Abstract
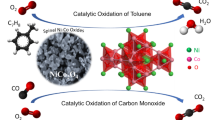
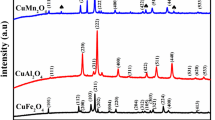
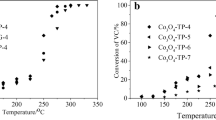
Co3O4 has been applied in several catalytic fields as a favorite catalyst. However, its performance is still not enough to replace noble metal catalysts in the catalytic oxidation of toluene. Modifications are needed to enhance its activity. Herein, a series of spinel nanoparticle catalysts ACo2O4 (A = Cu, Ni, and Mn) were synthesized by a simple template-free solvothermal process and applied to toluene oxidation. A fixed-bed reactor was used to investigate the catalytic activity. The CuCo2O4 catalyst showed the best activity with T50 = 225 °C and T90 = 239 °C, which was much better than the other two catalysts. This demonstrated that tetrahedral A-site cation is crucial in determining the activity of ACo2O4 catalysts. Higher Co3+ concentration (Co3+/Co2+ = 1.96), more surface-adsorbed oxygen species (Oads/O = 36.67%), and enhanced low-temperature reducibility, which are outcomes of cation substitution, are fundamental causes of efficient activity. In addition, the CuCo2O4 catalyst showed good long-term stability after 30 h of reaction, and the toluene conversion rate remained above 95% at 250 °C, which has considerable potential for practical application.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamal MS, Razzak SA, Hossain MM (2016) Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—A review. Atmos Environ 140:117–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.05.031
Deng J, He S, Xie S, Yang H, Liu Y, Guo G, Dai H (2015) Ultralow loading of silver nanoparticles on Mn2O3 nanowires derived with molten salts: a high-efficiency catalyst for the oxidative removal of toluene. Environ Sci Technol 49(18):11089–11095. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02350
Charbotel B, Fervers B, Droz JP (2014) Occupational exposures in rare cancers: A critical review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 90(2):99–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.12.004
Vandenbroucke AM, Morent R, De Geyter N, Leys C (2011) Non-thermal plasmas for non-catalytic and catalytic VOC abatement. J Hazard Mater 195:30–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.060
Li X, Zhang L, Yang Z, Wang P, Yan Y, Ran J (2020) Adsorption materials for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the key factors for VOCs adsorption process: A review. Sep Purif Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116213
Everaert K, Baeyens J (2004) Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds. J Hazard Mater 109(1–3):113–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.03.019
Xia Y, Xia L, Liu Y, Yang T, Deng J, Dai H (2018) Concurrent catalytic removal of typical volatile organic compound mixtures over Au-Pd/alpha-MnO(2) nanotubes. J Environ Sci (China) 64:276–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.06.025
Sedjame H-J, Fontaine C, Lafaye G, Barbier J Jr (2014) On the promoting effect of the addition of ceria to platinum based alumina catalysts for VOCs oxidation. Appl Catal B 144:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.022
Liotta LF (2010) Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds on supported noble metals. Appl Catal B 100(3–4):403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.08.023
Li J-J, Yu E-Q, Cai S-C, Chen X, Chen J, Jia H-P, Xu Y-J (2019) Noble metal free, CeO2/LaMnO3 hybrid achieving efficient photo-thermal catalytic decomposition of volatile organic compounds under IR light. Appl Catal B 240:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.08.069
Einaga H, Hyodo S, Teraoka Y (2010) Complete oxidation of benzene over perovskite-type oxide catalysts. Top Catal 53(7–10):629–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-010-9497-5
Liu Q, Wang L-C, Chen M, Cao Y, He H-Y, Fan K-N (2009) Dry citrate-precursor synthesized nanocrystalline cobalt oxide as highly active catalyst for total oxidation of propane. J Catal 263(1):104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2009.01.018
Kołodziej A, Łojewska J, Tyczkowski J, Jodłowski P, Redzynia W, Iwaniszyn M, Zapotoczny S, Kuśtrowski P (2012) Coupled engineering and chemical approach to the design of a catalytic structured reactor for combustion of VOCs: Cobalt oxide catalyst on knitted wire gauzes. Chem Eng J 200–202:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.067
Xie X, Li Y, Liu ZQ, Haruta M, Shen W (2009) Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods. Nature 458(7239):746–749. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07877
Zhai G, Wang J, Chen Z, An W, Men Y (2018) Boosting soot combustion efficiency of Co3O4 nanocrystals via tailoring crystal facets. Chem Eng J 337:488–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.141
Bai G, Dai H, Deng J, Liu Y, Wang F, Zhao Z, Qiu W, Au CT (2013) Porous Co3O4 nanowires and nanorods: Highly active catalysts for the combustion of toluene. Appl Catal A 450:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2012.09.054
X Wang, Y Liu, T Zhang, Y Luo, Z Lan, K Zhang, J Zuo, L Jiang, R Wang (2017) Geometrical-site-dependent catalytic activity of ordered mesoporous co-based spinel for benzene oxidation: in situ DRIFTS study coupled with Raman and XAFS spectroscopy. ACS Catal. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b03547
González-Prior J, López-Fonseca R, Gutiérrez-Ortiz JI, de Rivas B (2016) Oxidation of 1,2-dichloroethane over nanocube-shaped Co3O4 catalysts. Appl Catal B 199:384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.046
Lim TH, Park SB, Kim JM, Kim DH (2017) Ordered mesoporous MCo2O4 (M = Cu, Zn and Ni) spinel catalysts with high catalytic performance for methane combustion. J Mol Catal A: Chem 426:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.11.002
Wang X, Zhao W, Wu X, Zhang T, Liu Y, Zhang K, Xiao Y, Jiang L (2017) Total oxidation of benzene over ACo 2 O 4 (A = Cu, Ni and Mn) catalysts: In situ DRIFTS account for understanding the reaction mechanism. Appl Surf Sci 426:1198–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.269
Li H, Sun Z, Tian Y, Cui G, Yan S (2015) Facile and cost-effective synthesis of CNT@MCo2O4 (M = Ni, Mn, Cu, Zn) core–shell hybrid nanostructures for organic dye removal. RSC Adv 5(97):79765–79773. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra14748d
Zhu J, Gao Q (2009) Mesoporous MCo2O4 (M=Cu, Mn and Ni) spinels: Structural replication, characterization and catalytic application in CO oxidation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 124(1–3):144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.05.003
Hu J, Zhou J, Zhang T, Liu S, Du K (2022) Characterization and performance of SmxA1-xMnO3 (A=Ce, Sr, Ca) perovskite for efficient catalytic oxidation of toluene. Korean J Chem Eng 39(11):3032–3038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1194-0
Li G, Li L, Shi J, Yuan Y, Li Y, Zhao W, Shi J (2014) One-pot pyrolytic synthesis of mesoporous MCo2O4(4.5) (M=Mn, Ni, Fe, Cu) spinels and its high efficient catalytic properties for CO oxidation at low temperature. J Mol Catal A: Chem 390:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2014.03.012
K Li, T Li, Y Dai, Y Quan, J Zhao, J Ren 2022 Highly active urchin-like MCo2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Ni or Zn) spinel for toluene catalytic combustion. Fuel. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123648
Marco JF, Gancedo JR, Gracia M, Gautier JL, Ríos E, Berry FJ (2000) Characterization of the nickel cobaltite, NiCo2O4, Prepared by several methods: An XRD, XANES, EXAFS, and XPS study. J Solid State Chem 153(1):74–81. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.2000.8749
Ma F-X, Yu L, Xu C-Y, Lou XW (2016) Self-supported formation of hierarchical NiCo2O4tetragonal microtubes with enhanced electrochemical properties. Energy Environ Sci 9(3):862–866. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ee03772g
Han X, He G, He Y, Zhang J, Zheng X, Li L, Zhong C, Hu W, Deng Y, Ma TY (2017) Engineering catalytic active sites on cobalt oxide surface for enhanced oxygen electrocatalysis. Adv Energy Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201702222
Zeng J, Xie H, Zhang G, Cheng X, Zhou G, Jiang Y (2020) Facile synthesis of CuCo spinel composite oxides for toluene oxidation in air. Ceram Int 46(13):21542–21550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.257
Wang D, Cuo Z, Li S, Zhang M, Chen Y (2020) In situ anchored NiCo2O4 on a nickel foam as a monolithic catalyst by electro-deposition for improved benzene combustion performance. CrystEngComm 22(13):2371–2379. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ce00095g
Fang Z, Rehman Su, Sun M, Yuan Y, Jin S, Bi H (2018) Hybrid NiO–CuO mesoporous nanowire array with abundant oxygen vacancies and a hollow structure as a high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor. J Mater Chem A 6(42):21131–21142. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta08262f
Zhao S, Li K, Jiang S, Li J (2016) Pd–Co based spinel oxides derived from pd nanoparticles immobilized on layered double hydroxides for toluene combustion. Appl Catal B 181:236–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.08.001
Teng F, Chen M, Li G, Teng Y, Xu T, Hang Y, Yao W, Santhanagopalan S, Meng DD, Zhu Y (2011) High combustion activity of CH4 and catalluminescence properties of CO oxidation over porous Co3O4 nanorods. Appl Catal B 110:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.08.035
Zhang C, Wang J, Yang S, Liang H, Men Y (2019) Boosting total oxidation of acetone over spinel MCo(2)O(4) (M = Co, Ni, Cu) hollow mesoporous spheres by cation-substituting effect. J Colloid Interface Sci 539:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.12.061
Lu C-Y, Tseng H-H, Wey M-Y, Liu L-Y, Kuo J-H, Chuang K-H (2009) Al2O3-supported Cu–Co bimetallic catalysts prepared with polyol process for removal of BTEX and PAH in the incineration flue gas. Fuel 88(2):340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.09.012
Yan Q, Li X, Zhao Q, Chen G (2012) Shape-controlled fabrication of the porous Co3O4 nanoflower clusters for efficient catalytic oxidation of gaseous toluene. J Hazard Mater 209–210:385–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.039
Wang Y, Arandiyan H, Liu Y, Liang Y, Peng Y, Bartlett S, Dai H, Rostamnia S, Li J (2018) Template-free scalable synthesis of flower-like Co3-xMnxO4 spinel catalysts for toluene oxidation. ChemCatChem 10(16):3429–3434. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201800598
Wang X, Wen W, Mi J, Li X, Wang R (2015) The ordered mesoporous transition metal oxides for selective catalytic reduction of NOx at low temperature. Appl Catal B 176–177:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.038
Zhao H, Wang H, Qu Z (2022) Synergistic effects in Mn-Co mixed oxide supported on cordierite honeycomb for catalytic deep oxidation of VOCs. J Environ Sci (China) 112:231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.05.003
Tang W, Li W, Li D, Liu G, Wu X, Chen Y (2014) Synergistic effects in porous Mn–Co mixed oxide nanorods enhance catalytic deep oxidation of benzene. Catal Lett 144(11):1900–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-014-1340-3
Luo Y, Zheng Y, Zuo J, Feng X, Wang X, Zhang T, Zhang K, Jiang L (2018) Insights into the high performance of Mn-Co oxides derived from metal-organic frameworks for total toluene oxidation. J Hazard Mater 349:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.053
Li X, Li X, Zeng X, Zhu T (2019) Correlation between the physicochemical properties and catalytic performances of micro/mesoporous CoCeO mixed oxides for propane combustion. Appl Catal A 572:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2018.12.026
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chengdu Science and Technology Innovation Program (2022-YF05-00159-SN) and Opening Project of Oil & Gas Field Applied Chemistry Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (YQKF202113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuge, X., Zhou, J., Chen, Z. et al. Efficient Spinel Nanoparticle Catalysts ACo2O4(A = Cu, Ni, Mn) for Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene: Cation Substitution Effects. Catal Lett 154, 2036–2045 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-023-04460-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-023-04460-6