Abstract
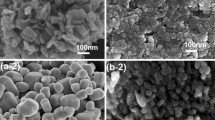
Nanocrystalline zinc oxide particles were synthesized and simultaneously incorporated into a three-dimensional nanofibrous matrix of bacterial cellulose (BC) pellicles by a newly created method called “ultrasonic-assisted in situ synthesis”. The BC pellicles were first immersed in a zinc acetate solution. Then the Zn2+-absorbed BC pellicle was further immersed in ammonium hydroxide solution with simultaneous ultrasonic treatment. The effect of immersion time of the BC pellicles in zinc acetate solution and ultrasonic treatment time on crystalline size and percent incorporation of ZnO into the BC pellicles were determined. The crystalline size of ZnO incorporated in BC pellicles was in the range of ~54–63 nm that were similar to the diameter of BC nanofibrils. The amount of ZnO into the BC pellicles was found to increase with increasing immersion time. A longer ultrasonic treatment time resulted in smaller crystalline size of the incorporated ZnO. The particle size, morphology and dispersion of the synthesized ZnO in the BC matrix were examined by transmission electron microscope and scanning electron microscope with inbuilt energy dispersive X-ray analysis. The mechanism of the formation of the nanocrystalline ZnO particles onto the BC nanofibrils was discussed. Moreover, the antibacterial activity of the nanocrystalline ZnO particle-incorporated BC sheet against Escherichia coli (Gram-negative) and Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive) was also evaluated.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
An X, Cao C, Zhu H (2007) Bio-inspired fabrication of ZnO nanorod arrays and their optical and photoresponse properties. J Cryst Growth 308(2):340–347. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2007.08.008
Applerot G, Perkas N, Amirian G, Girshevitz O, Gedanken A (2009a) Coating of glass with ZnO via ultrasonic irradiation and a study of its antibacterial properties. Appl Surf Sci 256S:S3–S8. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.04.198
Applerot G, Lipovsky A, Dror R, Perkas N, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken R (2009b) Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS-mediated cell injury. Adv Funct Mater 19:842–852. doi:10.1002/adfm.200801081
Breedon M, Rahmani MB, Kalantar-zadeh K (2010) Aqueous synthesis of interconnected ZnO nanowires using spray pyrolysis deposited seed layers. Mater Lett 64:291–294. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2009.10.065
Casavola M, Buonsanti R, Caputo G, Cozzoli PD (2008) Colloidal strategies for preparing oxide-based hybrid nanocrystals. Eur J Inorg Chem 6:837–854. doi:10.1002/ejic.200701047
Chen Y, Bagnall D, Yao T (2000) ZnO as a novel photonic material for the UV region. Mater Sci Eng B 75:190–198. doi:10.1016/S0921-5107(00)00372-X
Chen SJ, Liu YC, Shao CL, Mu R, Lu YM, Zhang JY, Shen DZ, Fan XW (2005a) Structural and optical properties of uniform ZnO nanosheets. Adv Mater 17:586–590. doi:10.1002/adma.200401263
Chen YW, Liu YC, Lu SX, Xu CS, Shao CL, Wang C, Zhang JY, Lu YM, Shen DZ, Fan XW (2005b) Optical properties of ZnO and ZnO: in nanorods assembled by sol-gel method. J Chem Phys 123:134701–134705. doi:10.1063/1.2009731
Cozzoli PD, Kornowski A, Weller H (2005) Colloidal synthesis of organic-capped ZnO nanocrystals via a sequential reduction–oxidation reaction. J Phys Chem B 109:2638–2644. doi:10.1021/jp0457139
Czaja WK, Romanovicz D, Brown RM (2004) Structural investigations of microbial cellulose produced in stationary and agitated culture. Cellulose 11:403–411. doi:10.1023/B:CELL.0000046412.11983.61
Czaja WK, Young DJ, Kawecki M, Brown RM (2007) The future prospects of microbial cellulose in biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 8:1–12. doi:10.1021/bm060620d
Didenko Y, Suslick KS (2002) The energy efficiency of formation of photons, radicals, and ions during single bubble cavitation. Nature 418:394–397. doi:10.1038/nature00895
Dubey V, Saxena C, Singh L, Ramana KV, Chauhan RS (2002) Pervaporation of binary water–ethanol mixtures through bacterial cellulose membrane. Sep Purif Technol 27:163–171. doi:10.1016/S1383-5866(01)00210-6
Dutta K, Das S, Pramanik A (2012) Concomitant synthesis of highly crystalline Zn–Al layered double hydroxide and ZnO: phase interconversion and enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 366:28–36. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.09.081
Gedanken A (2004) Using sonochemistry for the fabrication of nanomaterials. Ultrason Sonochem 11:47–55. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2004.01.037
Ghule K, Ghule AV, Chen B, Ling Y (2006) Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles coated paper and its antibacterial activity study. Green Chem 8:1034–1041. doi:10.1039/B605623G
Grzegorczyn S, Ezak A (2007) Kinetics of concentration boundary layers buildup in the system consisted of microbial cellulose biomembrane and electrolyte solutions. J Membr Sci 304:148–155. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2007.07.027
He J, Kunitake T, Nakao A (2003) Facile in situ synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles in porous cellulose fibers. Chem Mater 15:4401–4406. doi:10.1021/cm034720r
Hiller R, Putterman SJ, Barber BP (1992) Spectrum of synchronous picosecond sonoluminescence. Phys Rev Lett 69:1182–1184. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.1182
Hirai T, Asada Y (2005) Preparation of ZnO nanoparticles in a reverse micellar system and their photoluminescence properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:184–189. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.09.069
Hong R, Pan T, Qian J, Li H (2006) Synthesis and surface modification of ZnO nanoparticles. J Chem Eng 119:71–81. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2006.03.003
Hu W, Chen S, Li X, Shi S, Shen W, Zhang X, Wang H (2009) In situ synthesis of silver chloride nanoparticles into bacterial cellulose membranes. Mater Sci Eng C 29:1216–1219. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2008.09.017
Hu W, Chen S, Zhou B, Wang H (2010) Facile synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles based on bacterial cellulose. Mater Sci Eng B 170:88–92. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2010.02.034
Iguchi M, Yamanaka S, Budhiono A (2000) Bacterial cellulose—a masterpiece of nature’s arts. J Mater Sci 35(2):261–270. doi:10.1023/A:1004775229149
Ishikawa Y, Shimizu Y, Sasaki T, Koshizaki N (2006) Preparation of zinc oxide nanorods using pulsed laser ablation in water media at high temperature. J Colloid Interface Sci 300:612–615. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.04.005
Jing L, Xu Z, Shang J, Sun X, Cai W, Guo H (2002) The preparation and characterization of ZnO ultrafine particles. Mater Sci Eng 332:356–361. doi:10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01801-9
Jung S, Oh E, Lee K, Yang Y, Park C, Park W, Jeong S (2008) Sonochemical preparation of shape-selective ZnO nanostructures. Cryst Growth Des 8(1):265–269. doi:10.1021/cg070296l
Kamel S (2007) Nanotechnology and its applications in lignocellulosic composites, a mini review. Express Polym Lett 1:546–575. doi:10.3144/expresspolymlett.2007.78
Katepetch C, Rujiravanit R (2011) Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticle into bacterial cellulose matrix by ammonia gas-enhancing in situ co-precipitation method. Carbohydr Polym 86:162–170. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.04.024
Klemm D, Schumann D, Udhardt U, Marsch S (2001) Bacterial synthesized cellulose-artificial blood vessels for microsurgery. Prog Polym Sci 26(9):1561–1603. doi:10.1016/S0079-6700(01)00021-1
Kong XY, Wang ZL (2003) Spontaneous polarization-induced nanohelixes, nanosprings, and nanorings of piezoelectric nanobelts. Nano Lett 3:1625–1631. doi:10.1021/nl034463p
Kotlyar A, Perkas N, Amiryan G, Meyer M, Zimmermann W, Gedanken A (2007) Coating silver nanoparticles on poly(methyl methacrylate) chips and spheres via ultrasound irradiation. J Appl Polym Sci 104(5):2868–2876. doi:10.1002/app.25893
Lee JH, Ko KH, Park BO (2003) Electrical and optical properties of ZnO transparent conducting films by the sol–gel method. J Cryst Growth 247:119–125. doi:10.1016/S0022-0248(02)01907-3
Li X, Chen S, Hu W, Shi S, Shen W, Zhang X, Wang H (2009) In situ synthesis of CdS nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 76:509–512. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.11.014
Liu GY, Essex A, Buchanan JT, Datta V, Hoffman HM, Bastian JF, Fierer J, Nizet V (2005) Staphylococcus aureus golden pigment impairs neutrophil killing and promotes virulence through its antioxidant activity. J Exp Med 202:209–215. doi:10.1084/jem.20050846
Liu J, Huang X, Li Y, Duan J, Ai H (2006) Large-scale synthesis of flower-like ZnO structures by a surfactant free and low-temperature process. Mater Chem Phys 98(2–3):523–527. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.09.075
Ma X, Zhang W (2009) Effects of flower-like ZnO nanowhiskers on the mechanical, thermal and antibacterial properties of waterborne polyurethane. Polym Degrad Stab 94:1103–1109. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.03.024
Maneerung T, Tokura S, Rujiravanit R (2008) Impregnation of silver nanoparticles into bacterial cellulose for antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym 72:43–51. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.07.025
Meulenkamp EA (1998) Synthesis and growth of ZnO nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 102:5566–5572. doi:10.1021/jp980730h
Peng W, Qu S, Cong G, Wang Z (2006) Synthesis and structures of morphology-controlled ZnO nano- and microcrystals. Cryst Growth Des 6:1518–1522. doi:10.1021/cg0505261
Perelshtein I, Applerot G, Perkas N, Wehrschetz-Sigl E, Hasmann A, Guebitz GM, Gedanken A (2009) Antibacterial properties of an in situ generated and simultaneously deposited nanocrystalline ZnO on fabrics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1(2):361–366. doi:10.1021/am8000743
Perelshtein I, Applerot G, Perkas N, Grinblat J, Hulla E, Wehrschuetz-Sigl E, Hasmann A, Guebitz G, Gedanken A (2010) Ultrasound radiation as a “throwing stones” technique for the production of antibacterial nanocomposite textiles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(7):1999–2004. doi:10.1021/am100291w
Pol VG, Srivastava DN, Palchik O, Palchik V, Slifkin MA, Weiss AM, Gedanken A (2002) Sonochemical deposition of silver nanoparticles on silica spheres. Langmuir 18:3352–3357. doi:10.1021/la0155552
Pol VG, Wildermuth G, Felsche J, Gedanken A, Calderon-Moreno J (2005) Sonochemical deposition of Au nanoparticles on titania and the significant decrease in the melting point of gold. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5(6):975–979. doi:10.1166/jnn.2005.137
Raghupathi KR, Koodali RT, Manna AC (2011) Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:4020–4028. doi:10.1021/la104825u
Rezaee A, Solimani S, Forozandemogadam M (2005) Role of plasmid in production of Acetobacter xylinum biofilms. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 1:121–125. doi:10.3844/ajbbsp.2005.121.124
Roman M, Winter WT (2004) Effect of sulfate groups from sulfuric acid hydrolysis on the thermal degradation behavior of bacterial cellulose. Biomacromolecules 5:1671–1677. doi:10.1021/bm034519+
Saito N, Haneda H, Sekiguchi T, Ohashi N, Sakaguchi I, Koumoto K (2002) Low-temperature fabrication of light-emitting zinc oxide micropatterns using self-assembled monolayers. J Adv Mater 14:418–421. doi:10.1002/1521-4095(20020318)14:6<418:AID-ADMA418>3.0.CO;2-K
Silva AR, Unali G (2011) Controlled silver delivery by silver cellulose nanocomposites prepared by a one-pot green synthesis assisted by microwaves. Nanotechnology 22:1–6. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/31/315605
Sue K, Kimura K, Arai K (2004) Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanocrystals using microreactor. Mater Lett 58:3229–3231. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2004.06.016
Suslick KS, Choe SB, Cichowlas AA, Grinstaff MW (1991) Sonochemical synthesis of amorphous iron. Nature 353:414–416. doi:10.1038/353414a0
Tani T, Madler L, Pratsinis SE (2002) Homogeneous ZnO nanoparticles by flame spray pyrolysis. J Nanopart Res 4(4):337–343. doi:10.1023/A:1021153419671
Wan Y, Hong L, Jia S, Huang Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Jiang H (2006) Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite–bacterial cellulose nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 66:1825–1832. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.11.027
Wang LN, Muhammed M (1999) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles with controlled morphology. J Mater Chem 9:2871–2878. doi:10.1039/A907098B
Wang CL, Mao BD, Wang EB, Kang ZH, Tian CG (2007) Solution synthesis of ZnO nanotubes via a template-free hydrothermal route. Solid State Commun 141:620–623. doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2006.12.028
Wen B, Huang Y, Boland JJ (2008) Controllable growth of ZnO nanostructures by a simple solvothermal process. J Phys Chem C 112:106–111. doi:10.1021/jp076789i
Westermark K, Rensmo H, Lees TC, Vos JG, Siegbahn HT (2002) Electron spectroscopic studies of bis-(2,2′-bipyridine)-(4,4′-dicarboxy-2,2′-bipyridine)-ruthenium(II) and bis-(2,2′-bipyridine)-(4,4′-dicarboxy-2,2′-bipyridine)-osmium(II) adsorbed on nanostructured TiO2 and ZnO surfaces. J Phys Chem B 106:10108–10113. doi:10.1021/jp014218z
Wu JJ, Liu SC (2002) Catalyst-free growth and characterization of ZnO nanorods. J Phys Chem B 106(37):9546–9551. doi:10.1021/jp025969j
Xing YJ, Xi ZH, Zhang XD, Song JH, Wang RM, Xu J, Xue ZQ, Yu DP (2005) Thermal evaporation synthesis of zinc oxide nanowires. Appl Phys A 80:1527–1530. doi:10.1007/s00339-003-2388-x
Xu J, Pan Q, Shun Y, Tian Z (2000) Grain size control and gas sensing properties of ZnO gas sensor. Sens Actuators B 66:277–279. doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00381-6
Yadav RS, Mishra P, Pandey AC (2008) Growth mechanism and optical property of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sonochemical method. Ultrason Sonochem 15:863–868. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2007.11.003
Zhang D, Qi L (2005) Synthesis of mesoporous titania networks consisting of anatase nanowires by templating of bacterial cellulose membranes. Chem Commun 21:2735–2737. doi:10.1039/b501933h
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Wang S, Chen W, Lei Y (2001) A convenient route to polyacrylonitrile/silver nanoparticle composite by simultaneous polymerization–reduction approach. Polymer 42:8315–8318. doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00285-3
Zhang Y, Jia HB, Luo XH, Chen XH, Yu DP, Wang RM (2003) Synthesis, microstructure, and growth mechanism of dendrite ZnO nanowires. J Phys Chem B 107:8289–8293. doi:10.1021/jp034834q
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Chulalongkorn University Dutsadi Phiphat Scholarship; Ratchadapiseksomphot Endowment Fund, Chulalongkorn University; and the Center for Petroleum, Petrochemicals and Advanced aterials, Chulalongkorn University, Thailand are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katepetch, C., Rujiravanit, R. & Tamura, H. Formation of nanocrystalline ZnO particles into bacterial cellulose pellicle by ultrasonic-assisted in situ synthesis. Cellulose 20, 1275–1292 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9892-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9892-8