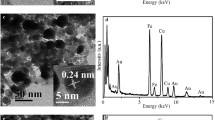
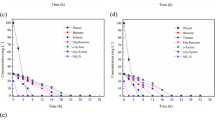
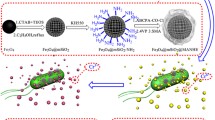
Abstract
Efficient biodegradation may offer a solution for the treatment of nitro-aromatic compounds (NACs) with toxicity, mutagenicity and persistence in the environment. In this study, dopamine (DA) functionalized magnetic nanoparticles with biocompatibility and hydrophilicity were synthesized and utilized for the immobilization of nitro-aromatic compounds degrading psychrophile Psychrobacter sp. ANT206 harboring the cold-adapted nitroreductase. The prepared nanocarriers were characterized using multiple methods. The highest immobilization yield of cells immobilized by Fe3O4@SiO2@DA was 90.67% under the optimized conditions of 10 °C, pH 7.5, 2 h and cell/support 1.2 mg/mg, and the activity recovery was 89.41%. In addition, the obtained immobilized cells displayed excellent salinity stability and reusability. Moreover, immobilized P. sp. ANT206 strains showed remarkable biodegradation capability on nitrobenzene and p-nitrophenol. This study introduced those novel Fe3O4@SiO2@DA nanoparticles could be applied as ideal and low-cost nanocarriers for the immobilization of cells and large-scale bioremediation of hazardous NACs with perspective applications under low temperature.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials are included in this article.
References
Ailijiang N, Chang JL, Liang P, Li P, Wu Q, Zhang XY, Huang X (2016) Electrical stimulation on biodegradation of phenol and responses of microbial communities in conductive carriers supported biofilms of the bioelectrochemical reactor. Bioresour Technol 201:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.026
Bilal M, Mehmood S, Rasheed T, Iqbal HMN (2019) Bio-catalysis and biomedical perspectives of magnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers. Magnetochemistry 5:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5030042
Chen P, Cao ZF, Wang S, Zhong H (2018) In situ nano-silicate functionalized magnetic composites by (poly)dopamine to improve MB removal. Colloid Surface A 552:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.05.027
Chuang J, Choi J, Chuang S (2020) Pilot study of specific microbe immobilization cells (SMICs) technology in removing tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide for reuse of low-strength electronics wastewater. J Hazard Mater 384:120829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120829
Deng MF, Zhao H, Zhang SP, Tian CY, Du PH, Liu CM, Cao HB, Li HP (2015) High catalytic activity of immobilized laccase on core-shell magnetic nanoparticles by dopamine self-polymerization[J]. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 112:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.11.012
Dey C, Das A, Goswami MM (2019) Dopamine loaded SiO2 coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles: a new anticancer agent in pH-dependent drug delivery. ChemistrySelect 4:12190–12196. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201902909
Ebrahimzadeh MA, Mortazavi-Derazkola S, Zazouli MA (2019) Eco-friendly green synthesis and characterization of novel Fe3O4/SiO2/Cu2O-Ag nanocomposites using Crataegus pentagyna fruit extract for photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants. J Mater Sci-Mater El 30:10994–11004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01440-8
Fan XM, Shen JJ, Xu YY, Gao J, Zhang YW (2021) Metabolic integration of azide functionalized glycan on Escherichia coli cell surface for specific covalent immobilization onto magnetic nanoparticles with click chemistry. Bioresour Technol 324:124689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124689
Gao HW (2000) Primary-secondary wavelengths spectrophotometry for improving the determination of nitrobenzene compounds in wastewater. Asian J Chem 12:93–96
Ghasemzadeh MA (2017) Fe3O4@SiO2-OSO3H nanocomposite as an efficient catalyst for the preparation of tricarboxamides. Quim Nova 40:47–53. https://doi.org/10.21577/0100-4042.20160157
Huang J, Tang W, Zhu SQ, Du MN (2018) Production of butyric acid by Clostridium tyrobutyricum coated with carboxyl functioned magnetic nanoparticles. J Chem Technol Biot 93:2364–2370. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5582
Huang JM, Yang XA, Wu QH, Mai SZ, Chi HC (2019) Application of independent immobilization in benzo[a]pyrene biodegradation by synthetic microbial consortium. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:21052–21058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05477-4
Ji J, Gao TP, Salama ES, El-Dalatony MM, Peng L, Gong YX, Liu P, Li XK (2021) Using Aspergillus Niger whole-cell biocatalyst mycelial aerobic granular sludge to treat pharmaceutical wastewater containing β-lactam antibiotics. Chem Eng J 412:128665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128665
Khatoon H, Rai JPN (2018) Augmentation of Atrazine biodegradation by two Bacilli immobilized on α-Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles. Sci Rep-UK 8:17831. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36296-1
Kiziltas H, Tekin T, Tekin D (2021) Preparation and characterization of recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 composite photocatalyst, and investigation of the photocatalytic activity. Chem Eng Commun 208:141–1053. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2020.1743694
Lei M, Hu D, Yang H, Lei ZL (2015) Preparation and characterization of hollow magnetic composite nanoparticles for immobilized pectinase. Surf Coat Tech 271:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.02.018
Lent M, Mullins AB, May AD, Honnold CL, Despain KE (2018) Characterization of the testicular toxicity of 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one and 2,4-dinitroanisole in rats (Rattus norvegicus). Int J Toxicol 37:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581818789878
Li T, Deng XP, Wang JJ, Chen YC, He L, Sun YC, Song CX, Zhou ZF (2014) Biodegradation of nitrobenzene in a lysogeny broth medium by a novel halophilic bacterium Bacillus licheniformis. Mar Pollut Bull 89:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.09.028
Li FL, Zhuang MY, Shen JJ, Fan XM, Choi H, Lee JK, Zhang YW (2019) Specific immobilization of Escherichia coli expressing recombinant glycerol dehydrogenase on mannose-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Catalysts 9:585. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070585
Liu F, Kozlovskaya V, Zavgorodnya O, Martinez-Lopez C, Catledge S, Kharlampieva E (2014) Encapsulation of anticancer drug by hydrogen-bonded multilayers of tannic acid. Soft Matter 10:9237–9247. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4sm01813c
Lu Y, Dai HQ, Shi HB, Tang L, Sun XY, Ou ZM (2020) Synthesis of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate by immobilized cells using amino acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Process Biochem 99:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.07.027
Mardani HR, Ziari M (2018) Synthesis and characterization of a new nanomagnetic coordination composite from Fe3O4 and Cu(II) complex: as an efficient catalyst in oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Res Che. Intermediat 44:6605–6619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3511-0
Moores LC, Kenndy AJ, May L, Jordan SM, Bednar AJ, Jones SJ, Henderson DL, Gurtowski L (2020) Identifying degradation products responsible for increased toxicity of UV-degraded insensitive munitions. Chemosphere 240:124958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124958
Nadi A, Melloul M, Boukhriss A, El Fahime E, Boyer D, Hannache H, Gmouh S (2019) Immobilization of Bacillus licheniformis using Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for the development of bacterial bioreactor. Orient J Chem 35:854–862. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/350249
Piccirillo C, Pereira SIA, Marques APGC, Pullar RC, Tobaldi DM, Pintado ME, Castro PML (2013) Bacteria immobilisation on hydroxyapatite surface for heavy metals removal. J Environ Manage 121:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.02.036
Rizzi C, Seveso D, Galli P, Villa S (2020) First record of emerging contaminants in sponges of an inhabited island in the Maldives. Mar Pollut Bull 156:111273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111273
Seenuvasan M, Vinodhini G, Malar CG, Balaji N, Kumar KS (2018) Magnetic nanoparticles: a versatile carrier for enzymes in bio-processing sectors. IET Nanobiotechnol 12:535–548. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0041
Shanmugam S, Krishnaswamy S, Chandrababu R, Veerabagu U, Pugazhendhi A, Mathimani T (2020) Optimal immobilization of Trichoderma asperellum laccase on polymer coated Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for enhanced biohydrogen production from delignified lignocellulosic biomass. Fuel 273:117777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117777
Singh RK, Zhang YW, Nguyen NPT, Jeya M, Lee JK (2011) Covalent immobilization of β-1,4-glucosidase from Agaricus arvensis onto functionalized silicon oxide nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biot 89:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2768-z
Sree BR, Sowjanya B, Divakar K (2019) Metagenomic bioprospecting of novel oxygen insensitive nitroreductase for degradation of nitro aromatic compounds. Int Biodeter Biodegr 143:104737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104737
Sun PF, Hui C, Wang S, Khan RA, Zhang QC, Zhao YH (2016) Enhancement of algicidal properties of immobilized Bacillus methylotrophicus ZJU by coating with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and wheat bran. J Hazar Mater 301:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.048
Wang F, Ma YQ (2018) MPC-973: a low-cost and effective adsorbent for the removal of nitrobenzene from aqueous solutions. Mater Chem Phys 208:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.01.049
Wang DZ, Zheng GY, Zhou LX (2012) Isolation and characterization of a nitrobenzene-degrading bacterium Klebsiella ornithinolytica NB1 from aerobic granular sludge. Bioresour Technol 110:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.105
Wang JH, Ren L, Jia Y, Ruth N, Shi YH, Qiao C, Yan YC (2016) Degradation characteristics and metabolic pathway of 4-nitrophenol by a halotolerant bacterium Arthrobacter sp. CN2. Toxicol Environ Chem 98:226–240. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2015.1115507
Wang HF, Zhao HP, Zhu LZ (2020) Structures of nitroaromatic compounds induce Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to adopt different electron transport pathways to reduce the contaminants. J Hazard Mater 384:121495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121495
Wang D, Lou JF, Yuan JG, Xu J, Zhu RF, Wang Q, Dan XR (2021a) Laccase immobilization on core-shell magnetic metal-organic framework microspheres for alkylphenol ethoxylate compound removal. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.105000
Wang YF, Hou YH, Wang YT, Zheng L, Wang QF (2019) A novel cold-adapted nitroreductase from Psychrobacter sp. ANT206: Heterologous expression, characterization and nitrobenzene reduction capacity. Enzyme Microb Tech 131:109434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109434
Wang YF, Hou YH, Wang QF, Wang YT (2021) The elucidation of the biodegradation of nitrobenzene and p-nitrophenol of nitroreductase from Antarctic psychrophile Psychrobacter sp. ANT206 under low temperature. J Hazard Mater 413:125377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021b.125377
Xu WJ, Zhao QL, Li ZL, Lu XY, Han SQ, Ye ZF (2019) Biodegradation of dinitrotoluene sulfonates and other nitro-aromatic compounds by Pseudomonas sp. X5 isolated from TNT red water contaminated soil. J Clean Prod 214:782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.025
Yazgan I, Noah NM, Toure O, Zhang SY, Sadik OA (2014) Biosensor for selective detection of E. coli in spinach using the strong affinity of derivatized mannose with fimbrial lectin. Biosens Bioelectron 61:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.05.008
Zhang HK, Hu XK (2017) Preparation of Fe3O4-rGO via a covalent chemical combination method and its catalytic performance on p-NP bioreduction. J Environ Chem Eng 5:3348–3353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.06.041
Zhang HY, Firempong CK, Wang YW, Xu WQ, Wang MM, Cao X, Zhu Y, Tong SS, Yu JN, Xu XM (2016) Ergosterol-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles with enhanced in vitro antitumor activity and oral bioavailability. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:834–844. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.37
Zhang D, Deng MF, Cao HB, Zhang SP, Zhao H (2017) Laccase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles by dopamine polymerization for 4-chlorophenol removal. Green Energy Environ 2:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2017.04.001
Zhang HK, Han KM, Hu XK (2020) Enhanced bioreduction of 2,5-dichlorobenzene by an AHQ/RGO binary nanocomposite through a synergistic effect with outer membrane proteins of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Chem Eng J 389:124464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124464
Zhao SM, Xu W, Zhang WL, Wu H, Guang C, Mu WM (2021) In-depth biochemical identification of a novel methyl parathion hydrolase from Azohydromonas australica and its high effectiveness in the degradation of various organophosphorus pesticides. Bioresour Technol 323:124641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124641
Zheng JY, Lan X, Huang LJ, Zhang YJ, Wang Z (2018) Kinetic resolution of N-acetyl-DL-alanine methyl ester using immobilized Escherichia coli cells bearing recombinant esterase from Bacillus cereus. Chirality 30:907–912. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22863
Zhou W, Song YMH, ZY, Xing JM, (2015) Enhanced sulfate reduction by Citrobacter sp. coated with Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0504-8
Zhuang MY, Wang C, Xu MQ, Ling XM, Shen JJ, Zhang YW (2017) Using concanavalin A as a spacer for immobilization of E. coli onto magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 104:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.150
Żur J, Piński A, Michalska J, Hupert-Kocurek K, Nowak A, Wojcieszyńska D, Guzik U (2020) A whole-cell immobilization system on bacterial cellulose for the paracetamol-degrading Pseudomonas moorei KB4 strain. Int Biodeter Biodegr 149:104919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.104919
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41876149), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2021MD040); School-local Cooperation Talent Funding Program of Weihai, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW: conceptualization, software, formal analysis, data curation, writing-original draft. YH: methodology, software, funding acquisition. YW: validation, investigation, writing-review & editing. AZ: methodology, formal analysis, data curation. QW: conceptualization, validation, writing-review & editing, supervision, writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hou, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Immobilization of psychrophile Psychrobacter sp. ANT206 onto novel reusable magnetic nanoparticles and its application for nitro-aromatic compounds biodegradation under low temperature. Biodegradation 33, 223–237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-022-09978-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-022-09978-x