Abstract
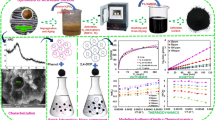
Adsorption is the most efficient technique for the removal of toxic organic dyes and metal ions from wastewater and it demands efficient, low-cost, environment friendly and collectable adsorbents. In this study, a one-pot strategy has been developed for the crosslinking of chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose with citric acid to form the cross-linked hydrogel. The synthesized biosorbent hydrogel was characterized by FTIR, XRD and SEM that have confirmed the successful crosslinking. The batch adsorption experiments were performed to examine the capacity of hydrogel for the adsorption of Cu(II). The optimization of the adsorption process was carried out on the basis of various factors including; metal ion concentration, time, temperature, pH, agitation speed and adsorbent dose. Different isothermal and kinetic models were applied to interpret the data. The thermodynamic studies revealed that Langmuir model was the best fit with > 90% Cu(II) removal at pH 6. The kinetic studies confirmed the suitability of pseudo-second-order kinetics with correlation coefficient (R2) value 1. Several adsorption–desorption cycles were performed to check the recovery and reusability of hydrogel without the loss of maximum adsorption capacity.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
These will be provided on request.
References
Benhalima, T., et al.: Fe3O4 imbuing carboxymethyl cellulose/dextran sulfate nanocomposite hydrogel beads: an effective adsorbent for methylene blue dye pollutant. J. Macromol. Sci. A 60, 442 (2023)
Gunasundari, E.: Adsorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic analysis of Cu (II) ions onto the dried algal biomass (Spirulina platensis). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 56, 129–144 (2017)
Benhalima, T., Ferfera-Harrar, H.: Eco-friendly porous carboxymethyl cellulose/dextran sulfate composite beads as reusable and efficient adsorbents of cationic dye methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 132, 126–141 (2019)
Benhalima, T., Ferfera-Harrar, H., Lerari, D.: Optimization of carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels beads generated by an anionic surfactant micelle templating for cationic dye uptake: swelling, sorption and reusability studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 105, 1025–1042 (2017)
Saravanan, A., Senthil Kumar, P., Mugilan, R.: Ultrasonic-assisted activated biomass (fishtail palm Caryota urens seeds) for the sequestration of copper ions from wastewater. Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 3117–3146 (2016)
Pearlin Kiruba, U., et al.: Study of adsorption kinetic, mechanism, isotherm, thermodynamic, and design models for Cu (II) ions on sulfuric acid-modified Eucalyptus seeds: temperature effect. Desalin. Water Treat. 56(11), 2948–2965 (2015)
Prabu, D., et al.: Adsorption of copper ions onto nano-scale zero-valent iron impregnated cashew nut shell. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(14), 6487–6502 (2016)
Neeraj, G., et al.: Performance study on sequestration of copper ions from contaminated water using newly synthesized high effective chitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 214, 335–346 (2016)
Sandstead, H.H.: Requirements and toxicity of essential trace elements, illustrated by zinc and copper. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 61(3), 621S-624S (1995)
Prabu, D., et al.: Sorption of Cu (II) ions by nano-scale zero valent iron supported on rubber seed shell. IET Nanobiotechnol. 11(6), 714–724 (2017)
Senthil Kumar, P., et al.: Study of adsorption of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by surface-modified Eucalyptus globulus seeds in a fixed-bed column: experimental optimization and mathematical modeling. Res. Chem. Intermed. 41, 8681–8698 (2015)
Liu, Y., et al.: Electrochemical wastewater treatment with carbon nanotube filters coupled with in situ generated H 2 O 2. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 1(6), 769–778 (2015)
Zhang, H., et al.: Sorption behavior of cesium from aqueous solution on magnetic hexacyanoferrate materials. Nucl. Eng. Des. 275, 322–328 (2014)
Alyüz, B., Veli, S.: Kinetics and equilibrium studies for the removal of nickel and zinc from aqueous solutions by ion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 167(1–3), 482–488 (2009)
Ostroski, I.C., et al.: A comparative study for the ion exchange of Fe (III) and Zn (II) on zeolite NaY. J. Hazard. Mater. 161(2–3), 1404–1412 (2009)
Cabello, S.P., et al.: New bio-polymeric membranes composed of alginate-carrageenan to be applied as polymer electrolyte membranes for DMFC. J. Power. Sources 265, 345–355 (2014)
Zeng, M., et al.: Highly biocompatible, underwater superhydrophilic and multifunctional biopolymer membrane for efficient oil–water separation and aqueous pollutant removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(3), 3879–3887 (2018)
Kaksonen, A.H., Riekkola-Vanhanen, M.-L., Puhakka, J.: Optimization of metal sulphide precipitation in fluidized-bed treatment of acidic wastewater. Water Res. 37(2), 255–266 (2003)
Maturi, K., Reddy, K.R.: Simultaneous removal of organic compounds and heavy metals from soils by electrokinetic remediation with a modified cyclodextrin. Chemosphere 63(6), 1022–1031 (2006)
Ni, B.-J., et al.: Competitive adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution onto biochar derived from anaerobically digested sludge. Chemosphere 219, 351–357 (2019)
Park, J.-H., et al.: Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 142, 77–83 (2016)
Liang, W., et al.: Decontamination of Hg (II) from aqueous solution using polyamine-co-thiourea inarched chitosan gel derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 113, 106–115 (2018)
Li, R., et al.: High-efficiency removal of Pb (II) and humate by a CeO2–MoS2 hybrid magnetic biochar. Biores. Technol. 273, 335–340 (2019)
Saravanan, A., Kumar, P.S., Yaswanthraj, M.: Modeling and analysis of a packed-bed column for the effective removal of zinc from aqueous solution using dual surface-modified biomass. Part. Sci. Technol. 36(8), 934–944 (2018)
Kumar, P.S., et al.: Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 261(1–2), 52–60 (2010)
Akhlaq, M., et al.: A comparative study of different methods for cellulose extraction from lignocellulosic wastes and conversion into carboxymethyl cellulose. ChemistrySelect 7(29), e202201533 (2022)
Ahmad, M., et al.: Thiocarbohydrazide cross-linked oxidized chitosan and poly (vinyl alcohol): a green framework as efficient Cu (II), Pb (II), and Hg (II) adsorbent. J. Chem. Eng. Data 62(7), 2044–2055 (2017)
Li, N., Bai, R., Liu, C.: Enhanced and selective adsorption of mercury ions on chitosan beads grafted with polyacrylamide via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Langmuir 21(25), 11780–11787 (2005)
Yan, H., et al.: Enhanced and selective adsorption of copper (II) ions on surface carboxymethylated chitosan hydrogel beads. Chem. Eng. J. 174(2–3), 586–594 (2011)
Wu, S.-P., et al.: Fabrication of carboxymethyl chitosan–hemicellulose resin for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Chin. Chem. Lett. 28(3), 625–632 (2017)
Manzoor, K., et al.: Synthesis, characterization, kinetics, and thermodynamics of EDTA-modified chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose as Cu (II) ion adsorbent. ACS Omega 4(17), 17425–17437 (2019)
Allen, C.L., Chhatwal, A.R., Williams, J.M.: Direct amide formation from unactivated carboxylic acids and amines. Chem. Commun. 48(5), 666–668 (2012)
Akhlaq, M., et al.: Carboxymethyl cellulose-based materials as an alternative source for sustainable electrochemical devices: a review. RSC Adv. 13(9), 5723–5743 (2023)
Tangpasuthadol, V., Pongchaisirikul, N., Hoven, V.P.: Surface modification of chitosan films: effects of hydrophobicity on protein adsorption. Carbohy. Res. 338(9), 937–942 (2003)
Akhlaq, M., Uroos, M.: Evaluating the impact of cellulose extraction via traditional and ionosolv pretreatments from domestic matchstick waste on the properties of carboxymethyl cellulose. ACS Omega 8(9), 8722–8731 (2023)
Gorochovceva, N., Makuška, R.: Synthesis and study of water-soluble chitosan-O-poly (ethylene glycol) graft copolymers. Eur. Polymer J. 40(4), 685–691 (2004)
Fujita, S., Sakairi, N.: Water soluble EDTA-linked chitosan as a zwitterionic flocculant for pH sensitive removal of Cu (II) ion. RSC Adv. 6(13), 10385–10392 (2016)
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40(9), 1361–1403 (1918)
Christoforidis, A., et al.: Study of Cu (II) removal by Cystoseira crinitophylla biomass in batch and continuous flow biosorption. Chem. Eng. J. 277, 334–340 (2015)
Gupta, S.S., Bhattacharyya, K.G.: Immobilization of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manage. 87(1), 46–58 (2008)
Yang, S., et al.: Adsorption of Ni (II) on oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes: effect of contact time, pH, foreign ions and PAA. J. Hazard. Mater. 166(1), 109–116 (2009)
Zhou, S., et al.: Competitive adsorption of Hg2+, Pb2+ and Co2+ ions on polyacrylamide/attapulgite. Desalination 270(1–3), 269–274 (2011)
Yagub, M.T., et al.: Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv. Coll. Interface. Sci. 209, 172–184 (2014)
Yao, Z.-Y., Qi, J.-H., Wang, L.-H.: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the biosorption of Cu (II) onto chestnut shell. J. Hazard. Mater. 174(1–3), 137–143 (2010)
Al-Othman, Z.A., Ali, R., Naushad, M.: Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous medium by activated carbon prepared from peanut shell: adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 184, 238–247 (2012)
McKay, G.: Adsorption of dyestuffs from aqueous solutions with activated carbon I: equilibrium and batch contact-time studies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 32(7–12), 759–772 (1982)
Rahman, N., Haseen, U.: Equilibrium modeling, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on adsorption of Pb (II) by a hybrid inorganic–organic material: polyacrylamide zirconium (IV) iodate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(19), 8198–8207 (2014)
Horsfall Jnr, M., Spiff, A.I.: Effects of temperature on the sorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution by Caladium bicolor (Wild Cocoyam) biomass. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 8(2), 43–50 (2005)
Juang, R.-S., Shao, H.-J.: Effect of pH on competitive adsorption of Cu (II), Ni (II), and Zn (II) from water onto chitosan beads. Adsorption 8, 71–78 (2002)
He, J., Lu, Y., Luo, G.: Ca (II) imprinted chitosan microspheres: an effective and green adsorbent for the removal of Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 244, 202–208 (2014)
Saha, D., et al.: Noncompetitive and competitive adsorption of heavy metals in sulfur-functionalized ordered mesoporous carbon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(49), 34132–34142 (2016)
Tan, I., Ahmad, A., Hameed, B.: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol on oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 164(2–3), 473–482 (2009)
Funding
Higher Education Commission of Pakistan is acknowledged for providing funding through TDF03-294 and HEC/NRPU-8639. University of the Punjab is acknowledged for its support towards these projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA did the experimental work and writing, SN helped in kinetic, isothermal and thermodynamic studies and data validation. MU supervised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akhlaq, M., Naz, S. & Uroos, M. Facile fabrication of high capacity citric acid cross-linked chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel for fast kinetics removal of Cu(II). Adsorption 30, 363–375 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00446-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00446-x