Abstract
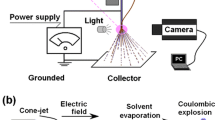
A solution treated by electrospraying often has a relatively low polymer concentration, thereby overlooking that pure solvent can be used as an additional working fluid. In this study, a modified coaxial electrospraying, characterized by the usage of pure solvent as a shell fluid, was developed to generate nano drug delivery systems for providing the desired drug sustained-release profiles. Ethylcellulose (EC) and tamoxifen citrate (TC) were exploited as a polymer matrix and a poorly water-soluble anticancer model, respectively. Comparing with those particles prepared using a traditional single-fluid process, the TC-loaded EC particles from the modified coaxial processes have a rounder shape, a smaller diameter, and a highly compact inner structure, as demonstrated by the scanning electron microscopic images. Given the favored secondary interactions between TC and EC, all the particles are similarly amorphous composites, as verified by their X-ray patterns and attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared spectra. Nevertheless, the rounder nanoparticles from the coaxial processes were able to provide a better drug sustained-release profile than their counterparts in terms of smaller initial burst release, longer release time period, and shorter time tailing-off later stage. Both microformation mechanisms of the medicated particles and drug sustained-release mechanisms are suggested. The protocols developed here facilitate the generation of functional nanomaterials from cellulose and its derivatives owing to breaking the traditional concept of electrospraying.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad Z, Zhang HB, Farook U, Edirisinghe M, Stride E, Colombo P (2008) Generation of multilayered structures for biomedical applications using a novel tri-needle coaxial device and electrohydrodynamic flow. J R Soc Interface 5:1255–1261
Bailey MM, Berkland CJ (2009) Nanoparticle formulations in pulmonary drug delivery. Med Res Rev 29:196–212
Bilati U, Allémann E, Doelker E (2005) Development of a nanoprecipitation method intended for the entrapment of hydrophilic drugs into nanoparticles. Eur J Pharm Sci 24:67–75
Bock N, Dargaville TR, Woodruff MA (2012) Electrospraying of polymers with therapeutic molecules: state of the art. Prog Polym Sci 37:1510–1551
Bohr A, Wan F, Kristensen J, Dyas M, Stride E, Baldursdottír S, Edirisinghe M, Yang M (2015) Pharmaceutical microparticle engineering with electrospraying: the role of mixed solvent systems in particle formation and characteristics. J Mater Sci Mater Med 26:1–13
Cao L, Luo J, Tu K, Wang LQ, Jiang H (2014) Generation of nano-sized core–shell particles using a coaxial tri-capillary electrospray-template removal method. Colloids Surf B 115:212–218
Chakraborty S, Liao IC, Adler A, Leong KW (2009) Electrohydrodynamics: a facile technique to fabricate drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:1043–1054
Cui L, Liu ZP, Yu DG, Zhang SP, Bligh SWA, Zhao N (2014) Electrosprayed core-shell nanopartciles of PVP and shellac for furnishing biphasic controlled release of ferulic acid. Colloid Polym Sci 292:2089–2096
Edgar KJ (2007) Cellulose esters in drug delivery. Cellulose 14:49–64
Eltayeb M, Stride E, Edirisinghe M (2015) Preparation, characterization and release kinetics of ethylcellulose nanoparticles encapsulating ethylvanillin as a model functional component. J Funct Foods 14:726–735
Eltayeb M, Stride E, Edirisinghe M, Harker A (2016) Electrosprayed nanoparticle delivery system for controlled release. Mater Sci Eng C 66:138–146
Enayati M, Ahmad Z, Stride E, Edirisinghe M (2010) One-step electrohydrodynamic production of drug-loaded micro-and nanoparticles. J R Soc Interface 7:667–675
Enayati M, Chang MW, Bragman F, Edirisinghe M, Stride E (2011) Electrohydrodynamic preparation of particles, capsules and bubbles for biomedical engineering applications. Colloids Surf A 382:154–164
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
French AD, Cintrón MS (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal crystallinity index. Cellulose 20:583–588
Gao Y, Zhao D, Chang MW, Ahmad Z, Li JS (2016) Optimising the shell thickness-to-radius ratio for the fabrication of oil-encapsulated polymeric microspheres. Chem Eng J 284:963–971
Han J, Zhou C, French AD, Han G, Wu Q (2013) Characterization of cellulose II nanoparticles regenerated from 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Carbohydr Polym 94:773–781
Hong X, Edirisinghe M, Mahalingam S (2016) Beads, beaded-fibres and fibres: tailoring the morphology of poly (caprolactone) using pressurised gyration. Mater Sci Eng C 69:1373–1382
Huang LY, Yu DG, Branford-White C, Zhu LM (2012) Sustained release of ethyl cellulose micro-particulate drug delivery systems prepared using electrospraying. J Mater Sci 47:1372–1377
Illangakoon UE, Yu DG, Ahmad BS, Chatterton NP, Williams GR (2015) 5-Fluorouracil loaded Eudragit fibers prepared by electrospinning. Int J Pharm 495:895–902
Illangakoon UE, Mahalingam S, Wang K, Cheong YK, Canales E, Ren GG, Cloutman-Green E, Edirisinghe M, Ciric L (2017) Gyrospun antimicrobial nanoparticle loaded fibrous polymeric filters. Mater Sci Eng C 74:315–324
Jin M, Yu DG, Wang X, Geraldes CFGC, Williams GR, Bligh SWA (2016) Electrospun contrast agent-loaded fibers for colon-targeted MRI. Adv Healthc Mater 5:977–985
Khalf A, Madihally SV (2017) Recent advances in multiaxial electrospinning for drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 112:1–17
Kim W, Kim SS (2011) Synthesis of biodegradable triple-layered capsules using a triaxial electrospray method. Polymer 52:3325–3336
Labbaf S, Ghanbar H, Stride E, Edirisinghe M (2014) Preparation of multilayered polymeric structures using a novel four-needle coaxial electrohydrodynamic device. Macromol Rapid Commun 35:618–623
Leuner C, Dressman J (2000) Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:47–60
Li C, Yu DG, Williams GR, Wang ZH (2014a) Fast-dissolving core-shell composite microparticles of quercetin fabricated using a coaxial electrospray process. PLoS ONE 9:e92106
Li C, Wang ZH, Yu DG, Williams GR (2014b) Tunable biphasic drug release from ethyl cellulose nanofibers fabricated using a modified coaxial electrospinning process. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:258
Liu L, Xu X (2008) Preparation of bilayer-core osmotic pump tablet by coating the indented core tablet. Int J Pharm 352:225–230
Liu ZP, Cui L, Yu DG, Zhao ZX, Chen L (2014) Electrosprayed core-shell solid dispersions of acyclovir fabricated using an epoxy-coated concentric spray head. Int J Nanomed 9:1967–1977
Loscertales IG, Barrero A, Guerrero I, Cortijo R, Marquez M, Ganan-Calvo AM (2002) Micro/nano encapsulation via electrified coaxial liquid jets. Science 295:1695–1698
Mehta P, Haj-Ahmad R, Rasekh M, Arshad MS, Smith A, van der Merwe SM, Ahmad Z (2017) Pharmaceutical and biomaterial engineering via electrohydrodynamic atomization technologies. Drug Discov Today 22:157–165
Mitragotri S, Lahann J (2009) Physical approaches to biomaterial design. Nat Mater 8:15–23
Moghaddam MK, Mortazavi SM, Khaymian T (2015) Micro/nano-encapsulation of a phase change material by coaxial electrospray method. Iran Polym J 24:759–774
Mohan Yallapu M, Ray Dobberpuhl M, Michele Maher D, Jaggi M, Chand Chauhan S (2012) Design of curcumin loaded cellulose nanoparticles for prostate cancer. Curr Drug Metab 13:120–128
Nguyen DN, Palangetic L, Clasen C, Van den Mooter G (2016a) One-step production of darunavir solid dispersion nanoparticles coated with enteric polymers using electrospraying. J Pharm Pharmacol 68:625–633
Nguyen DN, Clasen C, Van den Mooter G (2016b) Pharmaceutical applications of electrospraying. J Pharm Sci 105:2601–2620
Parhizkar M, Reardon PJ, Knowles JC, Browning RJ, Stride E, Pedley RB, Harker AH, Edirisinghe M (2016) Electrohydrodynamic encapsulation of cisplatin in poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. Nanomedicine 12:1919–1929
Peltonen L, Valo H, Kolakovic R, Laaksonen T, Hirvonen J (2010) Electrospraying, spray drying and related techniques for production and formulation of drug nanoparticles. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:705–719
Peppas NA (1985) Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm Acta Helv 60:110–111
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:615–627
Prasertmanakit S, Praphairaksit N, Chiangthong W, Muangsin N (2009) Ethyl cellulose microcapsules for protecting and controlled release of folic acid. AAPS PharmSciTech 10:1104–1112
Reis CP, Neufeld RJ, Ribeiro AJ, Veiga F (2006) Nanoencapsulation I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 2:8–21
Silmara CL, de Renata A, Andre CA, Fabiana CAC, Pedro PC, Hernane SB, Wilton RL (2016) Characterization of bilayer bacterial cellulose membranes with different fiber densities: a promising system for controlled release of the antibiotic ceftriaxone. Cellulose 23:737–748
Tao L, Hu W, Liu Y, Huang G, Sumer BD, Gao J (2011) Shape-specific polymeric nanomedicine: emerging opportunities and challenges. Exp Bio Med 236:20–29
Van Duong T, Van den Mooter G (2016a) The role of the carrier in the formulation of pharmaceutical solid dispersions. Part II: amorphous carriers. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13:1681–1694
Van Duong T, Van den Mooter G (2016b) The role of the carrier in the formulation of pharmaceutical solid dispersions. Part I: crystalline and semi-crystalline carriers. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 13:1583–1594
Wan F, Maltesen MJ, Andersen SK, Bjerregaard S, Foged C, Rantanen J, Yang M (2014) One-step production of protein-loaded PLGA microparticles via spray drying using 3-fluid nozzle. Pharm Res 31:1967–1977
Wang H, Roman M (2011) Formation and properties of chitosan—cellulose2 nanocrystal polyelectrolyte—macroion complexes for drug delivery applications. Biomacromol 12:1585–1593
Wang X, Li X, Stride E, Huang J, Edirisinghe M, Schroeder C, Donald A (2010) Novel preparation and characterization of porous alginate films. Carbohydr Polym 79:989–997
Wen HF, Yang C, Yu DG, Li XY, Zhang DF (2016) Electrospun zein nanoribbons for treatment of lead-contained wastewater. Chem Eng J 290:263–272
Wu YH, Yu DG, Li JJ, Wang Q, Li HP, Li XY (2017) Medicated multiple-component polymeric nanocomposites fabricated using electrospraying. Polym Polym Compos 25:57–62
Xie J, Ng WJ, Lee LY, Wang CH (2008) Encapsulation of protein drugs in biodegradable microparticles by co-axial electrospray. J Colloid Interface Sci 317:469–476
Yan J, White K, Yu DG, Zhao XY (2014) Sustained release multiple-component cellulose acetate nanofibers fabricated using a modified coaxial electrospinning process. J Mater Sci 49:538–547
Yang C, Yu DG, Pan D, Liu XK, Wang X, Bligh SWA, Williams GR (2016) Electrospun pH-sensitive core-shell polymer nanocomposites fabricated using a tri-axial processes. Acta Biomater 35:77–86
Yang GZ, Li JJ, Yu DG, He MF, Yang JH, Williams GR (2017) Nanosized sustained-release drug depots fabricated using modified tri-axial electrospinning. Acta Biomater 53:233–241
Yu DG, Yu JH, Chen L, Williams GR, Wang X (2012) Modified coaxial electrospinning for the preparation of high-quality ketoprofen-loaded cellulose acetate nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 90:1016–1023
Yu DG, Li XY, Wang X, Chian W, Liao YZ, Li Y (2013) Zero-order drug release cellulose acetate nanofibers prepared using coaxial electrospinning. Cellulose 20:379–389
Yu DG, Xu Y, Li Z, Du LP, Zhao BG, Wang X (2014) Coaxial electrospinning with mixed solvents: from flat to round Eudragit L100 nanofibers for better colon-targeted sustained drug release profiles. J Nanomater 2014. Article ID967295
Yu DG, Li XY, Wang X, Yang JH, Bligh SWA, Williams GR (2015) Nanofibers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning as zero order drug delivery systems. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces 7:18891–18897
Yu DG, Li JJ, Zhang M, Williams GR (2017) High-quality Janus nanofibers prepared using three-fluid electrospinning. Chem Commun 53:4542–4545
Yue H, Wei W, Yue Z, Lv P, Wang L, Ma G, Su Z (2010) Particle size affects the cellular response in macrophages. Eur J Pharm Sci 41:650–657
Yue Y, Han J, Han G, Zhang Q, French AD, Wu Q (2015) Characterization of cellulose I/II hybrid fibers isolated from energycane bagasse during the delignification process: morphology, crystallinity and percentage estimation. Carbohydr Polym 133:438–447
Zamani M, Prabhakaran MP, Ramakrishna S (2013) Advances in drug delivery via electrospun and electrosprayed nanomaterials. Int J Nanomed 8:2997–3017
Zhang F, Wu W, Zhang X, Meng X, Tong G, Deng Y (2016) Temperature-sensitive poly-NIPAm modified cellulose nanofibril cryogel microspheres for controlled drug release. Cellulose 23:415–425
Acknowledgments
The financial supports from the following projects are appreciated: the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51373101 and 51403128) and the College Student Innovation Project of USST (Nos. SH2017189-190-191).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XY., Zheng, ZB., Yu, DG. et al. Electrosprayed sperical ethylcellulose nanoparticles for an improved sustained-release profile of anticancer drug. Cellulose 24, 5551–5564 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1498-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1498-0