Abstract
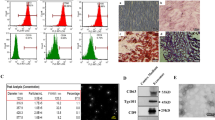
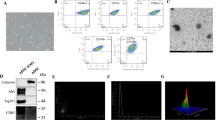
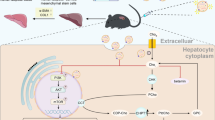
Cirrhosis is a familiar end-stage of multiple chronic liver diseases. The gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have become one of the most promising schemes for the treatment of cirrhosis. MSCs exhibit their therapeutic role mainly by secreting hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). The aim of this research was to probe the anti-fibrosis role of exosomes secreted by HGF modified-mouse adipose MSCs (ADMSCs) on activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and to preliminarily explore the possible mechanism. Firstly, mouse ADMSCs were isolated and identified. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction verified the transfection efficiency of ADMSC transfected with HGF lentivirus. Exosomes derived from ADMSC transfecting negative control/HGF (ADMSCNC-Exo/ADMSCHGF-Exo) were extracted by density gradient centrifugation. HSCs were allocated to the control, TGF-β, TGF-β + ADMSC-Exo, TGF-β + ADMSCNC-Exo, and TGF-β + ADMSCHGF-Exo groups. Moreover, all mice were distributed to the control, CCl4 (40% CCl4 in olive oil), CCl4+ADMSC-Exo, CCl4+ADMSCNC-Exo, and CCl4+ADMSCHGF-Exo groups. Exosomes derived from ADMSCs with or without HGF transfection suppressed HSC activation, as evidenced by attenuating cell viability and cell cycle arrest at S phase but inducing apoptosis. Moreover, ADMSC-Exo, ADMSCNC-Exo, and ADMSCHGF-Exo effectively repressed the gene and protein levels of α-SMA, Col-I, Rho A, Cdc42, and Rac1 in TGF-β-treated HSCs, and ADMSCHGF-Exo had the best effect. ADMSCHGF-Exo had a stronger regulatory effect on serum liver index than ADMSCNC-Exo in CCl4-induced mice. In conclusion, ADMSCHGF-Exo alleviated liver fibrosis by weakening the Rho pathway, thus reducing collagen production.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anger F, Camara M, Ellinger E, Germer CT, Schlegel N, Otto C, Klein I (2019) Human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles improve liver regeneration after ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Stem Cells Dev 28:1451–1462
Börger V, Bremer M, Ferrer-Tur R, Gockeln L, Stambouli O, Becic A, Giebel B (2017) Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles and their potential as novel immunomodulatory therapeutic agents. Int J Mol Sci 18:1450
Cao Y, Ji C, Lu L (2020) Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. Ann Transl Med 8:562
Cao XF, Jin SZ, Sun L, Zhan YB, Lin F, Li Y, Zhou YL, Wang XM, Gao L, Zhang B (2017) Therapeutic effects of hepatocyte growth factor-overexpressing dental pulp stem cells on liver cirrhosis in a rat model. Sci Rep 7:15812
Cao T, Xiao D, Ji P, Zhang Z, Cai WX, Han C, Li W, Tao K (2022) Effects of exosomes from hepatocyte growth factor-modified human adipose mesenchymal stem cells on full-thickness skin defect in diabetic mice. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi 38:1004–1013
Choi SS, Sicklick JK, Ma Q, Yang L, Huang J, Qi Y, Chen W, Li YX, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Diehl AM (2006) Sustained activation of Rac1 in hepatic stellate cells promotes liver injury and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 44:1267–1277
D’Amico G, Morabito A, D’Amico M, Pasta L, Malizia G, Rebora P, Valsecchi MG (2018) Clinical states of cirrhosis and competing risks. J Hepatol 68:563–576
Deng L, Liu G, Wu X, Wang Y, Tong M, Liu B, Wang K, Peng Y, Kong X (2014) Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells efficiently rescue carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver failure in mouse. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:103643
Driscoll J, Patel T (2019) The mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an acellular regenerative therapy for liver disease. J Gastroenterol 54:763–773
Ge J, Burnier L, Adamopoulou M, Kwa MQ, Schaks M, Rottner K, Brakebusch C (2018) RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 differentially regulate αSMA and collagen I expression in mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem 293:9358–9369
Goodman ZD (2007) Grading and staging systems for inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol 47:598–607
He Y, Guo X, Lan T, Xia J, Wang J, Li B, Peng C, Chen Y, Hu X, Meng Z (2021) Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the function of liver in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure via downregulating Notch and Stat1/Stat3 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther 12:396
Hennenberg M, Trebicka J, Stark C, Kohistani AZ, Heller J, Sauerbruch T (2009) Sorafenib targets dysregulated rho kinase expression and portal Hypertension in rats with secondary biliary cirrhosis. Br J Pharmacol 157:258–270
Hu C, Wu Z, Li L (2020) Mesenchymal stromal cells promote liver regeneration through regulation of immune cells. Int J Biol Sci 16:893–903
Hu C, Zhao L, Duan J, Li L (2019) Strategies to improve the efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for reversal of liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med 23:1657–1670
Hu C, Zhao L, Zhang L, Bao Q, Li L (2020) Mesenchymal stem cell-based cell-free strategies: safe and effective treatments for liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:377
Huang YW, Hu JT, Yang SS (2010) Complications of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: active assessment by endoscopy and sonography. Hepatology 52:1864–1865
Keating A (2012) Mesenchymal stromal cells: new directions. Cell Stem Cell 10:709–716
Kim MD, Kim SS, Cha HY, Jang SH, Chang DY, Kim W, Suh-Kim H, Lee JH (2014) Therapeutic effect of hepatocyte growth factor-secreting mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of liver fibrosis. Exp Mol Med 46:e110
Kisseleva T, Gigante E, Brenner DA (2010) Recent advances in liver stem cell therapy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 26:395–402
Li L, Wang JY, Yang CQ, Jiang W (2012) Effect of RhoA on transforming growth factor β1-induced rat hepatic stellate cell migration. Liver Int 32:1093–1102
Lou G, Chen Z, Zheng M, Liu Y (2017) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med 49:e346
Lurie Y, Webb M, Cytter-Kuint R, Shteingart S, Lederkremer GZ (2015) Non-invasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis and Cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 21:11567–11583
Ma L, Wei J, Zeng Y, Liu J, Xiao E, Kang Y, Kang Y (2022) Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal circDIDO1 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT pathway in human liver fibrosis. Drug Deliv 29:440–453
Piscaglia AC, Campanale M, Gasbarrini A, Gasbarrini G (2010) Stem cell-based therapies for liver diseases: state of the art and new perspectives. Stem Cells Int 2010:259461
Qiao H, Zhou Y, Qin X, Cheng J, He Y, Jiang Y (2018) NADPH oxidase signaling pathway mediates mesenchymal stem cell-induced inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation. Stem Cells Int 2018:1239143
Qin S, Jiang H, Su S, Wang D, Liang Z, Zhang J, Yang W (2012) Inhibition of hepatic stellate cell proliferation by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via regulation of the cell cycle in rat. Exp Ther Med 4:375–380
Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, Li F, Ma Z, Xu M, Lu L (2017) Exosomes derived from mir-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J Cell Mol Med 21:2491–2502
Ren X, Meng T, Ren X, Li X, Lu L (2021) Fasudil alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury via targeting Rhoa/ROCK signal pathway. J Toxicol Sci 46:255–262
Roehlen N, Crouchet E, Baumert TF (2020) Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives. Cells 9:875
Rong X, Liu J, Yao X, Jiang T, Wang Y, Xie F (2019) Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 10:98
Seki A, Sakai Y, Komura T, Nasti A, Yoshida K, Higashimoto M, Honda M, Usui S, Takamura M, Takamura T, Ochiya T, Furuichi K, Wada T, Kaneko S (2013) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells as a regenerative therapy for a mouse steatohepatitis-induced cirrhosis model. Hepatology 58:1133–1142
Seo KW, Sohn SY, Bhang DH, Nam MJ, Lee HW, Youn HY (2014) Therapeutic effects of hepatocyte growth factor-overexpressing human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on liver fibrosis in rats. Cell Biol Int 38:106–116
Shiels MS, Chernyavskiy P, Anderson WF, Best AF, Haozous EA, Hartge P, Rosenberg PS, Thomas D, Freedman ND, Berrington A, de Gonzalez, (2017) Trends in premature mortality in the USA by sex, race, and ethnicity from 1999 to 2014: an analysis of death certificate data. Lancet 389:1043–1054
Silveira MG, Brunt EM, Heathcote J, Gores GJ, Lindor KD, Mayo MJ (2010) American association for the study of liver diseases endpoints conference: design and endpoints for clinical trials in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 52:349–359
Terai S, Tsuchiya A (2017) Status of and candidates for cell therapy in liver cirrhosis: overcoming the point of no return in advanced liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 52:129–140
Wang L, Bai G, Chen F (2017) Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells by inhibiting the ubiquitination of p27. Biochem Cell Biol 95:628–633
Wang T, Rao D, Yu C, Sheng J, Luo Y, Xia L, Huang W (2022) RHO GTPase family in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Hematol Oncol 11:91
Wang R, Xu B, Xu H (2018) TGF-β1 promoted chondrocyte proliferation by regulating Sp1 through MSC-exosomes derived miR-135b. Cell Cycle 17:2756–2765
Wells CM, Ahmed T, Masters JR, Jones GE (2005) Rho family GTPases are activated during HGF-stimulated prostate cancer-cell scattering. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 62:180–194
Yin F, Mao LC, Cai QQ, Jiang WH (2021) Effect of hepatocyte growth factor-transfected human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic stellate cells by regulating transforming growth Factor-β1/Smads signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev 30:1070–1081
Yu B, Zhang X, Li X (2014) Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 15:4142–4157
Zhang Y, Li Y, Li W, Cai J, Yue M, Jiang L, Xu R, Zhang L, Li J, Zhu C (2018) Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells at various passages on acute liver failure in rats. Stem Cells Int 2018:7159465
Zhao S, Liu Y, Pu Z (2019) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by activating autophagy in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther 13:2887–2897
Zhu M, Hua T, Ouyang T, Qian H, Yu B (2021) Applications of mesenchymal stem cells in liver fibrosis: novel strategies, mechanisms, and clinical practice. Stem Cells Int 2021:6546780
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by WY, MJ and YZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JW. The manuscript for important intellectual content was revised by JZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Ye, W., Jiang, M. et al. Therapeutic potential of exosome derived from hepatocyte growth factor-overexpressing adipose mesenchymal stem cells in TGFβ1-stimulated hepatic stellate cells. Cytotechnology 76, 217–229 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-023-00611-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-023-00611-0