Abstract
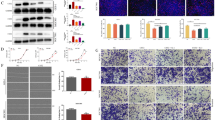
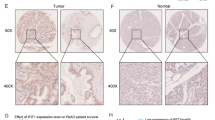
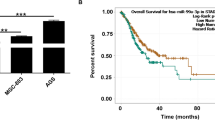
Proteasome 20S Subunit Beta 2 (PSMB2) has been suggested to play several roles in cancer. However, the role of PSMB2 and its underlying mechanisms in gastric cancer have not been studied. In this study, qRT-PCR was employed to detect the expression of genes that encode for 26 s proteasome subunit proteins. PSMB2 expression and its prognostic ability were assessed by collecting patient tissue samples and reviewing the TCGA and Kaplan–Meier Plotter databases. Immunofluorescence and western blotting experiments were performed to evaluate the expression of PSMB2 in human gastric cancer cells and normal gastric epithelial cells. Subsequently, PSMB2 was knocked down in HGC-27 and SNU-1 cells and overexpressed in N-87 and AGS cells. Proteasome activity assays, 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine staining, and TUNEL assays were used to assess proteasome activity, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Tumor xenograft assays were conducted to evaluate PSMB2 function in vivo. Our results showed that a total of 8 genes encoding for the 26 s proteasome subunit protein were highly expressed in a variety of gastric cancer cells. Next, PSMB2 was selected as the focus of subsequent studies which showed that PSMB2 was highly expressed in samples of gastric cancer tissue. Furthermore, a review of the TCGA database revealed that a high level of PSMB2 expression was associated with a poor clinical prognosis. Our results indicated that PSMB2 overexpression promoted proteasome activity, cell proliferation, and suppressed the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells, while those effects were reversed by treatment with a proteasome inhibitor (MG132). In contrast, PSMB2 knockdown produced the opposite effects and also blocked NRF1 activation. Moreover, PSMB2 knockdown inhibited tumor growth in vivo, decreased PSMB2 expression and cell proliferation, and promoted apoptosis in tumor tissues. Our findings revealed the role played by PSMB2 in gastric cancer and suggest PSMB2 as a new target molecule for use in diagnosing and treating gastric cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Baird L, Tsujita T, Kobayashi EH, Funayama R, Nagashima T et al (2017) A homeostatic shift facilitates endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis through transcriptional integration of proteostatic stress response pathways. Mol Cell Biol 37:e00439-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00439-16
Bard JAM, Goodall EA, Greene ER, Jonsson E, Dong KC et al (2018) Structure and function of the 26S proteasome. Annu Rev Biochem 87:697–724. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-011931
Bazzaro M, Lee MK, Zoso A, Stirling WL, Santillan A et al (2006) Ubiquitin-proteasome system stress sensitizes ovarian cancer to proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 66:3754–3763. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2321
Bedford L, Lowe J, Dick LR, Mayer RJ, Brownell JE (2011) Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation and the ubiquitin-proteasome system as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:29–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3321
Bossola M, Muscaritoli M, Costelli P, Grieco G, Bonelli G et al (2003) Increased muscle proteasome activity correlates with disease severity in gastric cancer patients. Ann Surg 237:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SLA.0000055225.96357.71
Bruzzoni-Giovanelli H, Gonzalez JR, Sigaux F, Villoutreix BO, Cayuela JM et al (2015) Genetic polymorphisms associated with increased risk of developing chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncotarget 6:36269–36277. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5915
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N, Chen WQ (2021) Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J 134:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000001474
Catalgol B (2012) Proteasome and cancer. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 109:277–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-397863-9.00008-0
Chen L, Madura K (2005) Increased proteasome activity, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and eEF1A translation factor detected in breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res 65:5599–5606. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0201
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H et al (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66:115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Collins GA, Goldberg AL (2017) The logic of the 26S proteasome. Cell 169:792–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.023
Cvek B (2012) Proteasome inhibitors. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 109:161–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-397863-9.00005-5
Fan XM, Wong BC, Wang WP, Zhou XM, Cho CH et al (2001) Inhibition of proteasome function induced apoptosis in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer 93:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.1373
Fricke B, Heink S, Steffen J, Kloetzel PM, Krüger E (2007) The proteasome maturation protein POMP facilitates major steps of 20S proteasome formation at the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO Rep 8:1170–1175. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7401091
Fricker LD (2020) Proteasome inhibitor drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 60:457–476. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010919-023603
Gaczynska M, Osmulski PA (2014) Harnessing proteasome dynamics and allostery in drug design. Antioxid Redox Signal 21:2286–2301. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5816
Gatti L, Zuco V, Zaffaroni N, Perego P (2013) Drug combinations with proteasome inhibitors in antitumor therapy. Curr Pharm Des 19:4094–4114. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612811319220015
Guo N, Peng Z (2013) MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 9:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-7563.2012.01535.x
Jankowska E, Stoj J, Karpowicz P, Osmulski PA, Gaczynska M (2013) The proteasome in health and disease. Curr Pharm Des 19:1010–1028
Jung T, Grune T (2012) Structure of the proteasome. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 109:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-397863-9.00001-8
Kim HM, Han JW, Chan JY (2016) Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2 Like 1 (NFE2L1): structure, function and regulation. Gene 584:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.03.002
Kwon CH, Park HJ, Choi YR, Kim A, Kim HW et al (2016) PSMB8 and PBK as potential gastric cancer subtype-specific biomarkers associated with prognosis. Oncotarget 7:21454–21468. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7411
Lee CS, Lee C, Hu T, Nguyen JM, Zhang J et al (2011) Loss of nuclear factor E2-related factor 1 in the brain leads to dysregulation of proteasome gene expression and neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:8408–8413. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1019209108
Livneh I, Cohen-Kaplan V, Cohen-Rosenzweig C, Avni N, Ciechanover A (2016) The life cycle of the 26S proteasome: from birth, through regulation and function, and onto its death. Cell Res 26:869–885. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.86
Micel LN, Tentler JJ, Smith PG, Eckhardt GS (2013) Role of ubiquitin ligases and the proteasome in oncogenesis: novel targets for anticancer therapies. J Clin Oncol 31:1231–1238. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.44.0958
Sekine H, Okazaki K, Kato K, Alam MM, Shima H et al (2018) O-GlcNAcylation signal mediates proteasome inhibitor resistance in cancer cells by stabilizing NRF1. Mol Cell Biol 38:e00252-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00252-18
Sha Z, Goldberg AL (2016) Reply to Vangala et al.: Complete inhibition of the proteasome reduces new proteasome production by causing Nrf1 aggregation. Curr Biol 26:R836–R837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.08.030
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Sorokin AV, Kim ER, Ovchinnikov LP (2009) Proteasome system of protein degradation and processing. Biochem Biokhimiia 74:1411–1442. https://doi.org/10.1134/s000629790913001x
Tan S, Li H, Zhang W, Shao Y, Liu Y et al (2018) NUDT21 negatively regulates PSMB2 and CXXC5 by alternative polyadenylation and contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma suppression. Oncogene 37:4887–4900. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0280-6
Tomlin FM, Gerling-Driessen UIM, Liu YC, Flynn RA, Vangala JR et al (2017) Inhibition of NGLY1 inactivates the transcription factor Nrf1 and potentiates proteasome inhibitor cytotoxicity. ACS Cent Sci 3:1143–1155. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00224
Wada T, Yamashita Y, Saga Y, Takahashi K, Koinuma K et al (2009) Screening for genetic abnormalities involved in ovarian carcinogenesis using retroviral expression libraries. Int J Oncol 35:973–976. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo_00000410
Weyburne ES, Wilkins OM, Sha Z, Williams DA, Pletnev AA et al (2017) Inhibition of the proteasome beta2 site sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to beta5 inhibitors and suppresses Nrf1 activation. Cell Chem Biol 24:218–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.12.016
Zhong JL, Huang CZ (2016) Ubiquitin proteasome system research in gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 8:198–206. https://doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v8.i2.198
Zhou X, Fan Y, Ye W, Jia B, Yang Y et al (2020) Identification of the novel target genes for osteosarcoma therapy based on comprehensive bioinformatic analysis. DNA Cell Biol 39:1172–1180. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2020.5377
Funding
This study was not funded by any specific public or private agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no commercial or other associations that might pose a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Samples of human gastric cancer and adjacent tissue were collected from the First Medical Center of PLA General Hospital. `The study protocol was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of the First Medical Center of PLA General Hospital.
Consent to participate
Each recruited patient provided their signed written informed consent for retention and analysis of their tissue.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Yu, C., Chen, Z. et al. PSMB2 knockdown suppressed proteasome activity and cell proliferation, promoted apoptosis, and blocked NRF1 activation in gastric cancer cells. Cytotechnology 74, 491–502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00538-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00538-y