Abstract
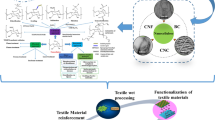
This study proposed a simple, efficient, and energy-saving one-pot strategy to produce nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) from bleached corn stalk, with concurrent NFC surface modifications. High-speed mechanical shearing and mechanochemical activation (urea/NaOH, oxalic acid, citric acid, and mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane) were involved in the strategy. The effects of different surface functionalizations on the morphological, crystalline, chemical, and thermal properties of the NFC were investigated. The results suggested that the bleached corn stalk fibers were decomposed into microfibrils through intensive mechanical shearing. Each microfibril is associated with abundant branched and networked cellulose nanofibrils. NFC showed an average diameter of 23 nm and an average length of 1530 nm, with an aspect ratio of 67. The hydroxyl groups on the NFC surface were functionalized and modified by forming amide (urea/NaOH), carboxyl (oxalic acid/citric acid), and hydrogen bond (mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane), respectively. This novel one-pot strategy opens up new application areas for production and surface functionalization of nanocellulose.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Babaei-Ghazvini A, Acharya B, Korber DR (2022) Multilayer photonic films based on interlocked chiral-nematic cellulose nanocrystals in starch/chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 275:18709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118709
Barbosa BM, Vaz S, Colodette JL, de Aguiar AR, Cabral CPT, de Freitas Homem de Faria B (2022) Structural and chemical characterization of lignin and hemicellulose isolated from corn fibers toward agroindustrial residue valorization. Cellulose 29:8117–8132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04769-2
Beaumont M, Winklehner S, Veigel S, Mundigler N, Gindl-Altmutter W, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2020) Wet esterification of never-dried cellulose: a simple process to surface-acetylated cellulose nanofibers. Green Chem 22(17):5605–5609. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0gc02116d
Beaumont M, Tardy BL, Reyes G, Koso TV, Schaubmayr E, Jusner P, King AWT, Dagastine RR, Potthast A, Rojas OJ, Rosenau T (2021) Assembling native elementary cellulose nanofibrils via a reversible and regioselective surface functionalization. J Am Chem Soc 143(41):17040–17046. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c06502
Beluns S, Platnieks O, Gaidukovs S, Starkova O, Sabalina A, Grase L, Thakur VK, Gaidukova G (2021) Lignin and xylan as interface engineering additives for improved environmental durability of sustainable cellulose nanopapers. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312939
Bozic M, Vivod V, Kavcic S, Leitgeb M, Kokol V (2015) New findings about the lipase acetylation of nanofibrillated cellulose using acetic anhydride as acyl donor. Carbohydr Polym 125:340–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.02.061
Chen L, Zhu JY, Baez C, Kitin P, Elder T (2016) Highly thermal-stable and functional cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils produced using fully recyclable organic acids. Green Chem 18:3835–3843. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC00687F
Chen JH, Liu JG, Su YQ, Xu ZH, Li MC, Ying RF, Wu JQ (2019) Preparation and properties of microfibrillated cellulose with different carboxyethyl content. Carbohydr Polym 206:616–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.024
Cheng L, Zhang D, Gu Z, Li Z, Hong Y, Li C (2018) Preparation of acetylated nanofibrillated cellulose from corn stalk microcrystalline cellulose and its reinforcing effect on starch films. Int J Biol Macromol 111:959–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.056
Douglass EF, Avci H, Boy R, Rojas OJ, Kotek R (2017) A review of cellulose and cellulose blends for preparation of bio-derived and conventional membranes, nanostructured thin films, and composites. Polym Rev 58:102–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2016.1269124
Fourati Y, Magnin A, Putaux JL, Boufi S (2020) One-step processing of plasticized starch/cellulose nanofibrils nanocomposites via twin-screw extrusion of starch and cellulose fibers. Carbohydr Polym 229:115554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115554
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24(11):4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
French AD (2020) Increment in evolution of cellulose crystallinity analysis. Cellulose 27(10):5445–5448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03172-z
Gao B, Yang J, Zhang S, Li X (2021) Green fabrication of thermally-stable oxidized cellulose nanocrystals by evolved Fenton reaction and in-situ nanoreinforced thermoplastic starch. Cellulose 28:8405–8418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04039-7
Golizadeh M, Karimi A, Gandomi-Ravandi S, Vossoughi M, Khafaji M, Joghataei MT, Faghihi F (2019) Evaluation of cellular attachment and proliferation on different surface charged functional cellulose electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 207:796–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.028
Henschen J, Li D, Ek M (2019) Preparation of cellulose nanomaterials via cellulose oxalates. Carbohydr Polym 213:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.056
Hong S, Song Y, Yuan Y, Lian H, Liimatainen H (2020) Production and characterization of lignin containing nanocellulose from luffa through an acidic deep eutectic solvent treatment and systematic fractionation. Ind Crop Prod 143:111913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111913
Hou Y, Wu W (2022) Derived from corn straw cellulose: modified used tire rubber powder composites. Cellulose 29:3935–3945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04549-y
Huang J, Du Y, Bao T, Lin M, Wang J, Yang ST (2019) Production of n-butanol from cassava bagasse hydrolysate by engineered Clostridium tyrobutyricum overexpressing adhE2: kinetics and cost analysis. Bioresour Technol 292:121969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121969
Ji H, Xiang Z, Qi H, Han T, Pranovich A, Song T (2019) Strategy towards one-step preparation of carboxylic cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils with high yield, carboxylation and highly stable dispersibility using innocuous citric acid. Green Chem 21:1956–1964. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03493A
Jiang B, Chen C, Liang Z, He S, Kuang Y, Song J, Mi R, Chen G, Jiao M, Hu L (2019) Lignin as a wood-inspired binder enabled strong, water stable, and biodegradable paper for plastic replacement. Adv Funct Mater 30:1906307. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201906307
Jiang J, Chen H, Yu J, Liu L, Fan Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2021) Rate-limited reaction in TEMPO/Laccase/O2 oxidation of cellulose. Macromol Rapid Commun 42:e2000501. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202000501
Kumar V, Bollström R, Yang A, Chen Q, Chen G, Salminen P, Bousfield D, Toivakka M (2014) Comparison of nano- and microfibrillated cellulose films. Cellulose 21:3443–3456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0357-5
Li D, Wang Y, Long F, Gan L, Huang J (2020a) Solvation-controlled elastification and shape-recovery of cellulose nanocrystal-based aerogels. Acs Appl Mater Inter 12:1549–1557. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18569
Li Z, Chen C, Mi R, Gan W, Dai J, Jiao M, Xie H, Yao Y, Xiao S, Hu L (2020) A strong, tough, and scalable structural material from fast-growing bamboo. Adv Mater 32:e1906308. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201906308
Li T, Chen C, Brozena AH, Zhu JY, Xu L, Driemeier C, Dai J, Rojas OJ, Isogai A, Wagberg L, Hu L (2021) Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 590:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03167-7
Ma Y, Qian S, Hu L, Qian J, Fontanillo Lopez CA, Xu L (2018) Mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of PLA biocomposites toughened with silylated bamboo cellulose nanowhiskers. Polym Composite 40:3012–3019. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25144
Meng F, Wang G, Du X, Wang Z, Xu S, Zhang Y (2019) Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanofibers and nanocrystals from liquefied banana pseudo-stem residue. Compos Part B-Eng 160:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.08.048
Omran AAB, Mohammed A, Sapuan SM, Ilyas RA, Asyraf MRM, Rahimian Koloor SS, Petru M (2021) Micro- and nanocellulose in polymer composite materials: a review. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020231
Qian S, Sheng K (2017) PLA toughened by bamboo cellulose nanowhiskers: role of silane compatibilization on the PLA bionanocomposite properties. Compos Sci Technol 148:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.05.020
Rana AK, Frollini E, Thakur VK (2021) Cellulose nanocrystals: pretreatments, preparation strategies, and surface functionalization. Int J Biol Macromol 182:1554–1581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.119
Sungsinchai S, Niamnuy C, Wattanapan P, Charoenchaitrakool M, Devahastin S (2022) Spray drying of non-chemically prepared nanofibrillated cellulose: improving water redispersibility of the dried product. Int J Biol Macromol 207:434–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.153
Thien DVH, Lam DN, Diem HN, Pham TYN, Bui NQ, Truc TNT, Van-Pham DT (2022) Synthesis of cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid) with high water absorbency using pineapple-leaf extracted cellulose fibers. Carbohydr Polym 288:119421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119421
Thongsomboon W, Serra DO, Possling A, Hadjineophytou C, Hengge R, Cegelski L (2018) Phosphoethanolamine cellulose: a naturally produced chemically modified cellulose. Science 359:334–338. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao4096
Tian J, Cao Z, Qian S, Xia Y, Zhang J, Kong Y, Sheng K, Zhang Y, Wan Y, Takahashi J (2022a) Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose. Nanotechnol Rev 11:2469–2482. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2022-0142
Tian Y, Zhou M, Luo T, Zhu P, Cheng F, Zhang Y, Lin Y (2022) A comparative investigation of gelatinized and regenerated starch composites reinforced by microfibrillated cellulose. Food chem 373:131470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131470
Wang W, Liang T, Bai H, Dong W, Liu X (2018) All cellulose composites based on cellulose diacetate and nanofibrillated cellulose prepared by alkali treatment. Carbohydr Polym 179:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.098
Wang X, Pang Z, Chen C, Xia Q, Zhou Y, Jing S, Wang R, Ray U, Gan W, Li C, Chen G, Foster B, Li T, Hu L (2020) All-natural, degradable, rolled-up straws based on cellulose micro- and nano-hybrid fibers. Adv Funct Mater 30:1910417. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201910417
Wang Y, Wang Q, Liu S, Ji X, Yang G, Chen J (2022) Lipase induced highly hydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose film for strain sensor application. Carbohydr Polym 284:119193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119193
Wu J, Zhu W, Shi X, Li Q, Huang C, Tian Y, Wang S (2020) Acid-free preparation and characterization of kelp (Laminaria japonica) nanocelluloses and their application in Pickering emulsions. Carbohydr Polym 236:115999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115999
Xu L, Zhao J, Qian S, Zhu X, Takahashi J (2021) Green-plasticized poly(lactic acid)/nanofibrillated cellulose biocomposites with high strength, good toughness and excellent heat resistance. Compos Sci Technol 203:108613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108613
Yang J, Lu X, Zhang Y, Xu J, Yang Y, Zhou Q (2020) A facile ionic liquid approach to prepare cellulose fiber with good mechanical properties directly from corn stalks. Green Energy Environ 5:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2019.12.004
Yang X, Biswas SK, Han J, Tanpichai S, Li MC, Chen C, Zhu S, Das AK, Yano H (2021) Surface and interface engineering for nanocellulosic advanced materials. Adv Mater 33:e2002264. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202002264
Yao W, Weng Y, Catchmark JM (2020) Improved cellulose X-ray diffraction analysis using Fourier series modeling. Cellulose 27:5563–5579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03177-8
Yokesahachart C, Yoksan R, Khanoonkon N, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2021) Effect of jute fibers on morphological characteristics and properties of thermoplastic starch/biodegradable polyester blend. Cellulose 28:5513–5530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03921-8
Zhang DY, Zhang XQ, Yao XH, Wan Y, Song P, Liu ZY, Fu YJ (2020) Microwave-assisted synthesis of PdNPs by cellulose solution to prepare 3D porous microspheres applied on dyes discoloration. Carbohydr Polym 247:116569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116569
Zheng C, Lu K, Lu Y, Zhu S, Yue Y, Xu X, Mei C, Xiao H, Wu Q, Han J (2020) A stretchable, self-healing conductive hydrogels based on nanocellulose supported graphene towards wearable monitoring of human motion. Carbohydr Polym 250:116905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116905
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. Cesar A. Fontanillo Lopez (KU-Leuven Center for IT and IP Law) and Dr. Shaoqing Cui (School of Biosystems Engineering and Food Science, Zhejiang University), for the language review.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Fund for Scientific Research in the Public Interest of Ningbo (No. 2021S067 and 2022S150), the Foundation of the Department of Education of Zhejiang Province (Y202148281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JT: Investigation, Data Curation, Writing-Original Draft, Visualization, Funding. ZZ and ZL: Investigation, Data Curation. YW: Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision. SQ: Writing-Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The article does not include human participants and/or animals research.
Consent for publication
All authors gave their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Qian, S., Zhang, Z. et al. A facile approach for preparing nanofibrillated cellulose from bleached corn stalk with tailored surface functions. Cellulose 30, 5641–5656 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05234-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05234-4