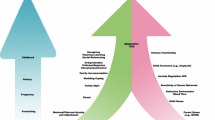
Abstract
Multiple theoretical frameworks have been proposed to provide a more comprehensive picture of the risk factors that influence anxiety-related developmental trajectories. Nonetheless, there remains a need for an integrative model that outlines: (1) which risk factors may be most pertinent at different points in development, and (2) how parenting may maintain, exacerbate, or attenuate an affective style that is characterized by high negative emotional reactivity to unfamiliar, uncertain, and threatening situations. A developmentally informed, integrative model has the potential to guide treatment development and delivery, which is critical to reducing the public health burden associated with these disorders. This paper outlines a model integrating research on many well-established risk mechanisms for anxiety disorders, focusing on (1) the developmental progression from emotional reactivity constructs early in life to those involving higher-level cognitive processes later in youth, and (2) potential pathways by which parenting may impact the stability of youth’s cognitive-affective responses to threat-relevant information across development.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, E., & Feldman, R. (2022). The neural basis of human fatherhood: A unique biocultural perspective on plasticity of brain and behavior. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 25(1), 93–109.
Adams, K. L., Edwards, A., Peart, C., Ellett, L., Mendes, I., Bird, G., & Murphy, J. (2022). The association between anxiety and cardiac interoceptive accuracy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 140, 104754.
Aktar, E. (2022). Intergenerational transmission of anxious information processing biases: An updated conceptual model. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 25(1), 182–203.
Aktar, E., Majdandžić, M., De Vente, W., & Bögels, S. (2013). The interplay between expressed parental anxiety and infant behavioural inhibition predicts infant avoidance in a social referencing paradigm. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54, 144–156.
Aktar, E., Nikolić, M., & Bögels, S. M. (2017). Environmental transmission of generalized anxiety disorder from parents to children: Worries, experiential avoidance, and intolerance of uncertainty. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 19(2), 137–146.
Aktar, E., Nimphy, C. A., Kret, M. E., Pérez-Edgar, K., Raijmakers, M. E., & Bögels, S. M. (2022). Attention biases to threat in infants and parents: Links to parental and infant anxiety dispositions. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 50, 387–402.
Allen, K. B., Benningfield, M., & Blackford, J. U. (2020a). Childhood anxiety—if we know so much, why are we doing so little? JAMA Psychiatry, 77(9), 887–888.
Allen, K. B., Woody, M. L., Rosen, D., Price, R. B., Amole, M. C., & Silk, J. S. (2020b). Validating a mobile eye tracking measure of integrated attention bias and interpretation bias in youth. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 44, 668–677.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596
Amir, N., Bomyea, J., & Beard, C. (2010). The effect of single-session interpretation modification on attention bias in socially anxious individuals. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 24(2), 178–182.
Anderson, E. R., & Hope, D. A. (2009). The relationship among social phobia, objective and perceived physiological reactivity, and anxiety sensitivity in an adolescent population. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23(1), 18–26.
Askew, C., & Field, A. P. (2008). The vicarious learning pathway to fear 40 years on. Clinical Psychology Review, 28(7), 1249–1265.
Atzil, S., Hendler, T., & Feldman, R. (2011). Specifying the neurobiological basis of human attachment: Brain, hormones, and behavior in synchronous and intrusive mothers. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(13), 2603–2615.
Bardeen, J. R., & Daniel, T. A. (2017). An eye-tracking examination of emotion regulation, attentional bias, and pupillary response to threat stimuli. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 41, 853–866.
Bardeen, J. R., Fergus, T. A., & Orcutt, H. K. (2013). Testing a hierarchical model of distress tolerance. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 35(4), 495–505.
Bardeen, J. R., Tull, M. T., Dixon-Gordon, K. L., Stevens, E. N., & Gratz, K. L. (2015). Attentional control as a moderator of the relationship between difficulties accessing effective emotion regulation strategies and distress tolerance. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 37, 79–84.
Bar-Haim, Y., Lamy, D., Pergamin, L., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2007). Threat-related attentional bias in anxious and nonanxious individuals: A meta-analytic study. Psychological Bulletin, 133(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.1
Barrett, P. M., Rapee, R. M., Dadds, M. M., & Ryan, S. M. (1996). Family enhancement of cognitive style in anxious and aggressive children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24(2), 187–203.
Beard, C., & Amir, N. (2009). Interpretation in social anxiety: When meaning precedes ambiguity. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 33, 406–415.
Beier, J. S., & Spelke, E. S. (2012). Infants’ developing understanding of social gaze. Child Development, 83, 486–496. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2011.01702.x
Best, J. R., Miller, P. H., & Jones, L. L. (2009). Executive functions after age 5: Changes and correlates. Developmental Review, 29(3), 180–200.
Boelen, P. A., Vrinssen, I., & van Tulder, F. (2010). Intolerance of uncertainty in adolescents: Correlations with worry, social anxiety, and depression. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease, 198(3), 194–200. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMD.0b013e3181d143de
Boettcher, H., Brake, C. A., & Barlow, D. H. (2016). Origins and outlook of interoceptive exposure. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 53, 41–51.
Bögels, S. M., & Phares, V. (2008). Fathers’ role in the etiology, prevention and treatment of child anxiety: A review and new model. Clinical Psychology Review, 28, 539–528.
Bögels, S. M., van Dongen, L., & Muris, P. (2003). Family influences on dysfunctional thinking in anxious children. Infant and Child Development, 12(3), 243–252.
Buss, K. A., & Qu, J. (2018). Psychobiological processes in the development of behavioral inhibition. In K. Pérez-Edgar & N. A. Fox (Eds.), Behavioral inhibition: Integrating theory, research, and clinical perspectives (pp. 91–111). Springer.
Cabecinha-Alati, S., O’Hara, G., Kennedy, H., & Montreuil, T. (2020). Parental emotion socialization and adult outcomes: The relationships between parental supportiveness, emotion regulation, and trait anxiety. Journal of Adult Development, 27, 268–280.
Calì, G., Ambrosini, E., Picconi, L., Mehling, W. E., & Committeri, G. (2015). Investigating the relationship between interoceptive accuracy, interoceptive awareness, and emotional susceptibility. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1202.
Carleton, R. N., Norton, M. P. J., & Asmundson, G. J. (2007). Fearing the unknown: A short version of the Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 21(1), 105–117.
Cederlund, R., & Öst, L. G. (2011). Perception of threat in children with social phobia: Comparison to nonsocially anxious children before and after treatment. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 40(6), 855–863.
Chorpita, B. F., Albano, A. M., & Barlow, D. H. (1996). Cognitive processing in children: Relation to anxiety and family influences. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 25(2), 170–176.
Chronis-Tuscano, A., Degnan, K. A., Pine, D. S., Pérez-Edgar, K., Henderson, H. A., Diaz, Y., & Fox, N. A. (2009). Stable early maternal report of behavioral inhibition predicts lifetime social anxiety disorder in adolescence. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 48(9), 928–935.
Cisler, J. M., & Koster, E. H. W. (2010). Mechanisms of attentional biases towards threat in anxiety disorders: An integrative review. Clinical Psychology Review, 30(2), 203–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.11.003
Clauss, J. A., & Blackford, J. U. (2012). Behavioral inhibition and risk for developing social anxiety disorder: A meta-analytic study. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 51(10), 1066–1075.
Cobham, V. E., & Dadds, M. R. (1999). Anxious children and their parents: What do they expect? Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 28(2), 220–231.
Comer, J. S., Roy, A. K., Furr, J. M., Gotimer, K., Beidas, R. S., Dugas, M. J., & Kendall, P. C. (2009). The intolerance of uncertainty scale for children: A psychometric evaluation. Psychological Assessment, 21(3), 402–411. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016719
Cornacchio, D., Sanchez, A. L., Coxe, S., Roy, A., Pincus, D. B., Read, K. L., Holaway, R. M., Kendall, P. C., & Comer, J. S. (2018). Factor structure of the intolerance of uncertainty scale for children. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 53, 100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2017.07.003
Cowie, J., Clementi, M. A., & Alfano, C. A. (2018). Examination of the intolerance of uncertainty construct in youth with generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 47(6), 1014–1022. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2016.1212358
Creswell, C., O’Connor, T. G., & Brewin, C. R. (2006). A longitudinal investigation of maternal and child ‘anxious cognitions.’ Cognitive Therapy and Research, 30, 135–147.
Creswell, C., Cooper, P., & Murray, L. (2010). Intergenerational transmission of anxious information processing biases. In J. P. Hadwin & A. P. Field (Eds.), Information processing biases and anxiety: A developmental perspective (pp. 279–295). Wiley.
Creswell, C., Shildrick, S., & Field, A. P. (2011). Interpretation of ambiguity in children: A prospective study of associations with anxiety and parental interpretations. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 20, 240–250.
Critchley, H. D., & Garfinkel, S. N. (2017). Interoception and emotion. Current Opinion in Psychology, 17, 7–14.
Crugnola, C. R., Gazzotti, S., Spinelli, M., Ierardi, E., Caprin, C., & Albizzati, A. (2013). Maternal attachment influences mother–infant styles of regulation and play with objects at nine months. Attachment & Human Development, 15(2), 107–131.
Cummings, J. R., Bornovalova, M. A., Ojanen, T., Hunt, E., MacPherson, L., & Lejuez, C. (2013). Time doesn’t change everything: The longitudinal course of distress tolerance and its relationship with externalizing and internalizing symptoms during early adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 41, 735–748.
Dadds, M. R., Barrett, P. M., Rapee, R. M., & Ryan, S. (1996). Family process and child anxiety and aggression: An observational analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24(6), 715–734.
Daleiden, E. L., & Vasey, M. W. (1997). An information-processing perspective on childhood anxiety. Clinical Psychology Review, 17(4), 407–429.
Daughters, S. B., Gorka, S. M., Rutherford, H. J., & Mayes, L. C. (2014). Maternal and adolescent distress tolerance: The moderating role of gender. Emotion, 14(2), 416–424.
Davidson, M. C., Amso, D., Anderson, L. C., & Diamond, A. (2006). Development of cognitive control and executive functions from 4 to 13 years: Evidence from manipulations of memory, inhibition, and task switching. Neuropsychologia, 44(11), 2037–2078.
de Lijster, J. M., Dierckx, B., Utens, E. M., Verhulst, F. C., Zieldorff, C., Dieleman, G. C., & Legerstee, J. S. (2017). The age of onset of anxiety disorders: A meta-analysis. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry Revue Canadienne De Psychiatrie, 62(4), 237.
DeCicco, J. M., Solomon, B., & Dennis, T. A. (2012). Neural correlates of cognitive reappraisal in children: An ERP study. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 2(1), 70–80.
Degnan, K. A., & Fox, N. A. (2007). Behavioral inhibition and anxiety disorders: Multiple levels of a resilience process. Development and Psychopathology, 19(3), 729–746.
Deichmann, F., & Ahnert, L. (2021). The terrible twos: How children cope with frustration and tantrums and the effect of maternal and paternal behaviors. Infancy, 26(3), 469–493.
Dennis, T. A., & Chen, C.-C. (2007). Neurophysiological mechanisms in the emotional modulation of attention: The interplay between threat sensitivity and attentional control. Biological Psychology, 76(1–2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2007.05.001
Doan, S. N., Son, H., & Kim, L. N. (2018). Maternal and paternal emotional contributions to children’s distress tolerance: Relations to child depressive symptoms. Psychiatry Research, 267, 215–220.
Dodd, H. F., Hudson, J. L., Morris, T. M., & Wise, C. K. (2012). Interpretation bias in preschool children at risk for anxiety: A prospective study. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121(1), 28.
Dodd, H. F., Stuijfzand, S., Morris, T., & Hudson, J. L. (2015). Child anxiety and the processing of ambiguity. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 39, 669–677.
Domschke, K., Stevens, S., Pfleiderer, B., & Gerlach, A. L. (2010). Interoceptive sensitivity in anxiety and anxiety disorders: An overview and integration of neurobiological findings. Clinical Psychology Review, 30(1), 1–11.
Donovan, C. L., Holmes, M. C., & Farrell, L. J. (2016). Investigation of the cognitive variables associated with worry in children with Generalised Anxiety Disorder and their parents. Journal of Affective Disorders, 192, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.12.003
Drake, K. L., & Ginsburg, G. S. (2011). Parenting practices of anxious and nonanxious mothers: A multi-method, multi-informant approach. Child & Family Behavior Yherapy, 33(4), 299–321.
Dudeney, J., Sharpe, L., & Hunt, C. (2015). Attentional bias towards threatening stimuli in children with anxiety: A meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 40, 66–75.
Dugas, M. J., & Robichaud, M. (2007). Cognitive-behavioral treatment for generalized anxiety disorder. Taylor and Francis.
Dugas, M. J., Gosselin, P., & Ladouceur, R. (2001). Intolerance of uncertainty and worry: Investigating specificity in a nonclinical sample. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 25(5), 551–558.
Dugas, M. J., Laugesen, N., & Bukowski, W. M. (2012). Intolerance of uncertainty, fear of anxiety, and adolescent worry. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(6), 863–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9611-1
Dunbar, A. S., Leerkes, E. M., Coard, S. I., Supple, A. J., & Calkins, S. (2017). An integrative conceptual model of parental racial/ethnic and emotion socialization and links to children’s social-emotional development among African American families. Child Development Perspectives, 11(1), 16–22.
Dunn, B. D., Galton, H. C., Morgan, R., Evans, D., Oliver, C., Meyer, M., & Dalgleish, T. (2010). Listening to your heart: How interoception shapes emotion experience and intuitive decision making. Psychological Science, 21(12), 1835–1844.
Eisenberg, N., & Fabes, R. A. (1994). Mothers’ reactions to children’s negative emotions: Relations to children’s temperament and anger behavior. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 40(1), 138–156.
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (1998). Parental socialization of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 9(4), 241–273.
Eley, T. C., Gregory, A. M., Clark, D. M., & Ehlers, A. (2007). Feeling anxious: A twin study of panic/somatic ratings, anxiety sensitivity and heartbeat perception in children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48(12), 1184–1191.
Emerson, L.-M., Ogielda, C., & Rowse, G. (2019). A systematic review of the role of parents in the development of anxious cognitions in children. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 62, 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2018.11.002
Essex, M. J., Klein, M. H., Slattery, M. J., Goldsmith, H. H., & Kalin, N. H. (2010). Early risk factors and developmental pathways to chronic high inhibition and social anxiety disorder in adolescence. American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(1), 40–46.
Eysenck, M. W., Derakshan, N., Santos, R., & Calvo, M. G. (2007). Anxiety and cognitive performance: Attentional control theory. Emotion, 7(2), 336.
Feldman, R. (2015). Mutual influences between child emotion regulation and parent–child reciprocity support development across the first 10 years of life: Implications for developmental psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 27, 1007–1023.
Felton, J. W., Banducci, A. N., Shadur, J. M., Stadnik, R., MacPherson, L., & Lejuez, C. W. (2017). The developmental trajectory of perceived stress mediates the relations between distress tolerance and internalizing symptoms among youth. Development and Psychopathology, 29(4), 1391–1401.
Fialko, L., Bolton, D., & Perrin, S. (2012). Applicability of a cognitive model of worry to children and adolescents. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 50(5), 341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2012.02.003
Field, A. P., & Lester, K. J. (2010). Is there room for ‘development’ in developmental models of information processing biases to threat in children and adolescents? Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 13, 315–332.
Field, A. P., Lawson, J., & Banerjee, R. (2008). The verbal threat information pathway to fear in children: The longitudinal effects on fear cognitions and the immediate effects on avoidance behavior. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 117(1), 214–224. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.117.1.214
Filippetti, M. L. (2021). Being in tune with your body: The emergence of interoceptive processing through caregiver–infant feeding interactions. Child Development Perspectives, 15(3), 182–188.
Fitzgerald, J. M., Kinney, K. L., Phan, K. L., & Klumpp, H. (2020). Distinct neural engagement during implicit and explicit regulation of negative stimuli. Neuropsychologia, 145, 106675.
Fliek, L., Dibbets, P., Roelofs, J., & Muris, P. (2017). Cognitive bias as a mediator in the relation between fear-enhancing parental behaviors and anxiety symptoms in children: A cross-sectional study. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 48, 82–93.
Fliek, L., Roelofs, J., Van Breukelen, G., & Muris, P. (2019). A longitudinal study on the relations among fear-enhancing parenting, cognitive biases, and anxiety symptoms in non-clinical children. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 50, 631–646.
Fonagy, P., & Target, M. (2002). Early intervention and the development of self-regulation. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 22(3), 307–335.
Forkmann, T., Scherer, A., Meessen, J., Michal, M., Schächinger, H., Vögele, C., & Schulz, A. (2016). Making sense of what you sense: Disentangling interoceptive awareness, sensibility and accuracy. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 109, 71–80.
Fotopoulou, A., & Tsakiris, M. (2017). Mentalizing homeostasis: The social origins of interoceptive inference. Neuropsychoanalysis, 19(1), 3–28.
Fox, N. A., & Pine, D. S. (2012). Temperament and the emergence of anxiety disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 51(2), 125.
Fox, N. A., Henderson, H. A., Rubin, K. H., Calkins, S. D., & Schmidt, L. A. (2001). Continuity and discontinuity of behavioral inhibition and exuberance: Psychophysiological and behavioral influences across the first four years of life. Child Development, 72(1), 1–21.
Fox, N. A., Buzzell, G. A., Morales, S., Valadez, E. A., Wilson, M., & Henderson, H. A. (2021). Understanding the emergence of social anxiety in children with behavioral inhibition. Biological Psychiatry, 89(7), 681–689.
Fox, N. A., Zeytinoglu, S., Valadez, E. A., Buzzell, G. A., Morales, S., & Henderson, H. A. (2023). Annual Research Review: Developmental pathways linking early behavioral inhibition to later anxiety. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 64(4), 537–561.
Fu, X., & Pérez-Edgar, K. (2019). Threat-related attention bias in socioemotional development: A critical review and methodological considerations. Developmental Review, 51, 31–57.
Garfinkel, S. N., Seth, A. K., Barrett, A. B., Suzuki, K., & Critchley, H. D. (2015). Knowing your own heart: Distinguishing interoceptive accuracy from interoceptive awareness. Biological Psychology, 104, 65–74.
Geronimi, E. M. C., Richards, A., Gramszlo, C., & Woodruff-Borden, J. (2019). A preliminary investigation of cognitive features associated with worry among African American youth. Journal of Black Psychology, 45(6–7), 518–539. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095798419870076
Gerrans, P., & Murray, R. J. (2020). Interoceptive active inference and self-representation in social anxiety disorder (SAD): Exploring the neurocognitive traits of the SAD self. Neuroscience of Consciousness. https://doi.org/10.1093/nc/niaa026
Gillett, C. B., Bilek, E. L., Hanna, G. L., & Fitzgerald, K. D. (2018). Intolerance of uncertainty in youth with obsessive-compulsive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder: A transdiagnostic construct with implications for phenomenology and treatment. Clinical Psychology Review, 60, 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2018.01.007
Goldsmith, H. H., Hilton, E. C., Phan, J. M., Sarkisian, K. L., Carroll, I. C., Lemery-Chalfant, K., & Planalp, E. M. (2022). Childhood inhibition predicts adolescent social anxiety: Findings from a longitudinal twin study. Development and Psychopathology, 34, 1666–1685.
Gross, J. J. (2014). Emotion regulation: Conceptual and empirical foundations. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (2nd ed., pp. 3–20). Guilford.
Gulley, L. D., Oppenheimer, C. W., & Hankin, B. L. (2014). Associations among negative parenting, attention bias to anger, and social anxiety among youth. Developmental Psychology, 50(2), 577.
Hallion, L. S., & Ruscio, A. M. (2011). A meta-analysis of the effect of cognitive bias modification on anxiety and depression. Psychological Bulletin, 137(6), 940–958.
Hayes, S. C., Wilson, K. G., Gifford, E. V., Follette, V. M., & Strosahl, K. (1996). Experiential avoidance and behavioral disorders: A functional dimensional approach to diagnosis and treatment. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64(6), 1152.
Hearn, C. S., Donovan, C. L., Spence, S. H., & March, S. (2017a). A worrying trend in social anxiety: To what degree are worry and its cognitive factors associated with youth social anxiety disorder? Journal of Affective Disorders, 208, 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.09.052
Hearn, C. S., Donovan, C. L., Spence, S. H., March, S., & Holmes, M. C. (2017b). What’s the worry with social anxiety? Comparing cognitive processes in children with generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 48(5), 786–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-016-0703-y
Hechler, T. (2021). Altered interoception and its role for the co-occurrence of chronic primary pain and mental health problems in children. Pain, 162(3), 665–671.
Henricks, L. A., Lange, W. G., Luijten, M., van den Berg, Y. H., Stoltz, S. E., Cillessen, A. H., & Becker, E. S. (2022). The longitudinal interplay between attention bias and interpretation bias in social anxiety in adolescents. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 46(5), 940–955.
Hertel, P. T., & Mathews, A. (2011). Cognitive bias modification: Past perspectives, current findings, and future applications. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6(6), 521–536. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691611421205
Hirsch, C. R., Clark, D. M., & Mathews, A. (2006). Imagery and interpretations in social phobia: Support for the combined cognitive biases hypothesis. Behavior Therapy, 37(3), 223–236.
Holroyd, C. B., Nieuwenhuis, S., Yeung, N., & Cohen, J. D. (2003). Errors in reward prediction are reflected in the event-related brain potential. NeuroReport, 14(18), 2481–2484.
Hong, R. Y., Lee, S. S. M., Tsai, F.-F., & Tan, S. H. (2017). Developmental trajectories and origins of a core cognitive vulnerability to internalizing symptoms in middle childhood. Clinical Psychological Science, 5(2), 299–315. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702616679875
Hudson, J. L., Dodd, H. F., Lyneham, H. J., & Bovopoulous, N. (2011). Temperament and family environment in the development of anxiety disorder: Two-year follow-up. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 50(12), 1255–1264.
James, W. (1894). The physical basis of emotion. Psychological Review, 1, 516–529.
James, A. C., Reardon, T., Soler, A., James, G., & Creswell, C. (2020). Cognitive behavioural therapy for anxiety disorders in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013162.pub2
Jeffries, E. R., McLeish, A. C., Kraemer, K. M., Avallone, K. M., & Fleming, J. B. (2016). The role of distress tolerance in the use of specific emotion regulation strategies. Behavior Modification, 40(3), 439–451. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445515619596
Johnson, D. R. (2009). Goal-directed attentional deployment to emotional faces and individual differences in emotional regulation. Journal of Research in Personality, 43(1), 8–13.
Kagan, J. (2018). The history and theory of behavioral inhibition. In K. Pérez-Edgar & N. A. Fox (Eds.), Behavioral inhibition: Integrating theory, research, and clinical perspectives (pp. 1–15). Springer.
Kagan, J., Reznick, J. S., & Snidman, N. (1987). The physiology and psychology of behavioral inhibition in children. Child Development, 58, 1459–1473.
Katz, D., Rector, N. A., & Laposa, J. M. (2017). The interaction of distress tolerance and intolerance of uncertainty in the prediction of symptom reduction across CBT for social anxiety disorder. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, 46(6), 459–477.
Kendall, P. C., Norris, L. A., Rabner, J. C., Crane, M. E., & Rifkin, L. S. (2020). Intolerance of uncertainty and parental accommodation: Promising targets for personalized intervention for youth anxiety. Current Psychiatry Reports, 22, 1–8.
Kennedy, S. M., Tonarely, N. A., Halliday, E., & Ehrenreich-May, J. (2022). A person-centered approach to understanding heterogeneity of youth receiving transdiagnostic treatment for emotional disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 90(3), 234–245. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000710
Keough, M. E., Riccardi, C. J., Timpano, K. R., Mitchell, M. A., & Schmidt, N. B. (2010). Anxiety symptomatology: The association with distress tolerance and anxiety sensitivity. Behavior Therapy, 41(4), 567–574.
Kertz, S., & Woodruff-Borden, J. (2013). The role of metacognition, intolerance of uncertainty, and negative problem orientation in children’s worry. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 41(2), 243–248.
Khalsa, S. S., & Lapidus, R. C. (2016). Can interoception improve the pragmatic search for biomarkers in psychiatry? Frontiers in Psychiatry, 7, 121.
Khalsa, S. S., Adolphs, R., Cameron, O. G., Critchley, H. D., Davenport, P. W., Feinstein, J. S., & Zucker, N. (2018). Interoception and mental health: A roadmap. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 3(6), 501–513.
Khalsa, S. S., & Feinstein, J. S. (2018). The somatic error hypothesis of anxiety. In M. Tsakiris & K. De Preester (Eds.), The interoceptive mind. From homeostasis to awareness (pp. 144–164). Oxford University Press.
Khoury, N. M., Lutz, J., & Schuman-Olivier, Z. (2018). Interoception in psychiatric disorders: A review of randomized controlled trials with interoception-based interventions. Harvard Review of Psychiatry, 26(5), 250.
Klein, A. M., van Niekerk, R., Ten Brink, G., Rapee, R. M., Hudson, J. L., Bögels, S. M., & Rinck, M. (2017). Biases in attention, interpretation, memory, and associations in children with varying levels of spider fear: Inter-relations and prediction of behavior. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 54, 285–291.
Klein, A. M., Flokstra, E., van Niekerk, R., Klein, S., Rapee, R. M., Hudson, J. L., & Rinck, M. (2018). The role of self-reports and behavioral measures of interpretation biases in children with varying levels of anxiety. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 49, 897–905.
Kodal, A., Fjermestad, K. W., Bjelland, I., Gjestad, R., Öst, L. G., Bjaastad, J. F., & Wergeland, G. J. H. (2018). Predictors of long-term outcome of CBT for youth with anxiety disorders treated in community clinics. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 59, 53–63.
Kolk, S. M., & Rakic, P. (2022). Development of prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology, 47(1), 41–57.
Lange, C. G. (1885). The mechanism of the emotions. In B. Rand (Ed.), The Classical Psychologists (pp. 672–684). Houghton Mifflin.
Laposa, J. M., Collimore, K. C., Hawley, L. L., & Rector, N. A. (2015). Distress tolerance in OCD and anxiety disorders, and its relationship with anxiety sensitivity and intolerance of uncertainty. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 33, 8–14.
Laugesen, N., Dugas, M. J., & Bukowski, W. M. (2003). Understanding adolescent worry: The application of a cognitive model. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(1), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021721332181
Lebowitz, E. R., Woolston, J., Bar-Haim, Y., Calvocoressi, L., Dauser, C., Warnick, E., & Leckman, J. F. (2013). Family accommodation in pediatric anxiety disorders. Depression and Anxiety, 30(1), 47–54.
Lee, A. H., & Woodruff-Borden, J. (2018). Roles of emotional reactivity, intolerance of uncertainty, and negative problem orientation on developing childhood worry. Personality and Individual Differences, 135, 25–30.
Leen-Feldner, E. W., Zvolensky, M. J., Feldner, M. T., & Lejuez, C. W. (2004). Behavioral inhibition: Relation to negative emotion regulation and reactivity. Personality and Individual Differences, 36(6), 1235–1247.
Lester, K. J., Lisk, S. C., Carr, E., Patrick, F., & Eley, T. C. (2019). Associations between attentional bias and interpretation bias and change in school concerns and anxiety symptoms during the transition from primary to secondary school. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 47(9), 1521–1532.
Liu, P., & Pérez-Edgar, K. E. (2019). Developmental pathways from early behavioral inhibition to later anxiety: An integrative review of developmental psychopathology research and translational implications. Adolescent Research Review, 4, 45–58.
Lu, W., Daleiden, E., & Lu, S. E. (2007). Threat perception bias and anxiety among Chinese school children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(4), 568–580.
Luis-Joaquin, G. L., Lourdes, E. F., José, A., & M. M. (2020). Behavioral inhibition in childhood as a risk factor for development of social anxiety disorder: A longitudinal study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(11), 3941.
Lyyra, P., & Parviainen, T. (2018). Behavioral inhibition underlies the link between interoceptive sensitivity and anxiety-related temperamental traits. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1026.
Macatee, R. J., Capron, D. W., Guthrie, W., Schmidt, N. B., & Cougle, J. R. (2015). Distress tolerance and pathological worry: Tests of incremental and prospective relationships. Behavior Therapy, 46(4), 449–462.
Macatee, R. J., Albanese, B. J., Clancy, K., Allan, N. P., Bernat, E. M., Cougle, J. R., & Schmidt, N. B. (2018a). Distress intolerance modulation of neurophysiological markers of cognitive control during a complex go/no-go task. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 127(1), 12.
Macatee, R. J., McDermott, K. A., Albanese, B. J., Schmidt, N. B., & Cougle, J. R. (2018b). Distress intolerance moderation of attention to emotion: An eye-tracking study. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 42, 48–62.
MacDonald, E. M., Koerner, N., & Antony, M. M. (2013). Modification of interpretive bias: Impact on anxiety sensitivity, information processing and response to induced bodily sensations. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 37, 860–871.
MacLeod, C., & Mathews, A. (2012). Cognitive bias modification approaches to anxiety. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 8, 189–217.
MacLeod, C., Rutherford, E., Campbell, L., Ebsworthy, G., & Holker, L. (2002). Selective attention and emotional vulnerability: Assessing the causal basis of their association through the experimental manipulation of attentional bias. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 111(1), 107–123. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.111.1.107
MacLeod, C., Koster, E. H. W., & Fox, E. (2009). Whither cognitive bias modification research? Commentary on the special section articles. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 118(1), 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014878
Malivoire, B. L., Marcos, M., Pawluk, E. J., Tallon, K., Kusec, A., & Koerner, N. (2019). Look before you leap: The role of negative urgency in appraisals of ambiguous and unambiguous scenarios in individuals high in generalized anxiety disorder symptoms. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, 48(3), 217–240.
Mangelsdorf, S. C., Shapiro, J. R., & Marzolf, D. (1995). Developmental and temperamental differences in emotion regulation in infancy. Child Development, 66(6), 1817–1828.
Marques, T., Pereira, A. I., Barros, L., & Muris, P. (2013). Cognitive vulnerability profiles of highly anxious and non-anxious children. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 44, 777–785.
Mathews, A., & Mackintosh, B. (2000). Induced emotional interpretation bias and anxiety. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109(4), 602.
Mathews, A., Mackintosh, B., & Fulcher, E. P. (1997). Cognitive biases in anxiety and attention to threat. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 1(9), 340–345.
McLeod, B. D., Wood, J. J., & Weisz, J. R. (2007). Examining the association between parenting and childhood anxiety: A meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 27(2), 155–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2006.09.002
Merikangas, K. R., He, J. P., Brody, D., Fisher, P., Bourdon, K., & Koretz, D. S. (2010). Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders among US children in the 2001–2004 NHANES. Pediatrics, 125, 75–81.
Mezulis, A. H., Hyde, J. S., & Clark, R. (2004). Father involvement moderates the effect of maternal depression during a child’s infancy on child behavior problems in kindergarten. Journal of Family Psychology, 18(4), 575.
Micco, J. A., & Ehrenreich, J. T. (2008). Children’s interpretation and avoidant response biases in response to non-salient and salient situations: Relationships with mothers’ threat perception and coping expectations. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 22(3), 371–385.
Michel, N. M., Rowa, K., Young, L., & McCabe, R. E. (2016). Emotional distress tolerance across anxiety disorders. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 40, 94–103.
Mirabile, S. P., Oertwig, D., & Halberstadt, A. G. (2018). Parent emotion socialization and children’s socioemotional adjustment: When is supportiveness no longer supportive? Social Development, 27(3), 466–481.
Morales, M., Mundy, P., Crowson, M., Neal, A. R., & Delgado, C. (2005). Individual differences in infant attention skills, joint attention, and emotion regulation behaviour. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 29(3), 259–263.
Morales, S., Fu, X., & Pérez-Edgar, K. E. (2016). A developmental neuroscience perspective on affect-biased attention. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 21, 26–41.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16(2), 361–388.
Mundy, P., & Jarrold, W. (2010). Infant joint attention, neural networks and social cognition. Neural Networks, 23(8–9), 985–997.
Murphy, J., Brewer, R., Catmur, C., & Bird, G. (2017). Interoception and psychopathology: A developmental neuroscience perspective. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 23, 45–56.
Naragon-Gainey, K., McMahon, T. P., & Chacko, T. P. (2017). The structure of common emotion regulation strategies: A meta-analytic examination. Psychological Bulletin, 143(4), 384.
Nelson, J. A., & Boyer, B. P. (2018). Maternal responses to negative emotions and child externalizing behavior: Different relations for 5-, 6-, and 7-year-olds. Social Development, 27(3), 482–494.
Nord, C. L., & Garfinkel, S. N. (2022). Interoceptive pathways to understand and treat mental health conditions. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 6, 499–513.
Obradović, J. (2016). Physiological responsivity and executive functioning: Implications for adaptation and resilience in early childhood. Child Development Perspectives, 10(1), 65–70.
O’Connor, E. E., Holly, L. E., Chevalier, L. L., Pincus, D. B., & Langer, D. A. (2020). Parent and child emotion and distress responses associated with parental accommodation of child anxiety symptoms. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 76(7), 1390–1407.
Oglesby, M. E., Raines, A. M., Short, N. A., Capron, D. W., & Schmidt, N. B. (2016). Interpretation bias for uncertain threat: A replication and extension. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 51, 35–42.
Oglesby, M. E., Stentz, L. A., Portero, A. K., King, S. L., & Schmidt, N. B. (2019). Exaggerated interpretation bias for uncertain information as a predictor of anxiety-related symptoms: A new method of assessment for IU. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 64, 64–71.
Olatunji, B. O., & Wolitzky-Taylor, K. B. (2009). Anxiety sensitivity and the anxiety disorders: A meta-analytic review and synthesis. Psychological Bulletin, 135(6), 974.
Olatunji, B. O., Deacon, B. J., Abramowitz, J. S., & Valentiner, D. P. (2007). Body vigilance in nonclinical and anxiety disorder samples: Structure, correlates, and prediction of health concerns. Behavior Therapy, 38(4), 392–401.
Ollendick, T. H., & Benoit, K. E. (2012). A parent–child interactional model of social anxiety disorder in youth. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 15, 81–91.
Ollendick, T. H., & Horsch, L. M. (2007). Fears in clinic-referred children: Relations with child anxiety sensitivity, maternal overcontrol, and maternal phobic anxiety. Behavior Therapy, 38(4), 402–411.
Osmanağaoğlu, N., Creswell, C., & Dodd, H. F. (2018). Intolerance of Uncertainty, anxiety, and worry in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 225, 80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.07.035
Ouellet, C., Langlois, F., Provencher, M. D., & Gosselin, P. (2019). Intolerance of uncertainty and difficulties in emotion regulation: Proposal for an integrative model of generalized anxiety disorder. European Review of Applied Psychology, 69(1), 9–18.
Pace-Schott, E. F., Amole, M. C., Aue, T., Balconi, M., Bylsma, L. M., Critchley, H., & VanElzakker, M. B. (2019). Physiological feelings. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 103, 267–304.
Panarello, B., & Bukowski, W. M. (2021). Young adolescent experiences with the intolerance of uncertainty, worry, and anxious arousal across contexts. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science, 53(4), 514–521.
Păsărelu, C. R., Dobrean, A., Balazsi, R., Podina, I. R., & Mongoose, C. (2017). Interpretation biases in the intergenerational transmission of worry: A path analysis. Journal of Evidence-Based Psychotherapies, 17, 1.
Paulus, M. P., & Stein, M. B. (2006). An insular view of anxiety. Biological Psychiatry, 60(4), 383–387.
Paulus, M. P., & Stein, M. B. (2010). Interoception in anxiety and depression. Brain Structure and Function, 214, 451–463.
Paulus, M. P., Feinstein, J. S., & Khalsa, S. S. (2019). An active inference approach to interoceptive psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 15, 97–122.
Pearcey, S., Alkozei, A., Chakrabarti, B., Dodd, H., Murayama, K., Stuijfzand, S., & Creswell, C. (2018). Do clinically anxious children cluster according to their expression of factors that maintain child anxiety? Journal of Affective Disorders, 229, 469–476.
Pérez-Edgar, K., Bar-Haim, Y., McDermott, J. M., Chronis-Tuscano, A., Pine, D. S., & Fox, N. A. (2010). Attention biases to threat and behavioral inhibition in early childhood shape adolescent social withdrawal. Emotion, 10(3), 349.
Pergamin-Hight, L., Bitton, S., Pine, D. S., Fox, N. A., & Bar-Haim, Y. (2016). Attention and interpretation biases and attention control in youth with social anxiety disorder. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology, 7(3), 484–498.
Perlman, S. B., Lunkenheimer, E., Panlilio, C., & Pérez-Edgar, K. (2022). Parent-to-child anxiety transmission through dyadic social dynamics: A dynamic developmental model. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 25(1), 110–129.
Phillips, M. L., Ladouceur, C. D., & Drevets, W. C. (2008). A neural model of voluntary and automatic emotion regulation: Implications for understanding the pathophysiology and neurodevelopment of bipolar disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 13(9), 833–857.
Piao, J., Huang, Y., Han, C., Li, Y., Xu, Y., Liu, Y., & He, X. (2022). Alarming changes in the global burden of mental disorders in children and adolescents from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 31(11), 1827–1845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-022-02040-4
Pickard, H., Hirsch, C., Simonoff, E., & Happé, F. (2020). Exploring the cognitive, emotional and sensory correlates of social anxiety in autistic and neurotypical adolescents. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 61(12), 1317–1327.
Pollatos, O., & Schandry, R. (2008). Emotional processing and emotional memory are modulated by interoceptive awareness. Cognition & Emotion, 22(2), 272–287.
Posner, M. I., & Rothbart, M. K. (2000). Developing mechanisms of self-regulation. Development and Psychopathology, 12(3), 427–441.
Pratt, M., Singer, M., Kanat-Maymon, Y., & Feldman, R. (2015). Infant negative reactivity defines the effects of parent–child synchrony on physiological and behavioral regulation of social stress. Development and Psychopathology, 27(4pt1), 1191–1204.
Qi, J., Rappaport, L. M., Cecilione, J., Hettema, J. M., & Roberson-Nay, R. (2019). Differential associations of distress tolerance and anxiety sensitivity with adolescent internalizing psychopathology. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 50, 97–104.
Quadt, L., Critchley, H. D., & Garfinkel, S. N. (2018). Interoception and emotion: Shared mechanisms and clinical implications. In M. Tsakiris & H. De Preester (Eds.), The interoceptive mind: From homeostasis to awareness (pp. 27–45). Oxford University Press.
Quattrocki, E., & Friston, K. (2014). Autism, oxytocin and interoception. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 47, 410–430.
Quigley, K. S., Kanoski, S., Grill, W. M., Barrett, L. F., & Tsakiris, M. (2021). Functions of interoception: From energy regulation to experience of the self. Trends in Neurosciences, 44(1), 29–38.
Ratliff, E. L., Kerr, K. L., Cosgrove, K. T., Simmons, W. K., & Morris, A. S. (2022). The role of neurobiological bases of dyadic emotion regulation in the development of psychopathology: Cross-brain associations between parents and children. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 25(1), 5–18.
Raval, V. V., & Walker, B. L. (2019). Unpacking ‘culture’: Caregiver socialization of emotion and child functioning in diverse families. Developmental Review, 51, 146–174.
Robinson, L. J., & Freeston, M. H. (2014). Emotion and internal experience in obsessive compulsive disorder: Reviewing the role of alexithymia, anxiety sensitivity and distress tolerance. Clinical Psychology Review, 34(3), 256–271.
Romens, S. E., & Pollak, S. D. (2012). Emotion regulation predicts attention bias in maltreated children at-risk for depression. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(2), 120–127.
Rosenbaum, J. F., Biederman, J., Bolduc-Murphy, E. A., Faraone, S. V., Chaloff, J., Hirshfeld, D. R., & Kagan, J. (1993). Behavioral inhibition in childhood: A risk factor for anxiety disorders. Harvard Review of Psychiatry, 1(1), 2–16.
Roy, A. K., Dennis, T. A., & Warner, C. M. (2015). A critical review of attentional threat bias and its role in the treatment of pediatric anxiety disorders. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 29(3), 171–184.
Roy, A. K., Vasa, R. A., Bruck, M., Mogg, K., Bradley, B. P., Sweeney, M., . . . Pine, D. S. (2008). Attention bias toward threat in pediatric anxiety disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 47, 1189–1196.
Rozenman, M., Amir, N., & Weersing, V. R. (2014). Performance-based interpretation bias in clinically anxious youths: Relationships with attention, anxiety, and negative cognition. Behavior Therapy, 45(5), 594–605.
Sahib, A., Chen, J., Cárdenas, D., & Calear, A. L. (2023). Intolerance of uncertainty and emotion regulation: A meta-analytic and systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2023.102270
Saleem, S., Renshaw, K. D., Azhar, M., Giff, S. T., & Mahmood, Z. (2021). Interactive effects of perceived parental rearing styles on distress tolerance and psychological distress in Pakistani university students. Journal of Adult Development, 28, 309–318.
San Martín, C., Jacobs, B., & Vervliet, B. (2020). Further characterization of relief dynamics in the conditioning and generalization of avoidance: Effects of distress tolerance and intolerance of uncertainty. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 124, 103526.
Sandstrom, A., Uher, R., & Pavlova, B. (2020). Prospective association between childhood behavioral inhibition and anxiety: A meta-analysis. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 48, 57–66.
Schaan, L., Schulz, A., Nuraydin, S., Bergert, C., Hilger, A., Rach, H., & Hechler, T. (2019). Interoceptive accuracy, emotion recognition, and emotion regulation in preschool children. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 138, 47–56.
Schachter, S., & Singer, J. (1962). Cognitive, social, and physiological determinants of emotional state. Psychological Review, 69(5), 379.
Schiele, M. A., Vietz, M., Gajewska, A., Unterecker, S., Gottschalk, M. G., Deckert, J., & Domschke, K. (2021). The cognitive anxiety sensitivity treatment (CAST) in anxiety prevention-Focus on separation anxiety and interoception. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 53, 104–113.
Schmeichel, B. J., & Tang, D. (2014). The relationship between individual differences in executive functioning and emotion regulation: A comprehensive review. In J. P. Forgas & E. Harmon-Jones (Eds.), Motivation and its regulation: The control within (pp. 133–152). Psychology Press.
Schmidt, N. B., Keough, M. E., Mitchell, M. A., Reynolds, E. K., MacPherson, L., Zvolensky, M. J., & Lejuez, C. W. (2010). Anxiety sensitivity: Prospective prediction of anxiety among early adolescents. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 24(5), 503–508.
Schwartz, C. E., Snidman, N., & Kagan, J. (1999). Adolescent social anxiety as an outcome of inhibited temperament in childhood. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 38(8), 1008–1015.
Segal, S. C., & Gobin, K. C. (2022). Threat-biased attention in childhood anxiety: A cognitive-affective developmental model. Journal of Affective Disorders Reports, 8, 1–9.
Seth, A. K. (2014). A predictive processing theory of sensorimotor contingencies: Explaining the puzzle of perceptual presence and its absence in synesthesia. Cognitive Neuroscience, 5(2), 97–118.
Shaffer, A., Suveg, C., Thomassin, K., & Bradbury, L. L. (2012). Emotion socialization in the context of family risks: Links to child emotion regulation. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 21, 917–924.
Shaw, A. M., Halliday, E. R., Tonarely, N. A., & Ehrenreich-May, J. (2021). Relationship of affect intolerance with anxiety, depressive, and obsessive-compulsive symptoms in youth. Journal of Affective Disorders, 280, 34–44.
Shechner, T., Britton, J. C., Pérez-Edgar, K., Bar-Haim, Y., Ernst, M., Fox, N. A., & Pine, D. S. (2012). Attention biases, anxiety, and development: Toward or away from threats or rewards? Depression and Anxiety, 29(4), 282–294.
Shen, Y., Luo, Z., Fu, D., Qie, M., & Wang, L. (2020). Parenting profiles, intolerance of uncertainty, and worry among Chinese primary school children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 29(8), 2303–2313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-020-01755-9
Simons, J. S., & Gaher, R. M. (2005). The Distress Tolerance Scale: Development and validation of a self-report measure. Motivation and Emotion, 29(2), 83–102.
Simons, R. L., Simons, L. G., Burt, C. H., Drummund, H., Stewart, E., Brody, G. H., & Cutrona, C. (2006). Supportive parenting moderates the effect of discrimination upon anger, hostile view of relationships, and violence among African American boys. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 47(4), 373–389.
Smith, E. M., Reynolds, S., Orchard, F., Whalley, H. C., & Chan, S. W. (2018). Cognitive biases predict symptoms of depression, anxiety and wellbeing above and beyond neuroticism in adolescence. Journal of Affective Disorders, 241, 446–453.
Song, J. H., Miller, A. L., Leung, C. Y., Lumeng, J. C., & Rosenblum, K. L. (2018). Positive parenting moderates the association between temperament and self-regulation in low-income toddlers. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 27, 2354–2364.
Songco, A., Booth, C., Spiegler, O., Parsons, S., & Fox, E. (2020). Anxiety and depressive symptom trajectories in adolescence and the co-occurring development of cognitive biases: Evidence from the CogBIAS longitudinal study. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 48, 1617–1633.
Spence, S. H., & Rapee, R. M. (2016). The etiology of social anxiety disorder: An evidence-based model. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 86, 50–67.
Stein, D. J. (2006). Advances in understanding the anxiety disorders: The cognitive-affective neuroscience of ‘false alarms.’ Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 18(3), 173–182.
Stuijfzand, S., Creswell, C., Field, A. P., Pearcey, S., & Dodd, H. (2018). Research Review: Is anxiety associated with negative interpretations of ambiguity in children and adolescents? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 59(11), 1127–1142.
Suarez, L., & Bell-Dolan, D. (2001). The relationship of child worry to cognitive biases: Threat interpretation and likelihood of event occurrence. Behavior Therapy, 32(3), 425–442.
Suarez, G. L., Morales, S., Miller, N. V., Penela, E. C., Chronis-Tuscano, A., Henderson, H. A., & Fox, N. A. (2021). Examining a developmental pathway from early behavioral inhibition to emotion regulation and social anxiety: The moderating role of parenting. Developmental Psychology, 57(8), 1261.
Tan, P. Z., Forbes, E. E., Dahl, R. E., Ryan, N. D., Siegle, G. J., Ladouceur, C. D., & Silk, J. S. (2012). Emotional reactivity and regulation in anxious and nonanxious youth: A cell-phone ecological momentary assessment study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(2), 197–206.
Tan, P. Z., Oppenheimer, C. W., Ladouceur, C. D., Butterfield, R. D., & Silk, J. S. (2020). A review of associations between parental emotion socialization behaviors and the neural substrates of emotional reactivity and regulation in youth. Developmental Psychology, 56(3), 516.
Teachman, B. A. (2005). Information processing and anxiety sensitivity: Cognitive vulnerability to panic reflected in interpretation and memory biases. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 29, 479–499.
Terasawa, Y., Moriguchi, Y., Tochizawa, S., & Umeda, S. (2014). Interoceptive sensitivity predicts sensitivity to the emotions of others. Cognition and Emotion, 28(8), 1435–1448.
Thomas, A., & Chess, S. (1977). Temperament and development. Brunner/Mazel.
Thompson-Hollands, J., Kerns, C. E., Pincus, D. B., & Comer, J. S. (2014). Parental accommodation of child anxiety and related symptoms: Range, impact, and correlates. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 28(8), 765–773.
Tottenham, N., & Gabard-Durnam, L. J. (2017). The developing amygdala: A student of the world and a teacher of the cortex. Current Opinion in Psychology, 17, 55–60.
Trent, E. S., Viana, A. G., Raines, E. M., Woodward, E. C., Candelari, A. E., Storch, E. A., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2020). Interpretation biases and childhood anxiety: The moderating role of parasympathetic nervous system reactivity. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 48(3), 419–433.
Trent, E. S., Viana, A. G., Raines, E. M., Conroy, H. E., Storch, E. A., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2021). Interpretation biases and depressive symptoms among anxiety-disordered children: The role of individual differences in respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Developmental Psychobiology, 63(2), 320–337.
Trent, E. S., Viana, A. G., Raines, E. M., Conroy, H. E., Woodward, E. C., Storch, E. A., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2022). Fearful temperament and child social anxiety symptoms: Clarifying the influence of maternal punitive responses. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 50(1), 63–75.
Troller‐Renfree, S. V., Buzzell, G. A., Bowers, M. E., Salo, V. C., Forman‐Alberti, A., Smith, E., ... & Fox, N. A. (2019). Development of inhibitory control during childhood and its relations to early temperament and later social anxiety: Unique insights provided by latent growth modeling and signal detection theory. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 60(6), 622–629.
Tsakiris, M., & Critchley, H. (2016). Interoception beyond homeostasis: Affect, cognition and mental health. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B, 371, 0002.
Tsujimoto, S. (2008). The prefrontal cortex: Functional neural development during early childhood. The Neuroscientist, 14(4), 345–358.
Valadez, E. A., Troller-Renfree, S. V., Buzzell, G. A., Henderson, H. A., Chronis-Tuscano, A., Pine, D. S., & Fox, N. A. (2021). Behavioral inhibition and dual mechanisms of anxiety risk: Disentangling neural correlates of proactive and reactive control. JCPP Advances, 1(2), e12022.
van Bockstaele, B., Notebaert, L., MacLeod, C., Salemink, E., Clarke, P. J., Verschuere, B., & Wiers, R. W. (2019). The effects of attentional bias modification on emotion regulation. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 62, 38–48.
van der Bruggen, C. O., Stams, G. J. J. M., & Bögels, S. M. (2008). Research review: The relation between child and parent anxiety and parental control: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(12), 1257–1269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01898.x
Varela, R. E., Niditch, L. A., Hensley-Maloney, L., Moore, K. W., & Creveling, C. C. (2013). Parenting practices, interpretive biases, and anxiety in Latino children. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 27(2), 171–177.
Viana, A. G., Dixon, L. J., Stevens, E. N., & Ebesutani, C. (2016). Parental emotion socialization strategies and their interaction with child interpretation biases among children with anxiety disorders. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 40, 717–731.
Waite, P., & Creswell, C. (2015). Observing interactions between children and adolescents and their parents: The effects of anxiety disorder and age. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 43(6), 1079–1091.
Waite, P., Codd, J., & Creswell, C. (2015). Interpretation of ambiguity: Differences between children and adolescents with and without an anxiety disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 188, 194–201.
Wang, Z., Whiteside, S. P., Sim, L., Farah, W., Morrow, A. S., Alsawas, M., & Murad, M. H. (2017). Comparative effectiveness and safety of cognitive behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy for childhood anxiety disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatrics, 171(11), 1049–1056.
Warner, E. N., & Strawn, J. R. (2023). Risk Factors for Pediatric Anxiety Disorders. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics, 32(3), 485–510.
Waters, A. M., Mogg, K., Bradley, B. P., & Pine, D. S. (2008). Attentional bias for emotional faces in children with generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 47, 435–442. https://doi.org/10.1097/CHI.0b013e3181642992
Waters, A. M., Henry, J., Mogg, K., Bradley, B. P., & Pine, D. S. (2010). Attentional bias towards angry faces in childhood anxiety disorders. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 41(2), 158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2009.12.001
Watts, S. E., & Weems, C. F. (2006). Associations among selective attention, memory bias, cognitive errors and symptoms of anxiety in youth. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 34, 838–849.
Wauters, A., Noel, M., Van Ryckeghem, D. M., Sanchez-Lopez, A., & Vervoort, T. (2020). Parental (non-) pain attending verbalizations moderate the relationship between child attention and memory bias for pain. European Journal of Pain, 24(9), 1797–1811.
Weinberg, A., Riesel, A., & Hajcak, G. (2012). Integrating multiple perspectives on error-related brain activity: The ERN as a neural indicator of trait defensive reactivity. Motivation and Emotion, 36, 84–100.
White, L. K., Helfinstein, S. M., & Fox, N. A. (2010). Temperamental factors associated with the acquisition of information processing biases and anxiety. In J. A. Hadwin & A. P. Field (Eds.), Information processing biases and anxiety: A developmental perspective (pp. 233–252). Wiley-Blackwell.
White, L. K., Suway, J. G., Pine, D. S., Bar-Haim, Y., & Fox, N. A. (2011). Cascading effects: The influence of attention bias to threat on the interpretation of ambiguous information. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49(4), 244–251.
White, L. K., Degnan, K. A., Henderson, H. A., Pérez-Edgar, K., Walker, O. L., Shechner, T., Leibenluft, E., Bar-Haim, Y., Pine, D. S., & Fox, N. A. (2017). Developmental relations among behavioral inhibition, anxiety, and attention biases to threat and positive information. Child Development, 88(1), 141–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12696
Wieser, M. J., & Keil, A. (2020). Attentional threat biases and their role in anxiety: A neurophysiological perspective. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 153, 148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2020.05.004
Woodruff-Borden, J., Morrow, C., Bourland, S., & Cambron, S. (2002). The behavior of anxious parents: Examining mechanisms of transmission of anxiety from parent to child. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 31, 364–374.
Woodward, E. C., Viana, A. G., Raines, E. M., Trent, E. S., Candelari, A. E., Storch, E. A., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2020). Parental emotion-focused behaviors moderate the relationship between perceptual sensitivity and fear reactivity in anxious children. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 51, 542–551.
Wright, K. D., Lebell, M. A. N. A., & Carleton, R. N. (2016). Intolerance of uncertainty, anxiety sensitivity, health anxiety, and anxiety disorder symptoms in youth. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 41, 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2016.04.011
Yiend, J. (2010). The effects of emotion on attention: A review of attentional processing of emotional information. Cognition and Emotion, 24(1), 3–47.
Zelazo, P. D., Carlson, S. M., & Kesek, A. (2008). The development of executive function in childhood. In C. A. Nelson & M. Luciana (Eds.), Handbook of Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience (pp. 553–574). Boston Review.
Zlomke, K. R., & Young, J. N. (2009). A retrospective examination of the role of parental anxious rearing behaviors in contributing to intolerance of uncertainty. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 18, 670–679.
Zvolensky, M. J., Vujanovic, A. A., Bernstein, A., & Leyro, T. (2010). Distress tolerance: Theory, measurement, and relations to psychopathology. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 19(6), 406–410.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, K.B., Tan, P.Z., Sullivan, J.A. et al. An Integrative Model of Youth Anxiety: Cognitive-Affective Processes and Parenting in Developmental Context. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 26, 1025–1051 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-023-00458-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-023-00458-z