Abstract
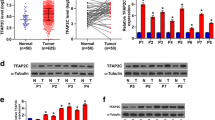
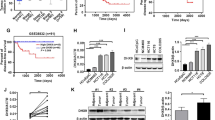
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha factor (LITAF) is a transcription factor that activates the transcription of TNF-α and regulates the inflammatory response. LITAF has been found to have potential anti-cancer effects of in several tumors. However, the role of LITAF in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear. Through a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), LITAF was identified as a differentially downregulated gene in CRC. We hypothesized that LITAF may participate in the modulation of CRC progression. The present study was aimed to investigate the expression profile of LITAF in CRC and its effect on metastatic behavior and stemness as well as the underlying molecular mechanism. The expression profile of LITAF in CRC, and its relationship with the prognosis of CRC were explored using public databases. LITAF expression was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), western blot, and immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, the effects of overexpression or knockdown of LITAF on cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and stemness of CRC cells were investigated in vitro. The regulatory effect of LITAF on forkhead Box O 1 (FOXO1)-sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) signaling axis was also explored. In addition, a xenograft mouse model was used to investigate the in-vivo role of LITAF. LITAF was downregulated in tumor tissues and its expression was associated with the prognosis, pathological stage and liver metastasis. In-vitro experiments confirmed that LITAF inhibited tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion and stemness, and induced cell apoptosis. In vivo experiments demonstrated that LITAF inhibited the tumorigenicity and liver metastasis in tumor-bearing mice. Additionally, LITAF promoted FOXO1-mediated SIRT1 inhibition, thus regulating cancer stemness and malignant phenotypes. LITAF was silenced in CRC and it participated in the progression of CRC by inhibiting CRC cell stemness, and malignant phenotypes. Therefore, LITAF may serve as a novel biomarker of CRC prognosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Dekker E et al (2019) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 394(10207):1467–1480
Dariya B et al (2020) Colorectal cancer biology, diagnosis, and therapeutic approaches. Crit Rev Oncog 25(2):71–94
Wang J et al (2020) Cinobufacini inhibits colon cancer invasion and metastasis via suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and EMT. Am J Chin Med 48(3):703–718
Fiorentino F et al (2022) Sirtuin modulators: past, present, and future perspectives. Future Med Chem 14(12):915–939
Imai S, Guarente L (2014) NAD+ and sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends Cell Biol 24(8):464–471
Garcia-Peterson LM, Li X (2021) Trending topics of SIRT1 in tumorigenicity. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1865(9):129952
Zu G et al (2016) Clinicopathological significance of SIRT1 expression in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta analysis. Int J Surg 26:32–37
Sun LN et al (2017) SIRT1 suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis by transcriptional repression of miR-15b-5p. Cancer Lett 409:104–115
Fang H et al (2022) SIRT1 induces the accumulation of TAMs at colorectal cancer tumor sites via the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis. Cell Immunol 371:104458
An Y et al (2020) SIRT1 inhibits chemoresistance and cancer stemness of gastric cancer by initiating an AMPK/FOXO3 positive feedback loop. Cell Death Dis 11(2):115
Wang TW et al (2020) SIRT1-mediated expression of CD24 and epigenetic suppression of novel tumor suppressor miR-1185-1 increases colorectal cancer stemness. Cancer Res 80(23):5257–5269
Yao J et al (2021) FBXW11 contributes to stem-cell-like features and liver metastasis through regulating HIC1-mediated SIRT1 transcription in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis 12(10):930
Yang S et al (2021) Role of forkhead box O proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma biology and progression (review). Front Oncol 11:667730
Liu Y et al (2022) The FOXO family of transcription factors: key molecular players in gastric cancer. J Mol Med 100(7):997–1015
Chen F et al (2021) Circular RNA ubiquitin-associated protein 2 enhances autophagy and promotes colorectal cancer progression and metastasis via miR-582-5p/FOXO1 signaling. J Genet Genomics 48(12):1091–1103
Dai X, Xie Y, Dong M (2022) Cancer-associated fibroblasts derived extracellular vesicles promote angiogenesis of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells through miR-135b-5p/FOXO1 axis. Cancer Biol Ther 23(1):76–88
Kim SY et al (2016) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO1 inhibits angiogenesis in gastric cancer in relation to SIRT1. Cancer Res Treat 48(1):345–354
Liu H et al (2019) Oncogenic USP22 supports gastric cancer growth and metastasis by activating c-Myc/NAMPT/SIRT1-dependent FOXO1 and YAP signaling. Aging 11(21):9643–9660
Fukui M et al (2021) Mechanism underlying resveratrol’s attenuation of paclitaxel cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells: role of the SIRT1-FOXO1-HER3 signaling pathway. Cancer Treat Res Commun 28:100386
Liu H et al (2015) UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A determinates intracellular accumulation and anti-cancer effect of beta-lapachone in human colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117051
Ko YS, Kim NY, Pyo JS (2020) Clinicopathological significance and angiogenic role of the constitutive phosphorylation of the FOXO1 transcription factor in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract 216(11):153150
Zou J et al (2015) Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha factor enhances inflammation and is associated with cancer (review). Mol Med Rep 12(5):6399–6404
Zhou Y et al (2018) LITAF is a potential tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 9(3):3131–3142
Hoey C et al (2018) miRNA-106a and prostate cancer radioresistance: a novel role for LITAF in ATM regulation. Mol Oncol 12(8):1324–1341
Huang C et al (2019) LITAF enhances radiosensitivity of human glioma cells via the FoxO1 pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39(6):871–882
Yu Z et al (2022) Increased expression of INHBA is correlated with poor prognosis and high immune infiltrating level in breast cancer. Front Bioinform 2:729902
Chen X et al (2023) Prognostic biomarker SLCO4A1 is correlated with tumor immune infiltration in colon adenocarcinoma. Mediat Inflamm 2023:4926474
Jian L et al (2023) GLUT10 is a novel immune regulator involved in lung cancer immune cell infiltration and predicts worse survival when transcriptionally downregulated. Heliyon 9(3):e13836
World Medical, A (2013) World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 310(20):2191–2194
in Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, th, Editor. (2011) Washington
Chang TY et al (2022) ANGPTL1 attenuates cancer migration, invasion, and stemness through regulating FOXO3a-mediated SOX2 expression in colorectal cancer. Clin Sci 136(9):657–673
Chandra R et al (2021) The colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment and its impact on liver and lung metastasis. Cancers 13(24):6206
Zheng X et al (2021) Communication between epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity and cancer stem cells: new insights into cancer progression. Front Oncol 11:617597
Matsumura Y et al (2004) PIG7/LITAF gene mutation and overexpression of its gene product in extramammary Paget’s disease. Int J Cancer 111(2):218–223
Chen YC et al (2020) Involvement of the MicroRNA-1-LITAF axis in gastric cancer cell growth and invasion. Anticancer Res 40(11):6247–6256
Pastushenko I, Blanpain C (2019) EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol 29(3):212–226
Zhang N et al (2021) Novel therapeutic strategies: targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 22(8):e358–e368
Wong SHM et al (2018) E-cadherin: its dysregulation in carcinogenesis and clinical implications. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 121:11–22
Luo Y et al (2018) Upregulated N-cadherin expression is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial-derived solid tumours: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest 48(4):e12903
Chi Z et al (2021) LINC00473 downregulation facilitates trophoblast cell migration and invasion via the miR-15a-5p/LITAF axis in pre-eclampsia. Environ Toxicol 36(8):1618–1627
Celia-Terrassa T, Jolly MK (2020) Cancer stem cells and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 10(7):036905
You L, Guo X, Huang Y (2018) Correlation of cancer stem-cell markers OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG with clinicopathological features and prognosis in operative patients with rectal cancer. Yonsei Med J 59(1):35–42
Li Y et al (2019) Chemical compound cinobufotalin potently induces FOXO1-stimulated cisplatin sensitivity by antagonizing its binding partner MYH9. Signal Transduct Target Ther 4:48
Lin X et al (2019) HBX-induced miR-5188 impairs FOXO1 to stimulate beta-catenin nuclear translocation and promotes tumor stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 9(25):7583–7598
Zou Y et al (2020) Timeless-stimulated miR-5188-FOXO1/beta-catenin-c-Jun feedback loop promotes stemness via ubiquitination of beta-catenin in breast cancer. Mol Ther 28(1):313–327
Jiang Y et al (2020) Resveratrol promotes osteogenesis via activating SIRT1/FoxO1 pathway in osteoporosis mice. Life Sci 246:117422
Jing Z et al (2021) Phosphocreatine promotes osteoblastic activities in H2O2-induced MC3T3-E1 cells by regulating SIRT1/FOXO1/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 22(5):609–621
Chen X et al (2022) Asiatic acid improves high-fat-diet-induced osteoporosis in mice via regulating SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling and inhibiting oxidative stress. Histol Histopathol 37(8):769–777
Ren BC et al (2020) Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via Sirt1-Foxo1 and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med 24(21):12355–12367
Mao ZJ, Xia WS, Chai F (2021) Yunpi Heluo decoction attenuates insulin resistance by regulating SIRT1-FoxO1 autophagy pathway in skeletal muscle of Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Ethnopharmacol 270:113828
Mao Z et al (2022) Yunpi Heluo decoction reduces ectopic deposition of lipids by regulating the SIRT1-FoxO1 autophagy pathway in diabetic rats. Pharm Biol 60(1):579–588
Tan Y et al (2022) Lingbao huxin pill alleviates apoptosis and inflammation at infarct border zone through SIRT1-mediated FOXO1 and NF- kappa B pathways in rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Chin J Integr Med 28(4):330–338
Yang X, Wu K (2022) Artemisinin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of the forkhead transcription factor O1 signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022:7824436
Zhang D et al (2022) LncRNA SNHG8 sponges miR-449c-5p and regulates the SIRT1/FoxO1 pathway to affect microglia activation and blood-brain barrier permeability in ischemic stroke. J Leukoc Biol 111(5):953–966
Wang Y et al (2018) Roles of SIRT1/FoxO1/SREBP-1 in the development of progestin resistance in endometrial cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet 298(5):961–969
Liu CL et al (2022) Inhibition of glioblastoma progression by Urolithin A in vitro and in vivo by regulating Sirt1-FOXO1 axis via ERK/AKT signaling pathways. Neoplasma 69(1):80–94
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81974379), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Grant No. 19ZR1438700) and the Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Grant No. ZH2018QNB05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, and Writing—Original Draft were performed by JG; Formal analysis, Resources, and Investigation were performed by Z-YZ; Formal analysis, Visualization and Data Curation were performed by J-HS; Project administration, Supervision, and Validation were performed by X-PW; Validation, Supervision, and Writing—Review & Editing were performed by Z-QZ and LQ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All procedures were approved by the human Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University. The animal experiment was supported by the Animal Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University.
Consent for publication
All the patients signed written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, J., Zhang, ZY., Sun, JH. et al. LITAF inhibits colorectal cancer stemness and metastatic behavior by regulating FOXO1-mediated SIRT1 expression. Clin Exp Metastasis 40, 309–320 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-023-10213-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-023-10213-x