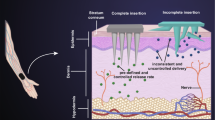
Abstract
Traditional drug delivery systems, using invasive, transdermal, and oral routes, are limited by various factors, such as the digestive system environment, skin protection, and sensory nerve stimulation. To improve the drug delivery system, we fabricated a polysaccharide-based, dissolvable microneedle-based array, which combines the advantages of both invasive and transdermal delivery systems, and promises to be an innovative solution for minimally invasive drug delivery. In this study, we designed a reusable aluminum mold that greatly improved the efficiency and convenience of microneedle fabrication. Physical characterization of the polysaccharides, individual or mixed at different ratios, was performed to identify a suitable molecule to fabricate the dissolvable microneedle. We used a vacuum deposition-based micro-molding method at low temperature to fabricate the model. Using a series of checkpoints from material into product, a systematic feedback mechanism was built into the “all-in-one” fabrication step, which helped to improve production yields. The physical properties of the fabricated microneedle were assessed. The cytotoxicity analysis and animal testing of the microneedle demonstrated the safety and compatibility of the microneedle, and the successful penetration and effective release of a model protein.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Agarwal, S.N. Narayana, K. Pal, K. Pramanik, S. Giri, I. Banerjee, Calcium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose beads for colon-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 75, 409–417 (2015)
C.S. Asbill, B.B. Michniak, Percutaneous penetration enhancers: Local versus transdermal activity. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 3, 36–41 (2000)
M.M. Badran, J. Kuntsche, A. Fahr, Skin penetration enhancement by a microneedle device (Dermaroller) in vitro: Dependency on needle size and applied formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 36, 511–523 (2009)
R.L. Bronaugh, H.I. Maibach, Percutaneous absorption : Drugs, cosmetics, mechanisms, methodology, 4th edn. (Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, 2005)
Y.C. Chen, H.O. Ho, D.Z. Liu, W.S. Siow, M.T. Sheu, Swelling/floating capability and drug release characterizations of gastroretentive drug delivery system based on a combination of hydroxyethyl cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. PLoS One 10, e0116914 (2015)
K. Cheung, T. Han, D.B. Das, Effect of force of microneedle insertion on the permeability of insulin in skin. J. Diabetes. Sci. Technol. 8, 444–452 (2014)
S. Chillo, J. Laverse, P.M. Falcone, M.A. Del Nobile, Effect of carboxymethylcellulose and pregelatinized corn starch on the quality of amaranthus spaghetti. J. Food Eng. 83, 492–500 (2007)
L.Y. Chu, M.R. Prausnitz, Separable arrowhead microneedles. J. Control. Release 149, 242–249 (2011)
Z. Ding, F.J. Verbaan, M. Bivas-Benita, L. Bungener, A. Huckriede, D.J. van den Berg, G. Kersten, J.A. Bouwstra, Microneedle arrays for the transcutaneous immunization of diphtheria and influenza in BALB/c mice. J. Control. Release 136, 71–78 (2009)
J. Hadgraft, J. Peck, D.G. Williams, W.J. Pugh, G. Allan, Mechanisms of action of skin penetration enhancers/retarders: Azone and analogues. Int. J. Pharm. 141, 17–25 (1996)
U.O. Hafeli, A. Mokhtari, D. Liepmann, B. Stoeber, In vivo evaluation of a microneedle-based miniature syringe for intradermal drug delivery. Biomed. Microdevices 11, 943–950 (2009)
T. Higashiyama, Novel functions and applications of trehalose. Pure Appl. Chem. 74, 1263–1269 (2002)
S. Hirobe, H. Azukizawa, T. Hanafusa, K. Matsuo, Y.S. Quan, F. Kamiyama, I. Katayama, N. Okada, S. Nakagawa, Clinical study and stability assessment of a novel transcutaneous influenza vaccination using a dissolving microneedle patch. Biomaterials 57, 50–58 (2015)
H. Jeong, K.B. Shepard, G.E. Purdum, Y.L. Guo, Y.L. Loo, C.B. Arnold, R.D. Priestley, Additive growth and crystallization of polymer films. Macromolecules 49, 2860–2867 (2016)
S. Kaushik, A.H. Hord, D.D. Denson, D.V. McAllister, S. Smitra, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Lack of pain associated with microfabricated microneedles. Anesth. Analg. 92, 502–504 (2001)
C.J. Ke, Y.J. Lin, Y.C. Hu, W.L. Chiang, K.J. Chen, W.C. Yang, H.L. Liu, C.C. Fu, H.W. Sung, Multidrug release based on microneedle arrays filled with pH-responsive PLGA hollow microspheres. Biomaterials 33, 5156–5165 (2012)
Y.C. Kim, J.H. Park, M.R. Prausnitz, Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 1547–1568 (2012)
S. Kommareddy, B.C. Baudner, S. Oh, S.Y. Kwon, M. Singh, D.T. O'Hagan, Dissolvable microneedle patches for the delivery of cell-culture-derived influenza vaccine antigens. J. Pharm. Sci. 101, 1021–1027 (2012)
R. Langer, Drug delivery. Drugs on target. Science 293, 58–59 (2001)
J.W. Lee, J.H. Park, M.R. Prausnitz, Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Biomaterials 29, 2113–2124 (2008)
K. Lee, C.Y. Lee, H. Jung, Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug administration prepared by stepwise controlled drawing of maltose. Biomaterials 32, 3134–3140 (2011)
I.C. Lee, W.M. Lin, J.C. Shu, S.W. Tsai, C.H. Chen, M.T. Tsai, Formulation of two-layer dissolving polymeric microneedle patches for insulin transdermal delivery in diabetic mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 105, 84–93 (2017)
G. Li, A. Badkar, S. Nema, C.S. Kolli, A.K. Banga, In vitro transdermal delivery of therapeutic antibodies using maltose microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 368, 109–115 (2009)
W. Lin, M. Cormier, A. Samiee, A. Griffin, B. Johnson, C.L. Teng, G.E. Hardee, P.E. Daddona, Transdermal delivery of antisense oligonucleotides with microprojection patch (Macroflux) technology. Pharm. Res. 18, 1789–1793 (2001)
S. Liu, M.N. Jin, Y.S. Quan, F. Kamiyama, H. Katsumi, T. Sakane, A. Yamamoto, The development and characteristics of novel microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid, and their application in the transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 161, 933–941 (2012)
W. Martanto, S.P. Davis, N.R. Holiday, J. Wang, H.S. Gill, M.R. Prausnitz, Transdermal delivery of insulin using microneedles in vivo. Pharm. Res. 21, 947–952 (2004)
C.J. Martin, C.J. Allender, K.R. Brain, A. Morrissey, J.C. Birchall, Low temperature fabrication of biodegradable sugar glass microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 158, 93–101 (2012)
D.V. McAllister, P.M. Wang, S.P. Davis, J.H. Park, P.J. Canatella, M.G. Allen, M.R. Prausnitz, Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 13755–13760 (2003)
K. Migalska, D.I. Morrow, M.J. Garland, R. Thakur, A.D. Woolfson, R.F. Donnelly, Laser-engineered dissolving microneedle arrays for transdermal macromolecular drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 28, 1919–1930 (2011)
J.A. Mikszta, J.B. Alarcon, J.M. Brittingham, D.E. Sutter, R.J. Pettis, N.G. Harvey, Improved genetic immunization via micromechanical disruption of skin-barrier function and targeted epidermal delivery. Nat. Med. 8, 415–419 (2002)
Y.H. Park, S.K. Ha, I. Choi, K.S. Kim, J. Park, N. Choi, B. Kim, J.H. Sung, Fabrication of degradable carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) microneedle with laser writing and replica molding process for enhancement of transdermal drug delivery. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 21, 110–118 (2016)
D. Pasqui, P. Torricelli, M. De Cagna, M. Fini, R. Barbucci, Carboxymethyl cellulose-hydroxyapatite hybrid hydrogel as a composite material for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 102, 1568–1579 (2014)
R.J. Pettis, A.J. Harvey, Microneedle delivery: Clinical studies and emerging medical applications. Ther. Deliv. 3, 357–371 (2012)
M.R. Prausnitz, R. Langer, Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1261–1268 (2008)
A.P. Raphael, T.W. Prow, M.L. Crichton, X. Chen, G.J. Fernando, M.A. Kendall, Targeted, needle-free vaccinations in skin using multilayered, densely-packed dissolving microprojection arrays. Small 6, 1785–1793 (2010)
S.P. Sullivan, N. Murthy, M.R. Prausnitz, Minimally invasive protein delivery with rapidly dissolving polymer microneedles. Adv. Mater. 20, 933–938 (2008)
S.P. Sullivan, D.G. Koutsonanos, M. Del Pilar Martin, J.W. Lee, V. Zarnitsyn, S.O. Choi, N. Murthy, R.W. Compans, I. Skountzou, M.R. Prausnitz, Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 16, 915–920 (2010)
T.M. Tuan-Mahmood, M.T. McCrudden, B.M. Torrisi, E. McAlister, M.J. Garland, T.R. Singh, R.F. Donnelly, Microneedles for intradermal and transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 50, 623–637 (2013)
A.M. Wokovich, S. Prodduturi, W.H. Doub, A.S. Hussain, L.F. Buhse, Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 64, 1–8 (2006)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University System of Taipei Joint Research Program for funding support (NTUT-TMU-103-03; USTP-NTUT-TMU-105-04). We also thank the National Laboratory Animal Center for their help in carrying out the skin penetration studies in mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwa, KY., Chang, V.H.S., Cheng, YY. et al. Analyzing polymeric matrix for fabrication of a biodegradable microneedle array to enhance transdermal delivery. Biomed Microdevices 19, 84 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0224-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0224-x