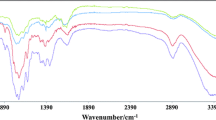
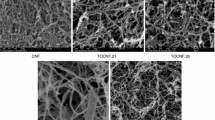
Abstract
We report on the use of fique natural fibers as solid matrices for the deposition of zinc oxide (ZnO). Fique fibers, native to Colombia, are composed of cellulose (63–70 %) and have a heterogeneous surface morphology with high oxygen density that facilitates metal oxide nanoparticle growth and stabilization. Fique fiber–ZnO biocomposites were synthesized by a co-precipitation method using ZnSO4 as precursor, NaOH for hydroxide formation and thermal/ultrasound energy to promote Zn(OH)2/Zn(OH) 2−4 decomposition and ZnO formation. The biocomposite was characterized using X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy with attenuated total reflectance, field emission scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles has been widely reported on inorganic substrates and soft natural fibers; however studies on how experimental parameters affect ZnO features on heterogeneous phase reactions are scarce, as well as the use of hard complex cellulosic fibers as solid supports for its growth. We observed that [OH−]/[Zn2+] ratios, heating or sonication time wield a strong influence on the amount, shape, size and distribution of ZnO crystals on the fique fibers; hence confirming the potential of hard natural fibers as surface active materials for novel biocomposites synthesis. We believe these materials, where the hard fiber robustness and the transition metal oxide catalytic properties are synergistically combined, could be promising functional alternatives that will favor a widespread nanoparticle usage for environmental applications such as wastewater treatment processes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA et al (2011) Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: a novel approach. Carbohydr Polym 86:1468–1475
Al-Gaashani R, Radiman S, Daud AR et al (2013) XPS and optical studies of different morphologies of ZnO nanostructures prepared by microwave methods. Ceram Int 39:2283–2292. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.08.075
Asar N, Erol A, Okur S, Arikan MC (2012) Morphology-dependent humidity adsorption kinetics of ZnO nanostructures. Sens Actuators A Phys 187:37–42. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2012.08.019
Azizian-Kalandaragh Y, Khodayari A, Behboudnia M (2009) Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of ZnO semiconductor nanostructures. Mater Sci Semicond Process 12:142–145. doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2009.09.006
Barua S, Das G, Aidew L et al (2013) Copper–copper oxide coated nanofibrillar cellulose: a promising biomaterial. RSC Adv 3:14997–15004. doi:10.1039/c3ra42209g
Becheri A, Dürr M, Lo Nostro P, Baglioni P (2007) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles: application to textiles as UV-absorbers. J Nanopart Res 10:679–689. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9318-3
Cao B, Cai W (2008) From ZnO nanorods to nanoplates: chemical bath deposition growth and surface-related emissions. J Phys Chem C 112:680–685. doi:10.1021/jp076870l
Castellanos LJ, Blanco-Tirado C, Hinestroza JP, Combariza MY (2012) In situ synthesis of gold nanoparticles using fique natural fibers as template. Cellulose 19:1933–1943. doi:10.1007/s10570-012-9763-8
Chacón-Patiño ML, Blanco-Tirado C, Hinestroza JP, Combariza MY (2013) Biocomposite of nanostructured MnO2 and fique fibers for efficient dye degradation. Green Chem 15:2920. doi:10.1039/c3gc40911b
Chen W, Yu H, Liu Y et al (2011) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from four plant cellulose fibers using a chemical-ultrasonic process. Cellulose 18:433–442. doi:10.1007/s10570-011-9497-z
Chen S, Zhou B, Hu W et al (2013) Polyol mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles templated by bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 92:1953–1959. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.059
Cheng JP, Zhang XB, Luo ZQ (2008) Oriented growth of ZnO nanostructures on Si and Al substrates. Surf Coat Technol 202:4681–4686. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.03.032
Dong BH, Hinestroza JP (2009) Metal nanoparticles on natural cellulose fibers: electrostatic assembly and in situ synthesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:797–803. doi:10.1021/am800225j
Dutta K, Das S, Pramanik A (2012) Concomitant synthesis of highly crystalline Zn-Al layered double hydroxide and ZnO: phase interconversion and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 366:28–36. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.09.081
Faruk O, Bledzki AK, Fink H-P, Sain M (2012) Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog Polym Sci 37:1552–1596. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.04.003
French AD (2013) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Galland S, Andersson RL, Salajková M et al (2013) Cellulose nanofibers decorated with magnetic nanoparticles—synthesis, structure and use in magnetized high toughness membranes for a prototype loudspeaker. J Mater Chem C 1:7963. doi:10.1039/c3tc31748j
Gañán P, Mondragon I (2002) Surface modification of fique fibers. Effect on their physico-mechanical properties. Polym Compos 23:383–394. doi:10.1002/pc.10440
Gaya UI, Abdullah AH, Hussein MZ, Zainal Z (2010) Photocatalytic removal of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol from water exploiting commercial ZnO powder. Desalination 263:176–182. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.055
Heinze T (2004) Chemical functionalization of cellulose. In: Dumitriu S (ed) Polysaccharides: structural diversity and functional versatility, 2nd edn. CRC Press, United States of America, pp 551–590. doi:10.1201/978120030822
Hu QR, Wang SL, Jiang P et al (2010) Synthesis of ZnO nanostructures in organic solvents and their photoluminescence properties. J Alloys Compd 496:494–499. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.02.086
Iskalieva A, Yimmou BM, Gogate PR et al (2012) Cavitation assisted delignification of wheat straw: a review. Ultrason Sonochem 19:984–993. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.02.007
Jaber B, Laânab L (2014) One step synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles in free organic medium: structural and optical characterizations. Mater Sci Semicond Process 27:446–451. doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2014.07.025
John M, Thomas S (2008) Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 71:343–364. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.05.040
Katepetch C, Rujiravanit R, Tamura H (2013) Formation of nanocrystalline ZnO particles into bacterial cellulose pellicle by ultrasonic-assisted in situ synthesis. Cellulose 20:1275–1292. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-9892-8
Kawano T, Imai H (2006) Fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles with various aspect ratios through acidic and basic routes. Cryst Growth Des 6:1054–1056. doi:10.1021/cg050338a
Khorsand Zak A, Majid WHA, Wang HZ et al (2013) Sonochemical synthesis of hierarchical ZnO nanostructures. Ultrason Sonochem 20:395–400. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.07.001
Kuriakose S, Bhardwaj N, Singh J et al (2013) Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of flower-like ZnO nanostructures prepared by a facile wet chemical method. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 4:763–770. doi:10.3762/bjnano.4.87
Li X, Tabil LG, Panigrahi S (2007) Chemical Treatments of Natural Fiber for Use in Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: a Review. J Polym Environ 15:25–33. doi:10.1007/s10924-006-0042-3
Li H, Ni Y, Hong J (2009) Ultrasound-assisted preparation, characterization and properties of flower-like ZnO microstructures. Scr Mater 60:524–527. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.11.047
Lin S-T, Thirumavalavan M, Jiang T-Y, Lee J-F (2014) Synthesis of ZnO/Zn nano photocatalyst using modified polysaccharides for photodegradation of dyes. Carbohydr Polym 105:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.017
Link S, El-Sayed MA (1999) Size and temperature dependence of the plasmon absorption of colloidal gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 103:4212–4217. doi:10.1021/jp984796o
Liu B, Zeng HC (2004) Room temperature solution synthesis of monodispersed single-crystalline ZnO nanorods and derived hierarchical nanostructures. Langmuir 20:4196–4204. doi:10.1021/la035264o
Luzi F, Fortunati E, Puglia D et al (2014) Optimized extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from pristine and carded hemp fibres. Ind Crops Prod 56:175–186. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.03.006
Morán JI, Alvarez VA, Cyras VP, Vázquez A (2007) Extraction of cellulose and preparation of nanocellulose from sisal fibers. Cellulose 15:149–159. doi:10.1007/s10570-007-9145-9
Ovalle SA, Blanco-Tirado C, Combariza MY (2014) Síntesis in situ de nanopartículas de plata sobre fibras de fique. Rev Colomb Química 42:30–37
Patil AB, Patil DS, Bhanage BM (2012) ZnO nanoparticle by solar energy and their catalytic application for α-amino phosphonates synthesis. Mater Lett 86:50–53. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2012.07.009
Perelshtein I, Applerot G, Perkas N et al (2009) Antibacterial properties of an in situ generated and simultaneously deposited nanocrystalline ZnO on fabrics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:361–366. doi:10.1021/am8000743
Persson I (2010) Hydrated metal ions in aqueous solution: how regular are their structures? Pure Appl Chem 82:1901–1917. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-09-10-22
Ramadoss G, Muthukumar K (2014) Ultrasound assisted ammonia pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for fermentable sugar production. Biochem Eng J 83:33–41. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2013.11.013
Sèbe G, Ham-Pichavant F, Ibarboure E et al (2012) Supramolecular structure characterization of cellulose II nanowhiskers produced by acid hydrolysis of cellulose I substrates. Biomacromolecules 13:570–578. doi:10.1021/bm201777j
Selvam NCS, Narayanan S, Kennedy LJ, Vijaya JJ (2013) Pure and Mg-doped self-assembled ZnO nano-particles for the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol. J Environ Sci 25:2157–2167. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60277-0
Shateri Khalil-Abad M, Yazdanshenas ME, Nateghi MR (2009) Effect of cationization on adsorption of silver nanoparticles on cotton surfaces and its antibacterial activity. Cellulose 16:1147–1157. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9351-8
Wang H, Zheng M, Chen J et al (2010) Synthesis of MnO2 microfiber with secondary nanostructure by cotton template. J Nanotechnol 2010:1–5. doi:10.1155/2010/479172
Wang M, Zhang Y, Zhou Y et al (2013) Rapid room-temperature synthesis of nanosheet-assembled ZnO mesocrystals with excellent photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 15:754. doi:10.1039/c2ce26660a
Xue C-H, Chen J, Yin W et al (2012) Superhydrophobic conductive textiles with antibacterial property by coating fibers with silver nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 258:2468–2472. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.10.074
Yadav RS, Mishra P, Pandey AC (2008) Growth mechanism and optical property of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sonochemical method. Ultrason Sonochem 15:863–868. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2007.11.003
Yamabi S, Imai H (2002) Growth conditions for wurtzite zinc oxide films in aqueous solutions. J Mater Chem 12:3773–3778. doi:10.1039/b205384e
Yang YH, Yang GW (2010) Temperature dependence and activation energy of ZnO nanowires grown on amorphous carbon. Chem Phys Lett 494:64–68. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2010.05.074
Yao L, Zheng M, Li C et al (2012) Facile synthesis of superhydrophobic surface of ZnO nanoflakes: chemical coating and UV-induced wettability conversion. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:216. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-7-216
Ye C, Bando Y, Shen G, Golberg D (2006) Thickness-dependent photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanoplatelets. J Phys Chem B 110:15146–15151. doi:10.1021/jp061874w
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge funding from COLCIENCIAS and the World Bank (Grant RC No. 0373). We also thank Guatiguará Technology Park, the Central Research Laboratory Facility and the X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy laboratories at Universidad Industrial de Santander for infrastructural support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ovalle-Serrano, S.A., Carrillo, V.S., Blanco-Tirado, C. et al. Controlled synthesis of ZnO particles on the surface of natural cellulosic fibers: effect of concentration, heating and sonication. Cellulose 22, 1841–1852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0620-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0620-4