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity are related to increased ventricular mass in patients with liver cirrhosis. Circ J. 2012;76:2807–2813.
Møller S, Mortensen C, Bendtsen F, Jensen LT, Gotze JP, Madsen JL. Cardiac sympathetic imaging with mIBG in cirrhosis and portal hypertension: Relation to autonomic and cardiac function. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G1228–G1235.
Jalan R, Fernandez J, Wiest R, et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis. A position statement based on the EASL special conference 2013. J Hepatol. 2014;60:1310–1324.
Grace JA, Angus PW. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: update on recent advances in pathophysiology, investigation and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:313–319.
Koch DG, Fallon MB. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Clin Liver Dis. 2014;18:407–420.
Møller S, Hillingsø J, Christensen E, Henriksen JH. Arterial hypoxaemia in cirrhosis: fact or fiction? Gut. 1998;42:868–874.
Scarlata S, Conte ME, Cesari M, et al. Gas exchanges and pulmonary vascular abnormalities at different stages of chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2011;31:525–533.
Gaines DI, Fallon MB. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Liver Int. 2004;24:397–401.
Rodriguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ, Herve P, Fallon MB. Pulmonary-hepatic vascular disorders (PHD). Eur Respir J. 2004;24:861–880.
Deibert P, Allgaier HP, Stefanie L, et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with chronic liver disease: role of pulse oximetry. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:15.
Møller S, Krag A, Madsen JL, Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F. Pulmonary dysfunction and hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 2009;29:1528–1537.
Machicao VI, Fallon MB. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33:11–16.
Horvatits T, Fuhrmann V. Therapeutic options in pulmonary hepatic vascular diseases. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2014;7:31–42.
Zhang J, Fallon MB. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: update on pathogenesis and clinical features. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;130:1136–1144.
Machicao VI, Balakrishnan M, Fallon MB. Pulmonary complications in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2014;59:1627–1637.
Grace JA, Angus PW. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: update on recent advances in pathophysiology, investigation, and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:213–219.
Krishnamurthy GT, Krishnamurthy S. Nuclear hepatology. A textbook of hepatobiliary diseases. Berlin: Springer; 2000.
Schwartz JM, Beymer C, Althaus SJ, et al. Cardiopulmonary consequences of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: Role of increased pulmonary artery pressure. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:590–594.
Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of portal hypertension. Hepatology. 2005;41:386–400.
Iyer VN, Swanson KL, Cartin-Ceba R, et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: Favorable outcomes in the MELD exception era. Hepatology. 2013;57:2427–2435.
Pascasio JM, Grilo I, Lopez-Pardo FJ, et al. Prevalence and severity of hepatopulmonary syndrome and Its Influence on survival in cirrhotic patients evaluated for liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2014;14:1391–1399.
Katsuta Y, Zhang XJ, Kato Y, et al. Hemodynamic features and impaired arterial oxygenation in patients with portopulmonary hypertension. Hepatol Res. 2005;32:79–88.
Kawut SM, Taichman DB, Ahya VN, et al. Hemodynamics and survival of patients with portopulmonary hypertension. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:1107–1111.
Luo B, Liu L, Tang L, et al. Increased pulmonary vascular endothelin B receptor expression and responsiveness to endothelin-1 in cirrhotic and portal hypertensive rats: a potential mechanism in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. J Hepatol. 2003;38:556–563.
Giusca S, Jinga M, Jurcut C, Jurcut R, Serban M, Ginghina C. Portopulmonary hypertension: from diagnosis to treatment. Eur J Intern Med. 2011;22:441–447.
Koch DG, Bogatkevich G, Ramshesh V, Lemasters JJ, Uflacker R, Reuben A. Elevated levels of endothelin-1 in hepatic venous blood are associated with intrapulmonary vasodilatation in humans. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:516–523.
Krowka MJ. Portopulmonary hypertension. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33:17–25.
Krowka MJ. Portopulmonary hypertension and the issue of survival. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:1026–1027.
Kuo PC, Plotkin JS, Johnson LB, et al. Distinctive clinical features of portopulmonary hypertension. Chest. 1997;112:980–986.
Swanson KL, Krowka MJ. Screen for portopulmonary hypertension, especially in liver transplant candidates. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75:121–133.
Hoeper MM, Seyfarth HJ, Hoeffken G, et al. Experience with inhaled iloprost and bosentan in portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2007;30:1096–1102.
Grander W, Eller P, Fuschelberger R, Tilg H. Bosentan treatment of portopulmonary hypertension related to liver cirrhosis owing to hepatitis C. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006;36:67–70.
Hollatz TJ, Musat A, Westphal S, et al. Treatment with sildenafil and treprostinil allows successful liver transplantation of patients with moderate to severe portopulmonary hypertension. Liver Transpl. 2012;18:686–695.
Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: implications for liver transplantation. Clin Chest Med. 2005;26:587–597.
Murray KF, Carithers RL Jr. AASLD practice guidelines: evaluation of the patient for liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2006;41:1407–1432.
Safdar Z, Bartolome S, Sussman N. Portopulmonary hypertension: an update. Liver Transpl. 2012;18:881–891.
Koh C, Zhao X, Samala N, Sakiani S, Liang TJ, Talwalkar JA. AASLD clinical practice guidelines: a critical review of scientific evidence and evolving recommendations. Hepatology. 2013;58:2142–2152.
Rognant N, Lemoine S. Evaluation of renal function in patients with cirrhosis: Where are we now? World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:2533–2541.
Mindikoglu AL, Dowling TC, Weir MR, Seliger SL, Christenson RH, Magder LS. Performance of chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration creatinine-cystatin C equation for estimating kidney function in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2014;59:1532–1542.
Krag A, Bendtsen F, Burroughs AK, Møller S. The cardiorenal link in advanced cirrhosis. Med Hypotheses. 2012;79:53–55.
Garcia-Tsao G, Parikh CR, Viola A. Acute kidney injury in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:2064–2077.
Piano S, Rosi S, Maresio G, et al. Evaluation of the acute kidney injury network criteria in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis and ascites. J Hepatol. 2013;59:482–489.
Belcher JM, Parikh CR, Garcia-Tsao G. Acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: perils and promise. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1550–1558.
Cholongitas E, Arsos G, Goulis J, et al. Glomerular filtration rate is an independent factor of mortality in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 2014;44:145–155.
Fabrizi F, Aghemo A, Messa P. Hepatorenal syndrome and novel advances in its management. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2013;37:588–601.
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, et al. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007;11:R31.
Belcher JM, Sanyal AJ, Peixoto AJ, et al. Kidney biomarkers and differential diagnosis of patients with cirrhosis and acute kidney injury. Hepatology. 2014;60:622–632.
Møller S, Krag A, Bendtsen F. Kidney injury in cirrhosis: Pathophysiological and therapeutic aspects of hepatorenal syndromes. Liver Int. 2014;34:1153–1163.
K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification: Am J Kidney Dis 2002;39:S1–S266.
Trawale JM, Paradis V, Rautou PE, et al. The spectrum of renal lesions in patients with cirrhosis: a clinicopathological study. Liver Int. 2010;3:725–732.
Wong F, Nadim MK, Kellum JA, et al. Working Party proposal for a revised classification system of renal dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 2011;60:702–709.
Wong F, Murray P. Kidney damage biomarkers: novel tools for the diagnostic assessment of acute kidney injury in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2014;60:455–457.
Jalan R, Gines P, Olson JC, et al. Acute-on chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2012;57:1336–1348.
Fede G, D’amico G, Arvaniti V, et al. Renal failure and cirrhosis: a systematic review of mortality and prognosis. J Hepatol. 2012;56:810–818.
Gines P, Schrier RW. Renal failure in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1279–1290.
Gines P, Angeli P, Lenz K, et al. EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2010;53:397–417.
Angeli P, Gines P. Hepatorenal syndrome, MELD score and liver transplantation: an evolving issue with relevant implications for clinical practice. J Hepatol. 2012;57:1135–1140.
Barreto R, Fagundes C, Guevara M, et al. Type-1 hepatorenal syndrome associated with infections in cirrhosis: natural history, outcome of kidney function, and survival. Hepatology. 2014;59:1505–1513.
Salerno F, Gerbes A, Gines P, Wong F, Arroyo V. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of the hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. A consensus workshop of the international ascites club. Gut. 2007;56:1310–1318.
Stadlbauer VP, Wright GA, Banaji M, et al. Relationship between activation of the sympathetic nervous system and renal blood flow autoregulation in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:111–119.
Møller S, Krag A: Cardiorenal syndrome: A new entity? In Gerbes A, (ed) Hyponatremia and hepatorenal syndrome: progress in treatment. Front Gastrointest Res. Basel, Karger, 2011, pp 102–111.
Schrier RW. Decreased effective blood volume in edematous disorders: what does this mean? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:2028–2031.
Acevedo J, Fernandez J, Prado V, et al. Relative adrenal insufficiency in decompensated cirrhosis. Relationship to short-term risk of severe sepsis, hepatorenal syndrome and death. Hepatology. 2013;58:1757–1765.
Trifan A, Chiriac S, Stanciu C. Update on adrenal insufficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:445–456.
Theocharidou E, Krag A, Bendtsen F, Moller S, Burroughs AK. Cardiac dysfunction in cirrhosis—does adrenal function play a role? A hypothesis. Liver Int. 2012;32:1327–1332.
Galbois A, Thabut D. Adrenal insufficiency: diagnosis in patients with liver cirrhosis is difficult. J Hepatol. 2011;54:590–591.
Galbois A, Rudler M, Massard J, et al. Assessment of adrenal function in cirrhotic patients: salivary cortisol should be preferred. J Hepatol. 2010;52:839–845.
Amarapurkar DN. Adrenal function in cirrhosis: the pendulum swings. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:1543–1544.
Almdal T, Schroeder T, Ranek L. Cerebral blood flow and liver function in patients with encephalopathy due to acute and chronic liver diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989;24:299–303.
Larsen FS, Olsen KS, Ejlersen E, Hansen BA, Paulson OB, Knudsen GM. Cerebral blood flow autoregulation and transcranial doppler sonography in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1995;22:730–736.
O’Carroll RE, Hayes PC, Ebmeier KP, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive function in patients with chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1991;337:1250–1253.
Ede RJ, Gimson AES, Bihari D, Williams R. Controlled hyperventilation in the prevention of cerebral oedema in fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol. 1986;2:43–51.
Larsen FS, Knudsen GM, Hansen BA. Pathophysiological changes in cerebral circulation, oxidative metabolism and blood-brain barrier in patients with acute liver failure. Tailored cerebral oxygen utilization. J Hepatol. 1997;27:231–238.
Frokjaer VG, Strauss GI, Mehlsen J, Knudsen GM, Rasmussen V, Larsen FS. Autonomic dysfunction and impaired cerebral autoregulation in cirrhosis. Clin Auton Res. 2006;16:208–216.
Lagi A, Lavilla G, Barletta G, et al. Cerebral autoregulation in patients with cirrhosis and ascites: a transcranial doppler study. J Hepatol. 1997;27:114–120.
Dam M, Burra P, Tedeschi U, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow changes in patients with cirrhosis assessed with Tc-99 m-HM-PAO single-photon emission computed tomography: effect of liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 1998;29:78–84.
Jalan R, Newby DE, Damink SW, Redhead DN, Hayes PC, Lee A. Acute changes in cerebral blood flow and metabolism during portasystemic shunting. Liver Transpl. 2001;7:274–278.
Zheng G, Zhang LJ, Zhong J, et al. Cerebral blood flow measured by arterial-spin labeling MRI: a useful biomarker for characterization of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:1981–1988.
Zheng G, Zhang LJ, Wang Z, et al. Changes in cerebral blood flow after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt can help predict the development of hepatic encephalopathy: an arterial spin labeling MR study. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:3851–3856.
Zheng G, Zhang LJ, Cao Y, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt induced short- and long-term cerebral blood flow variations in cirrhotic patients: an arterial spin labeling MRI study. Metab Brain Dis. 2013;28:463–471.
Asrani SK, O’Leary JG. Acute-on-chronic liver failure. Clin Liver Dis. 2014;18:561–574.
Kumar A, Das K, Sharma P, Mehta V, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Hemodynamic studies in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:869–878.
Liu H, Lee SS. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: the heart and systemic hemodynamics. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2011;17:190–194.
Jalan R, Saliba F, Pavesi M, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic score to predict mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2014;61:1038–1047.
Silva PE, Fayad L, Lazzarotto C, Ronsoni MF, Bazzo ML, Colombo BS, Dantas-Correa EB, Narciso-Schiavon JL, Schiavon LL: Single-centre validation of the EASL-CLIF Consortium definition of acute-on-chronic liver failure and CLIF-SOFA for prediction of mortality in cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2014. doi: 10.1111/liv.12597.
Acknowledgments
Professor Søren Møller was supported by a grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and The University of Copenhagen.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Møller, S., Bendtsen, F. Cirrhotic Multiorgan Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 60, 3209–3225 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3752-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3752-3