Abstract
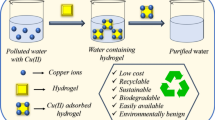
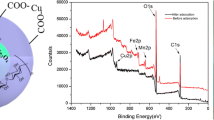
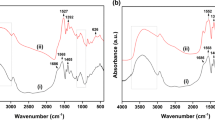
Removal of copper ions (Cu(II)) efficiently from water is crucial for water environment security. We use sustainable, low-cost, renewable cellulose derivatives (carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC-Na)) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as the matrix, and cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) as the functional addition. The CNC/CMC-Na/PVA hydrogel was prepared by the physical cross-linking method. Static adsorption experiments proved that CNC/CMC-Na/PVA hydrogel has a greater adsorption potential (108 mg/g) towards Cu(II). At the same time, the adsorption of Cu(II) on CNC/CMC-Na/PVA hydrogels is spontaneous and endothermic, and obeys the pseudo-second-order model with intra-particle diffusion. Furthermore, the primary adsorption mechanisms had been electrostatic attraction and surface complexation. Importantly, CNC/CMC-Na/PVA hydrogel has efficient absorbability and preferable reusability in actual water samples. Furthermore, the copper nanoparticles (Cu NPs) adsorbed on the surface of CNC/CMC-Na/PVA hydrogels were reduced with NaBH4 in situ to realize the secondary utilization in CNC/CMC-Na/PVA hydrogels supported by Cu NPs. It is found that the material can be used as a catalyst to efficiently catalyze the conversion of HMF to BHMF (99%). Consequently, we provide insights into the hydrogel preparation that would possibly be promising novel adsorbents for the elimination of heavy-ion from sustainable water purification.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Zhang B, Wang J, Xu J, Manzoor K, Ahmad S, Ikram S (2019) New method for hydrogel synthesis from diphenylcarbazide chitosan for selective copper removal. Int J Biol Macromol 136:189–198
Baiya C, Nannuan L, Tassanapukdee Y, Chailapakul O, Songsrirote K (2019) The synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel from sugarcane bagasse using microwave-assisted irradiation for selective adsorption of Copper(II) ions. Environ Prog Sustain 38:S157–S165
Chen S, Wojcieszak R, Dumeignil F, Marceau E, Royer S (2018) How catalysts and experimental conditions determine the selective hydroconversion of furfural and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. Chem Rev 118:11023–11117
Chen Y, Mu T (2019) Application of deep eutectic solvents in biomass pretreatment and conversion. Green Energy Environ 4:95–115
Dadvand Koohi A, Nasimi F (2017) Influence of Salt and surfactant on copper removal by Xanthan Gum-g-Itaconic acid/bentonite hydrogel composite from water using fractional factorial design. Chem Eng Commun 204:791–802
Dai L, Zhang L, Wang B, Yang B, Khan I, Khan A, Ni Y (2017) Multifunctional self-assembling hydrogel from guar gum. Chem Eng J 330:1044–1051
Ding J, Li Q, Xu X, Zhang X, Su Y, Yue Q, Gao B (2018) A wheat straw cellulose-based hydrogel for Cu (II) removal and preparation copper nanocomposite for reductive degradation of chloramphenicol. Carbohyd Polym 190:12–22
Dong C, Lu J, Qiu B, Shen B, Xing M, Zhang J (2018) Developing stretchable and graphene-oxide-based hydrogel for the removal of organic pollutants and metal ions. Appl Catal B-Environ 222:146–156
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609
French AD (2020) Increment in evolution of cellulose crystallinity analysis. Cellulose 27:5445–5448
Gao Z, Yu Z, Huang C, Duan L, Gao GH (2017) Carboxymethyl cellulose reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) with trimethylol melamine as a chemical crosslinker. J Appl Polym Sci 134:44590
Ge G, Zhang Y, Shao J, Wang W, Si W, Huang W, Dong X (2018) Stretchable, transparent, and self-patterned hydrogel-based pressure sensor for human motions detection. Adv Fun Mater 28:1802576
Hassan S, Yasin T, Imran Z, Batool SS (2018) Investigation of copper (Cu2+) adsorption performances and gamma radiation dose effect of polymeric hydrogel. AIP Adv 8:025301
He G, Wang C, Cao J, Fan L, Zhao S, Chai Y (2018) Carboxymethyl chitosan-kaolinite composite hydrogel for efficient copper ions trapping. J Envir Chem Eng 7:102953
Hou X, Li Y, Pan Y, Jin Y, Xiao H (2018) Controlled release of agrochemicals and heavy metal ion capture dual-functional redox-responsive hydrogel for soil remediation. Chem Commun 54:13714–13717
Lee I, Park CW, Yoon SS, Yang H (2019) Facile synthesis of copper ferrocyanide-embedded magnetic hydrogel beads for the enhanced removal of cesium from water. Chemosphere 224:776–785
Liu J, Su D, Yao J, Huang Y, Shao Z, Chen X (2017) Soy protein-based polyethylenimine hydrogel and its high selectivity for copper ion removal in wastewater treatment. J Mater Chem A 5:4163–4171
Liu C, Omer AM, Ouyang X (2018) Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye using carboxymethyl cellulose/k-carrageenan/activated montmorillonite composite beads: isotherm and kinetic studies. Int J Biol Macromol 106:823–833
Lv Y, Zhang R, Zeng S, Liu K, Huang S, Liu Y, Xu P, Lin C, Cheng Y, Liu M (2018) Removal of p-arsanilic acid by an amino-functionalized indium-based metal–organic framework: adsorption behavior and synergetic mechanism. Chem Eng J 339:359–368
Ma J, Lee J, Han SS, Oh KH, Nam KT, Sun J (2016) Highly stretchable and notch-insensitive hydrogel based on polyacrylamide and milk protein. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8:29220–29226
Ma J, Xiong Y, Dai X, Yu F (2020) Coadsorption behavior and mechanism of ciprofloxacin and Cu(II) on graphene hydrogel wetted surface. Chem Eng J 380:122387
Mao J, Ge M, Huang J, Lai Y, Lin C, Zhang K, Meng K, Tang Y (2017) Constructing multifunctional MOF@rGO hydro-/aerogels by the self-assembly process for customized water remediation. J Mater Chem A 5:11873–11881
Ohyama J, Kanao R, Ohira Y, Satsuma A (2016) The effect of heterogeneous acid–base catalysis on conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into a cyclopentanone derivative. Green Chem 18:676–680
Oun AA, Rhim J (2015) Preparation and characterization of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/cotton linter cellulose nanofibril composite films. Carbohyd Polym 127:101–109
Perumal S, Atchudan R, Yoon DH, Joo J, Cheong IW (2019) Spherical chitosan/gelatin hydrogel particles for removal of multiple heavy metal ions from wastewater. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:9900–9907
Sahraei R, Ghaemy M (2017) Synthesis of modified gum tragacanth/graphene oxide composite hydrogel for heavy metal ions removal and preparation of silver nanocomposite for antibacterial activity. Carbohyd Polym 157:823–833
Serag E, Nemr AE, El-Maghraby A (2017) Synthesis of highly effective novel graphene oxide-polyethylene glycol-polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite hydrogel for copper removal. J Water Environ Nanotech 2:223–234
Sun X, Hao Y, Cao Y, Zeng Q (2019) Superadsorbent hydrogel based on lignin and montmorillonite for Cu(II) ions removal from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 127:511–519
Wang L, Wang M (2016) Removal of heavy metal ions by poly(vinyl alcohol) and carboxymethyl cellulose composite hydrogels prepared by a freeze-thaw method. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:2830–2837
Wang X, Liang Y, An W, Hu J, Zhu Y, Cui W (2017) Removal of chromium (VI) by a self-regenerating and metal free g-C3N4/graphene hydrogel system via the synergy of adsorption and photo-catalysis under visible light. Appl Catal B-Environ 219:53–62
Wang H, Li J, Ding N, Zeng X, Tang X, Sun Y, Lei T, Lin L (2020a) Eco-friendly polymer nanocomposite hydrogel enhanced by cellulose nanocrystal and graphitic-like carbon nitride nanosheet. Chem Eng J 386:124021
Wang J, Wang Y, Ma Z, Yan L (2020b) Dissolution of highly molecular weight cellulose isolated from wheat straw in deep eutectic solvent of Choline/L-Lysine hydrochloride. Green Energy Environ 5:232–239
Yadav M, Rhee KY, Jung IH, Park SJ (2013) Eco-friendly synthesis, characterization and properties of a sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposite film. Cellulose 20:687–698
Zhang H, Omer AM, Hu Z, Yang L, Ji C, Ouyang X (2019a) Fabrication of magnetic bentonite/carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for Cu(II) adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 135:490–500
Zhang K, Li Z, Deng N, Ju J, Li Y, Cheng B, Kang W, Yan J (2019b) Tree-like cellulose nanofiber membranes modified by citric acid for heavy metal ion (Cu2+) removal. Cellulose 26:945–958
Zhou C, Wu Q, Lei T, Negulescu II (2014) Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium studies for methylene blue dye by partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite hydrogels. Chem Eng J 251:7–24
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21676223, 21978248), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (No.2019J06005) and the special fund for Fujian Ocean High-Tech Industry Development (No. FJHJF-L-2018-1), China.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Fang, S., Zuo, M. et al. Removal of copper ions by cellulose nanocrystal-based hydrogel and reduced adsorbents for its catalytic properties. Cellulose 29, 4525–4537 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04547-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04547-0