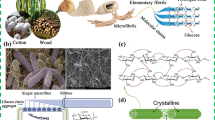
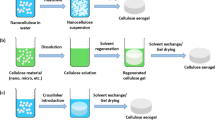
Abstract
Pollution and contamination of water with heavy metals is a global challenge which demands efficient, economic and sustainable solution. The grafting/addition of poly-functional groups (ligands) on the polysaccharides chains can high adsorption affinities towards heavy metals. Aerogels are a class of three-dimensional porous materials with outstanding physic-chemical characteristics (low density, high surface to volume ratio and controllable surface chemistry). In the recent years, aerogels have gained sufficient attention for the remediation of heavy metal ions from wastewater. The present review critically analyses the various synthesis routes for the cellulose aerogels and their applications as an adsorbent for heavy metal ions from water. This review critically analyzes the various synthesis routes for three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels, their physico-chemical characterizations and removal mechanisms for the adsorption of heavy metal ions from water with insights into isotherm and kinetic models. Challenges (reactor configuration, scale-up, and proper selection of drying technique) and future research directions for the development of robust and efficient cellulose aerogels for the mitigation of heavy metal ions from water have also been elucidated.



(Reproduced with permission from Elsevier)

(Reproduced with permission from Elsevier)

(Reproduced with permission from Maatar and Boufi (2015), Elsevier)

Reproduced with permission from Society of Plastics Engineers)

(Reproduced with permission from Mo et al. (2019), Elsevier)

(Reproduced with permission from Cui et al. (2018), Springer Nature)

(Reproduced with permission from Tang et al. (2020), Elsevier)

(Adapted from Lei et al. (2019))

(Reproduced with permission from RSC Advances)
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data and materials can be obtained from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Ahuja D, Dhiman S, Rattan G, Monga S, Singhal S, Kaushik A (2021) Superhydrophobic modification of cellulose sponge fabricated from discarded jute bags for oil water separation. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105063. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2021.105063
Alwin S, Sahaya Shajan X (2020) Aerogels: promising nanostructured materials for energy conversion and storage applications. Mater Renew Sustain Energy 9:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40243-020-00168-4/FIGURES/17
Amaly N, El-Moghazy AY, Nitin N, Sun G, Pandey PK (2022) Synergistic adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by microcrystalline cellulose composite aerogel dopped with montmorillonite hosted methylene blue. Chem Eng J 430:133077. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2021.133077
Anastopoulos I, Pashalidis I, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Giannakoudakis DA, Robalds A, Usman M, Escudero LB, Zhou Y, Colmenares JC, Núñez-Delgado A, Lima ÉC (2019) Agricultural biomass/waste as adsorbents for toxic metal decontamination of aqueous solutions. J Mol Liq 295:111684. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2019.111684
Aravind PR, Shajesh P, Soraru GD, Warrier KGK (2010) Ambient pressure drying: a successful approach for the preparation of silica and silica based mixed oxide aerogels. J Solgel Sci Technol 54:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-010-2164-2/FIGURES/9
Bello OS, Adegoke KA, Sarumi OO, Lameed OS (2019) Functionalized locust bean pod (Parkia biglobosa) activated carbon for Rhodamine B dye removal. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HELIYON.2019.E02323
Bernardo GRR, Rene RMJ, la Torre Ma. Catalina AD (2009) Chromium (III) uptake by agro-waste biosorbents: Chemical characterization, sorption–desorption studies, and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 170:845–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2009.05.046
Bhagyaraj S, Krupa I (2020) Alginate-halloysite nanocomposite aerogel: preparation, structure, and oil/water separation applications. Biomolecules 10:1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOM10121632
Bo S, Ren W, Lei C, Xie Y, Cai Y, Wang S, Gao J, Ni Q, Yao J (2018) Flexible and porous cellulose aerogels/zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) hybrids for adsorption removal of Cr(IV) from water. J Solid State Chem 262:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSSC.2018.02.022
Budtova T (2019a) Cellulose II aerogels: a review. Cellulose 26(1):81–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-018-2189-1
Budtova T (2019b) Cellulose II aerogels: a review. Cellulose 26(1):81–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-018-2189-1
Chami Khazraji A, Robert S (2013) Self-assembly and intermolecular forces when cellulose and water interact using molecular modeling. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/745979
Chen Y, Zhou L, Chen L, Duan G, Mei C, Huang C, Han J, Jiang S (2019) Anisotropic nanocellulose aerogels with ordered structures fabricated by directional freeze-drying for fast liquid transport. Cellulose 26:6653–6667. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-019-02557-Z/FIGURES/9
Chen Z, Zhang S, Yang J et al (2021) Rational design and controllable synthesis of polymer aerogel-based single-atom catalysts with high loading. Mater Adv 2:6885–6900. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00720C
Chen Y, Nie Z, Gao J, Wang J, Cai M (2021a) A novel adsorbent of bentonite modified chitosan-microcrystalline cellulose aerogel prepared by bidirectional regeneration strategy for Pb(II) removal. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105755. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2021.105755
Chen YX, Sepahvand S, Gauvin F, Schollbach K, Brouwers HJH, Yu Q (2021b) One-pot synthesis of monolithic silica-cellulose aerogel applying a sustainable sodium silicate precursor. Constr Build Mater 293:123289. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CONBUILDMAT.2021.123289
Chen M, Yang G, Liu Y, Lv Y, Sun S, Liu M (2022) Preparation of amino-modified cellulose aerogels and adsorption on typical diclofenac sodium contaminant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:19790–19802. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-17214-X/FIGURES/9
Cheng M, Hu J, Xia J, Liu Q, Wei T, Ling Y, Li W, Liu B (2022) One-step in-situ green synthesis of cellulose nanocrystal aerogel based shape stable phase change material. Chem Eng J 431:133935. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2021.133935
Cui S, Wang X, Zhang X, Xia W, Tang X, Lin B, Wu Q, Zhang X, Shen X (2018) Preparation of magnetic MnFe2O4-Cellulose aerogel composite and its kinetics and thermodynamics of Cu(II) adsorption. Cellulose 25:735–751. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-017-1598-X/FIGURES/18
Członka S, Bertino MF, Kośny J, Shukla N (2018) Freeze-drying method as a new approach to the synthesis of polyurea aerogels from isocyanate and water. J Solgel Sci Technol 87:685–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-018-4769-9/FIGURES/5
Darpentigny C, Nonglaton G, Bras J, Jean B (2020) Highly absorbent cellulose nanofibrils aerogels prepared by supercritical drying. Carbohydr Polym 229:115560. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2019.115560
De Andrade JR, Oliveira MF, Da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2018) Adsorption of pharmaceuticals from water and wastewater using nonconventional low-cost materials: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:3103–3127. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.IECR.7B05137/ASSET/IMAGES/MEDIUM/IE-2017-051372_0001.GIF
Deguchi S, Tsujii K, Horikoshi K (2008) Crystalline-to-amorphous transformation of cellulose in hot and compressed water and its implications for hydrothermal conversion. Green Chem 10:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1039/B713655B
Do NHN, Tran VT, Tran QBM, Le KA, Thai QB, Nguyen PTT, Duong HM, Le PK (2021) Recycling of pineapple leaf and cotton waste fibers into heat-insulating and flexible cellulose aerogel composites. J Polym Environ 29:1112–1121. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10924-020-01955-W/TABLES/2
Druel L, Bardl R, Vorwerg W, Budtova T (2017) Starch aerogels: a member of the family of thermal superinsulating materials. Biomacromol 18:4232–4239. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.BIOMAC.7B01272/SUPPL_FILE/BM7B01272_SI_001.PDF
Ejima H, Richardson JJ, Liang K et al (2013) One-step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science 341:154–157. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1237265/SUPPL_FILE/EJIMA.SM-CORRECTED.PDF
El-Naggar ME, Othman SI, Allam AA, Morsy OM (2020) Synthesis, drying process and medical application of polysaccharide-based aerogels. Int J Biol Macromol 145:1115–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2019.10.037
Ferreira-Neto EP, Ullah S, Da Silva TCA, Domeneguetti RR, Perissinotto AP, De Vicente FS, Rodrigues-Filho UP, Ribeiro SJL (2020) Bacterial nanocellulose/MoS2 hybrid aerogels as bifunctional adsorbent/photocatalyst membranes for in-flow water decontamination. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:41627–41643. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.0C14137/SUPPL_FILE/AM0C14137_SI_001.PDF
Fiol N, Vásquez MG, Pereira M et al (2019) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers as potential Cu(II) adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Cellulose 26:903–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-018-2106-7/FIGURES/5
Ganesan K, Budtova T, Ratke L, Gurikov P, Baudron V, Preibisch I, Niemeyer P, Smirnova I, Milow B (2018) Review on the production of polysaccharide aerogel particles. Materials 11:2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/MA11112144
Geng B, Wang H, Wu S, Ru J, Tong C, Chen Y, Liu H, Wu S, Liu X (2017) Surface-tailored nanocellulose aerogels with thiol-functional moieties for highly efficient and selective removal of Hg(II) ions from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:11715–11726. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSSUSCHEMENG.7B03188
Gong C, Ni J-P, Tian C, Su Z-H (2021) Research in porous structure of cellulose aerogel made from cellulose nanofibrils. Int J Biol Macromol 172:573–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2021.01.080
Guo D-M, An Q-D, Xiao Z-Y, Zhai S-R, Shi Z (2017) Polyethylenimine-functionalized cellulose aerogel beads for efficient dynamic removal of chromium(vi) from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 7:54039–54052. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA09940A
Gurgel LVA, Perin de Melo JC, de Lena JC, Gil LF (2009) Adsorption of chromium (VI) ion from aqueous solution by succinylated mercerized cellulose functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups. Bioresour Technol 100:3214–3220. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2009.01.068
Hasanpour M, Motahari S, Jing D, Hatami M (2021) Investigation of operation parameters on the removal efficiency of methyl orange pollutant by cellulose/zinc oxide hybrid aerogel. Chemosphere 284:131320. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.131320
He X, Cheng L, Wang Y et al (2014) Aerogels from quaternary ammonium-functionalized cellulose nanofibers for rapid removal of Cr(VI) from water. Carbohydr Polym 111:683–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2014.05.020
He X, Chen T, Jiang T, Wang C, Luan Y, Liu P, Liu Z (2021) Preparation and adsorption properties of magnetic hydrophobic cellulose aerogels based on refined fibers. Carbohydr Polym 260:117790. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2021.117790
Hokkanen S, Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2016) A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res 91:156–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2016.01.008
Hong HJ, Ban G, Kim HS, Jeong HS, Park MS (2021) Fabrication of cylindrical 3D cellulose nanofibril (CNF) aerogel for continuous removal of copper(Cu2+) from wastewater. Chemosphere 278:130288. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.130288
Hosseini H, Mousavi SM (2021) Bacterial cellulose/polyaniline nanocomposite aerogels as novel bioadsorbents for removal of hexavalent chromium: Experimental and simulation study. J Clean Prod 278:123817. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.123817
Huang C, Cai B, Zhang L, Zhang C, Pan H (2021) Preparation of iron-based metal-organic framework @cellulose aerogel by in situ growth method and its application to dye adsorption. J Solid State Chem 297:122030. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSSC.2021.122030
Huš M, Urbic T (2012) Strength of hydrogen bonds of water depends on local environment. J Chem Phys 136:144305. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3701616
Ji Y, Wen Y, Wang Z, Zhang S, Guo M (2020a) Eco-friendly fabrication of a cost-effective cellulose nanofiber-based aerogel for multifunctional applications in Cu(II) and organic pollutants removal. J Clean Prod 255:120276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.120276
Ji Y, Wen Y, Wang Z, Zhang S, Guo M (2020b) Eco-friendly fabrication of a cost-effective cellulose nanofiber-based aerogel for multifunctional applications in Cu(II) and organic pollutants removal. J Clean Prod 255:120276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.120276
Jiao Y, Wan C, Li J (2016) Synthesis of carbon fiber aerogel from natural bamboo fiber and its application as a green high-efficiency and recyclable adsorbent. Mater Des 107:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2016.06.015
Jiao Y, Wan C, Bao W, Gao H, Liang D, Li J (2018) Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@cellulose aerogel nanocomposite and its application in Fenton-like degradation of Rhodamine B. Carbohydr Polym 189:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.02.028
Joshi P, Sharma OP, Ganguly SK, Srivastava M, Khatri OP (2022) Fruit waste-derived cellulose and graphene-based aerogels: plausible adsorption pathways for fast and efficient removal of organic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 608:2870–2883. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2021.11.016
Kistler SS (1932) Coherent expanded aerogels. J Phys Chem 36:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1021/J150331A003/ASSET/J150331A003.FP.PNG_V03
Kołodyńska D (2013) Application of a new generation of complexing agents in removal of heavy metal ions from different wastes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5939–5949. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-013-1576-2/TABLES/4
Lei C, Gao J, Ren W, Xie Y, Abdalkarim SYH, Wang S, Ni Q, Yao J (2019) Fabrication of metal-organic frameworks@cellulose aerogels composite materials for removal of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr Polym 205:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.10.029
Li J, Zuo K, Wu W, Xu Z, Yi Y, Jing Y, Dai H, Fang G (2018a) Shape memory aerogels from nanocellulose and polyethyleneimine as a novel adsorbent for removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Carbohydr Polym 196:376–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.05.015
Li Z, Shao L, Ruan Z, Hu W, Lu L, Chen Y (2018b) Converting untreated waste office paper and chitosan into aerogel adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 193:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.04.003
Li Y, Guo C, Shi R, Zhang H, Gong L, Dai L (2019) Chitosan/ nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel with highly oriented microchannel structure for rapid removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 223:115048. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2019.115048
Li D, Tian X, Wang Z, Guan Z, Li X, Qiao H, Ke H, Luo L, Wei Q (2020) Multifunctional adsorbent based on metal-organic framework modified bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for high efficient removal of heavy metal ion and organic pollutant. Chem Eng J 383:123127. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2019.123127
Li H, Wang Y, Ye M, Zhang X, Zhang H, Wang G, Zhang Y (2021) Hierarchically porous poly(amidoxime)/bacterial cellulose composite aerogel for highly efficient scavenging of heavy metals. J Colloid Interface Sci 600:752–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2021.05.071
Liu X, Xu M, An B, Wu Z, Yang R, Ma C, Huang Q, Li W, Li J, Liu S (2019) A facile hydrothermal method–fabricated robust and ultralight weight cellulose nanocrystal-based hydro/aerogels for metal ion removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(25):25583–25595. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-019-05810-X
Liu J, Chen TW, Yang YL, Bai ZC, Xia LR, Wang M, Lv XL, Li L (2020) Removal of heavy metal ions and anionic dyes from aqueous solutions using amide-functionalized cellulose-based adsorbents. Carbohydr Polym 230:115619. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2019.115619
Liu Y, Pei R, Lv Y, Lin C, Huang J, Liu M (2021a) Removal behavior and mechanism of silver from low concentration wastewater using cellulose aerogel modified by thiosemicarbazide. J Appl Polym Sci 138:51226. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.51226
Liu Z, Zhang S, He B, Wang S, Kong F (2021b) Synthesis of cellulose aerogels as promising carriers for drug delivery: a review. Cellulose 28(5):2697–2714. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-021-03734-9
Liu Y, Liang Z, Lin C, Ye X, Lv Y, Xu P, Liu M (2022) Insights into efficient adsorption of the typical pharmaceutical pollutant with an amphiphilic cellulose aerogel. Chemosphere 291:132978. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2021.132978
Long LY, Weng YX, Wang YZ (2018) Cellulose Aerogels: Synthesis, Applications, and Prospects. Polymers 10:623. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM10060623
Lv Y, Yang HC, Liang HQ et al (2015) Nanofiltration membranes via co-deposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine followed by cross-linking. J Memb Sci 476:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2014.11.024
Lv Y, Liang Z, Li Y, Chen Y, Liu K, Yang G, Liu Y, Lin C, Ye X, Shi Y, Liu M (2021) Efficient adsorption of diclofenac sodium in water by a novel functionalized cellulose aerogel. Environ Res 194:110652. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2020.110652
Ma X, Lou Y, Chen XB, Shi Z, Xu Y (2019) Multifunctional flexible composite aerogels constructed through in-situ growth of metal-organic framework nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose. Chem Eng J 356:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2018.09.034
Maatar W, Boufi S (2015) Poly(methacylic acid-co-maleic acid) grafted nanofibrillated cellulose as a reusable novel heavy metal ions adsorbent. Carbohydr Polym 126:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2015.03.015
Mehanny S, Abu-El Magd EE, Ibrahim M et al (2021) Extraction and characterization of nanocellulose from three types of palm residues. J Mater Res Technol 10:526–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMRT.2020.12.027
Mo L, Pang H, Tan Y, Zhang S, Li J (2019) 3D multi-wall perforated nanocellulose-based polyethylenimine aerogels for ultrahigh efficient and reversible removal of Cu(II) ions from water. Chem Eng J 378:122157. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2019.122157
Najaflou S, Rad MF, Baghdadi M, Nabi Bidhendi GR (2021) Removal of Pb(II) from contaminated waters using cellulose sulfate/chitosan aerogel: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Manag 286:112167. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.112167
Oprea M, Voicu SI (2020) Recent advances in composites based on cellulose derivatives for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym 247:116683. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2020.116683
Pajonk GM (1989) Drying methods preserving the textural properties of gels. Le Journal De Physique Colloques 50(C4):13. https://doi.org/10.1051/JPHYSCOL:1989403
Pei R, Li Q, Liu J, Yang G, Wu Q, Wu M, Tong S, Lv Y, Ye X, Liu Y, Liu M (2020) Adsorption/reduction behaviors of modified cellulose aerogels for the removal of low content of Cr(VI). J Polym Environ 28(8):2199–2210. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10924-020-01761-4
Pircher N, Carbajal L, Schimper C, Bacher M, Rennhofer H, Nedelec JM, Lichtenegger HC, Rosenau T, Liebner F (2016) Impact of selected solvent systems on the pore and solid structure of cellulose aerogels. Cellulose 23:1949–1966. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-016-0896-Z/TABLES/5
Rahmanian V, Pirzada T, Wang S, Khan SA (2021) Cellulose-based hybrid aerogels: strategies toward design and functionality. Adv Mater 33:2102892. https://doi.org/10.1002/ADMA.202102892
Ren Y, Hersch SJ, He X, Zhou R, Dong TG, Lu Q (2022) A lightweight, mechanically strong, and shapeable copper-benzenedicarboxylate/cellulose aerogel for dye degradation and antibacterial applications. Sep Purif Technol 283:120229. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2021.120229
Salama A, Mohamed A, Aboamera NM et al (2018) Characterization and mechanical properties of cellulose acetate/carbon nanotube composite nanofibers. Adv Polym Technol 37:2446–2451. https://doi.org/10.1002/ADV.21919
Seddiqi H, Oliaei E, Honarkar H et al (2021) Cellulose and its derivatives: towards biomedical applications. Cellulose 28:1893–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-020-03674-W
Shahnaz T, Sharma V, Subbiah S, Narayanasamy S (2020) Multivariate optimisation of Cr(VI), Co(III) and Cu(II) adsorption onto nanobentonite incorporated nanocellulose/chitosan aerogel using response surface methodology. J Water Process Eng 36:101283. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JWPE.2020.101283
She J, Tian C, Wu Y, Li X, Luo S, Qing Y, Jiang Z (2017) Cellulose nanofibrils aerogel cross-linked by poly(vinyl alcohol) and acrylic acid for efficient and recycled adsorption with heavy metal ions. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18:4167–4175. https://doi.org/10.1166/JNN.2018.15264
Simón-Herrero C, Caminero-Huertas S, Romero A, Valverde JL, Sánchez-Silva L (2016) Effects of freeze-drying conditions on aerogel properties. J Mater Sci 51:8977–8985. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10853-016-0148-5/FIGURES/9
Siddique JA, Ansari SP, Yadav M (2021) Carbon aerogel composites for gas sensing. Adv Aerogel Composit Environ Remediat 49–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820732-1.00004-7
Singh SA, Shukla SR (2016) Adsorptive removal of cobalt ions on raw and alkali-treated lemon peels. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13762-015-0801-6/FIGURES/6
Singh K, Arora JK, Sinha TJM, Srivastava S (2014) Functionalization of nanocrystalline cellulose for decontamination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous system: computational modeling approach. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10098-014-0717-8/FIGURES/11
Song S, Liu Z, Zhang J, Jiao C, Ding L, Yang S (2020a) Synthesis and adsorption properties of novel bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide/attapulgite materials for Cu and Pb ions in aqueous solutions. Materials 13(17):3703. https://doi.org/10.3390/MA13173703
Song Z, Chen X, Gong X, Gao X, Dai Q, Nguyen TT, Guo M (2020cb) Luminescent carbon quantum dots/nanofibrillated cellulose composite aerogel for monitoring adsorption of heavy metal ions in water. Opt Mater (amst) 100:109642–110123. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OPTMAT.2019.109642
Syeda HI, Yap PS (2022) A review on three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels for the removal of heavy metals from water. Sci Total Environ 807:150606. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.150606
Tang J, Song Y, Zhao F, Spinney S, da Silva Bernardes J, Tam KC (2019) Compressible cellulose nanofibril (CNF) based aerogels produced via a bio-inspired strategy for heavy metal ion and dye removal. Carbohydr Polym 208:404–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.12.079
Tang C, Brodie P, Brunsting M, Tam KC (2020) Carboxylated cellulose cryogel beads via a one-step ester crosslinking of maleic anhydride for copper ions removal. Carbohydr Polym 242:116397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2020.116397
Tanpichai S, Boonmahitthisud A, Soykeabkaew N, Ongthip L (2022) Review of the recent developments in all-cellulose nanocomposites: properties and applications. Carbohydr Polym 286:119192. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2022.119192
Tian C, She J, Wu Y, Luo S, Wu Q, Qing Y (2018) Reusable and cross-linked cellulose nanofibrils aerogel for the removal of heavy metal ions. Polym Compos 39:4442–4451. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.24536
Tillet G, Boutevin B, Ameduri B (2011) Chemical reactions of polymer crosslinking and post-crosslinking at room and medium temperature. Prog Polym Sci 36:191–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROGPOLYMSCI.2010.08.003
Urbina L, Corcuera MÁ, Gabilondo N, Eceiza A, Retegi A (2021) A review of bacterial cellulose: sustainable production from agricultural waste and applications in various fields. Cellulose 28(13):8229–8253. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-021-04020-4
Veronovski A, Tkalec G, Knez Z, Novak Z (2014) Characterisation of biodegradable pectin aerogels and their potential use as drug carriers. Carbohydr Polym 113:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2014.06.054
Voisin H, Bergström L, Liu P, Mathew AP (2017) Nanocellulose-based materials for water purification. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO7030057
Wan C, Li J (2015) Facile synthesis of well-dispersed superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles encapsulated in three-dimensional architectures of cellulose aerogels and their applications for Cr(VI) removal from contaminated water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:2142–2152. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSSUSCHEMENG.5B00384/SUPPL_FILE/SC5B00384_SI_004.MPG
Wan C, Jiao Y, Wei S, Zhang L, Wu Y, Li J (2019) Functional nanocomposites from sustainable regenerated cellulose aerogels: a review. Chem Eng J 359:459–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2018.11.115
Wang H, Gong Y, Wang Y (2014) Cellulose-based hydrophobic carbon aerogels as versatile and superior adsorbents for sewage treatment. RSC Adv 4:45753–45759. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA08446B
Wang X, Jiang S, Cui S, Tang Y, Pei Z, Duan H (2019) Magnetic-controlled aerogels from carboxylated cellulose and MnFe2O4 as a novel adsorbent for removal of Cu(II). Cellulose 26:5051–5063. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-019-02444-7/TABLES/3
Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Li Y, Li W (2021) Nanocellulose aerogel for highly efficient adsorption of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 267:118233. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2021.118233
Wei J, Yang Z, Sun Y, Wang C, Fan J, Kang G, Zhang R, Dong X, Li Y (2019) Nanocellulose-based magnetic hybrid aerogel for adsorption of heavy metal ions from water. J Mater Sci 54:6709–6718. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10853-019-03322-0/FIGURES/5
Xiong Y, Wang C, Wang H et al (2017) A 3D titanate aerogel with cellulose as the adsorption-aggregator for highly efficient water purification. J Mater Chem A Mater 5:5813–5819. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA10638B
Yao C, Wang F, Cai Z, Wang X (2016) Aldehyde-functionalized porous nanocellulose for effective removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 6:92648–92654. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA20598D
Zaman A, Huang F, Jiang M et al (2020) Preparation, properties, and applications of natural cellulosic aerogels: a review. Energy Built Environ 1:60–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENBENV.2019.09.002
Zhang N, Zang GL, Shi C, Yu HQ, Sheng GP (2016) A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) removal. J Hazard Mater 316:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2016.05.018
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Wang X et al (2018) Characterization of the nano-cellulose aerogel from mixing CNF and CNC with different ratio. Mater Lett 229:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2018.06.101
Zhang X, Zhao X, Xue T, Yang F, Fan W, Liu T (2020) Bidirectional anisotropic polyimide/bacterial cellulose aerogels by freeze-drying for super-thermal insulation. Chem Eng J 385:123963. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2019.123963
Zheng Q, Cai Z, Gong S (2014) Green synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–cellulose nanofibril (CNF) hybrid aerogels and their use as superabsorbents. J Mater Chem A Mater 2:3110–3118. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14642A
Zhou T, Cheng X, Pan Y, Li C, Gong L (2019) Mechanical performance and thermal stability of polyvinyl alcohol–cellulose aerogels by freeze drying. Cellulose 26:1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-018-2179-3/FIGURES/8
Zhuang J, Rong N, Wang X, Chen C, Xu Z (2022) Adsorption of small size microplastics based on cellulose nanofiber aerogel modified by quaternary ammonium salt in water. Sep Purif Technol 293:121133. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2022.121133
Acknowledgments
ADG would like to thank computer center of UPL-UST and HS would like to thank computer center of MNNIT for providing infrastructure facilities.
Funding
No funding was received for the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ADG: Preparation and writing of the manuscript draft. NK: Formal manuscript drafting. PK: Manuscript finalization and correction. HS: Guidance and manuscript supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A.D., Kirti, N., Katiyar, P. et al. A critical review on three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels: synthesis, physico-chemical characterizations and applications as adsorbents for heavy metals removal from water. Cellulose 30, 3397–3427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05129-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05129-4