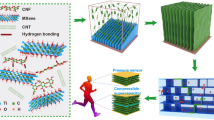
Abstract
The application of Aramid/mica composite paper in high-voltage electric insulation is hampered by its limited breakdown strength and mechanical robustness. In this work, Aramid fiber/Mica-NFC composite papers with varied amount of nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) were fabricated by vacuum-assisted self-assembly process, wherein NFC was used as carrier/adhesion polymer. The Aramid fiber/Mica-NFC composite papers exhibited high mechanical strength (~ 29.04 MPa), superior dielectric properties (~ 14.87 kV/mm) and good thermal stability (~ 300 °C). Importantly, NFC acts as interfacial layer since the physical properties of NaOH-Urea treated Aramid/Mica-NFC composite significantly decreased. Based on visualization of NFC by fluorescence tracking, the addition of NFC favors the formation of biomimetic multilayer structure. Furthermore, the co-continuous double-network-like multilayer structured composite achieved an integrated strong and tough character. Therefore, our work shed light on the importance of constructing rational-designed microstructures for the preparation of high-performance composite papers.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres WH (2016) Mica paper insulations for conductors and cables. In: Electrical/electronics insulation conference(Eic), pp 225–230
Bailey SW (1984) Classification and structures of the micas. Rev Miner Geochem 13(1):1–12
Billings MJ, Warren L, Wilkings R (1971) Thermal erosion of electrical insulating materials. IEEE Trans Electr Ins 6(2):82–90
Cai J, Zhang L, Liu S, Liu Y, Xu X, Chen X, Chu B, Guo X, Xu J, Cheng H (2008) Dynamic self-assembly induced rapid dissolution of cellulose at low temperatures. Macromolecules 41:9345–9351
Chen CT, Martinmartinez FJ, Ling S, Qin Z, Buehler MJ (2017) Nacre-inspired design of graphene oxide-polydopamine nanocomposites for enhanced mechanical properties and multi-functionalities. Nano Futures 1:011003
Cheng Q, Huang C, Tomsia AP (2017) Freeze casting for assembling bioinspired structural materials. Adv Mater 29:1703155–1703165
Cheng Q, Wu M, Li M, Jiang L, Tang Z (2013) Ultratough artificial nacre based on conjugated cross-linked graphene oxide. Angew Chem 52:3750–3755
Cui W, Li M, Liu J, Wang B, Zhang C, Jiang L, Cheng Q (2014) A strong integrated strength and toughness artificial nacre based on dopamine cross-linked graphene oxide. ACS Nano 8:9511–9517
Ding Q, Zeng J, Wang B, Gao W, Chen K, Yuan Z, Xu J (2017) Influence of binding mechanism on labeling efficiency and luminous properties of fluorescent cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr Polym 175:105
Ding Q, Zeng J, Wang B, Gao W, Chen K, Yuan Z, Xu J, Tang D (2018) Effect of retention rate of fluorescent cellulose nanofibrils on paper properties and structure. Carbohydr Polym 186:73–81
Doblhofer E, Schmid J, Riess M, Daab M, Suntinger M, Habel C, Bargel H, Hugenschmidt C, Rosenfeldt S, Breu J, Scheibel T (2016) Structural insights into water-based spider silk protein-nanoclay composites with excellent gas and water vapor barrier properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:25535–25543
Haktshorn L (1953) Electrical insulating materials. Nature 172:8–11
Ho TTT, Zimmermann T, Ohr S, Caseri WR (2012) Composites of cationic nanofibrillated cellulose and layered silicates: water vapor barrier and mechanical properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:4832–4840
Huang J, Zhou Y, Dong L, Zhou Z, Liu R (2017) Enhancement of mechanical and electrical performances of insulating presspaper by introduction of nanocellulose. Compos Sci Technol 13:40–48
Imai T, Sawa F, Nakano T, Ozaki T (2006) Effects of nano- and micro-filler mixture on electrical insulation properties of epoxy based composites. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Ins 13:319–326
Iwamoto S, Nakagaito AN, Yano H (2007) Nano-fibrillation of pulp fibers for the processing of transparent nanocomposites. Appl Phys A-Mater 89:461–466
Jia F, Yang L, Wang Q, Song S (2017) Correlation of natural muscovite exfoliation with interlayer and solvation forces. RSC Adv 7:1082–1088
Khalil HPSA, Davoudpour Y, Islam MN, Mustapha A, Sudesh K, Dungani R, Jawaid M (2014) Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: a review. Carbohydr Polym 99:649–665
Koreeda T, Matos J (2011) Thermal characterization of mica–epoxy composite used as insulation material for high voltage machines. J Therm Anal Calorim 106(2):619–623
Li S, Yu S, Feng Y (2016) Progress in and prospects for electrical insulating materials. High Volt 1:122–129
Li Y, Zhu H, Shen F, Wan J, Lacey S, Fang Z, Dai H, Hu L (2015) Nanocellulose as green dispersant for two-dimensional energy materials. Nano Energy 13:346–354
Liu Y, Sasamoto R, Matsumoto T, Izawa Y, Nishijima K (2016) Influence of barrier thickness on discharge behavior in air gap with GFRP insulator under impulse voltage stress. In: Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, pp 971–974
Lu Z, Hu W, Xie F, Hao Y (2017a) Highly improved mechanical strength of aramid paper composite via a bridge of cellulose nanofiber. Cellulose 24:2827–2835
Lu Z, Si L, Dang W, Zhao Y (2018) Transparent and mechanically robust poly (paraphenyleneterephthamide) PPTA nanopaper toward electrical insulation based on nanoscale fibrillated aramid-fibers. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 115:321–330
Lu Z, Su Z, Song S, Zhao Y, Ma S, Zhang M (2017b) Toward high-performance fibrillated cellulose-based air filter via constructing spider-web-like structure with the aid of TBA during freeze-drying process. Cellulose 25:619–629
Maciej O, John O, Stefan J, Helmut M, Nicholas K, Krzysztof KA, Giersig M (2004) Layer-by-layer assembled composites from multiwall carbon nanotubes with different morphologies. Nano Lett 4:1889–1895
Ming S, Gang C, Wu Z, Su L, He J, Kuang Y, Fang Z (2016) Effective dispersion of aqueous clay suspension using carboxylated nanofibrillated cellulose as dispersant. RSC Adv 6:37330–37336
Nascimento ED, Ramos A, Windmoller D, Rodrigo PR, Juanes RT, Greus AR, Borrás VA, Coelho LAF (2016) Breakdown, free-volume and dielectric behavior of the nanodielectric coatings based on epoxy/metal oxides. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:1–15
Pak VM, Safonov GP, Papkov AV, Vorobyov PV (2011) Prospective electric insulation materials for insulation systems of electric machines. Russ Electr Eng 82:194–196
Rotter HW, Weber HN (2016) Single conductor insulation of high voltage machines using mica tapes. In: Electrical/electronics insulation conference(Eic), pp 76–80
Shahrokhi M, Mortazavi B, Berdiyorov GR (2017) New two-dimensional boron nitride allotropes with attractive electronic and optical properties. Solid State Commun 253:51–56
Shao W, He J, Han Q, Feng S, Wang Q, Li C, Cui S, Ding B (2016) A biomimetic multilayer nanofiber fabric fabricated by electrospinning and textile technology from polylactic acid and Tussah silk fibroin as a scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater 67:599–610
Song N, Jiao D, Cui S, Hou X, Ding P, Shi L (2017) Highly anisotropic thermal conductivity of layer-by-layer assembled nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene nanosheets hybrid films for thermal management. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2924–2932
Tang Z, Kotov NA, Magonov S et al (2003) Nanostructured artificial nacre. Nat Mater 2(6):413–418
Vouyovitch L, Alberola ND, Flandin L, Beroual A (2006) Dielectric breakdown of epoxy-based composites: relative influence of physical and chemical aging. IEEE Trans Dielect Electr Ins 13:282–292
Wang J, Cheng Q, Lin L, Jiang L (2014) Synergistic toughening of bioinspired poly(vinyl alcohol)–clay–nanofibrillar cellulose artificial nacre. ACS Nano 8:2739–2745
Wang J, Cheng Q, Tang Z (2012) ChemInform abstract: layered nanocomposites inspired by the structure and mechanical properties of nacre. Chem Soc Rev 41:1111–1129
Wu W, Song R, Xu Z, Jing Y, Dai H, Fang G (2018) Fluorescent cellulose nanocrystals with responsiveness to solvent polarity and ionic strength. Sens Actuators B Chem 275:490–498
Yang B, Zhang M, Lu Z (2015) Effects of potassium titanate whiskers on the mechanical and thermal properties of poly (para-phenylene terephthalamide) paper sheet. Polym Compos 38:1390–1395
Yin F, Tang C, Li X, Wang X (2017) Effect of moisture on mechanical properties and thermal stability of meta-aramid fiber used in insulating paper. Polymers 9:537–550
Zammarano M, Maupin P, Sung L, Gilman J, McCarthy E, Kim Y, Fox D (2011) Revealing the interface in polymer nanocomposites. ACS Nano 5(4):3391–3399
Zhang Z, Chang H, Xue B, Zhang S, Li X, Wong W, Li K, Zhu X (2017) Near-infrared and visible dual emissive transparent nanopaper based on Yb(III)-carbon quantum dots grafted oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose for anti-counterfeiting applications. Cellulose 25(1):377–389
Zhang M, Huang L, Chen J, Li C, Shi G (2014) Ultratough, ultrastrong, and highly conductive graphene films with arbitrary sizes. Adv Mater 26:7588–7592
Zhang Y, Ma X, Gan L, Xia T, Shen J, Huang J (2018) Fabrication of fluorescent cellulose nanocrystal via controllable chemical modification towards selective and quantitative detection of Cu(II) ion. Cellulose 25:5831–5842
Zhao Y, Dang W, Lu Z, Wang L, Si L, Zhang M (2018) A novel mica-based composite via adding hybrid aramid fibers for electrical insulating application: largely improved mechanical properties and moisture-resistance. Polym Int 67:204–211
Zimmermann T, Bordeanu N, Strub E (2010) Properties of nanofibrillated cellulose from different raw materials and its reinforcement potential. Carbohydr Polym 79:1086–1093
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Plan (2017YFB0308300), Shaanxi Province Supporting Plan for Innovative Research (2017-KCT-02), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21704058), State Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Engineering (Project No. 201727) and Key Laboratory Research Project of Shaanxi Education Department (Project No. 18JS011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Dang, W., Si, L. et al. Enhanced mechanical and dielectric properties of Aramid fiber/Mica-nanofibrillated cellulose composite paper with biomimetic multilayered structure. Cellulose 26, 2035–2046 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2170-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2170-z