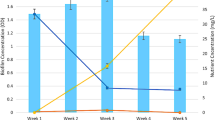
Abstract
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a ubiquitous toxic and carcinogenic pollutant. Screening for pure or mixed-culture microorganisms that can efficiently degrade THF is difficult due to its chemical stability. In this study, an enrichment culture, H-1, with a stable THF-degrading ability and microbial community structure was enriched from activated sludge and could efficiently degrade 95% of 40 mM THF within 6 days. The optimal THF degradation conditions for H-1 were an initial pH of 7.0–8.0 and a temperature of 30 °C. The substrate tolerance concentration of H-1 reached 200 mM. Heavy metals tolerance concentrations of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ of H-1 was 0.5 mM, 0.4 mM and 0.03 mM, and 4 mM Mn2+ did not significantly influence the THF degradation ratio or biomass of H-1. H-1 might be a good material for actual wastewater treatment because of its efficient THF degradation performance and ability to resist various stressful conditions. In addition, the THF-degrading efficiency of H-1 was enhanced by the addition of moderate carbon sources. High-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene showed that Rhodococcus sp. (a potential THF-degrading strain) and Hydrogenophaga sp. (a potential non-THF-degrading strain) were the dominant microorganisms in the H-1 culture. These results indicate the potential coexistence of cooperation and competition between THF-degrading bacteria and nondegrading bacteria in this enrichment culture.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam M (2016) Biodegradation of marine crude oil pollution using a salt-tolerant bacterial consortium isolated from Bohai Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 105:43–50
Arjoon A, Olaniran AO, Pillay B (2015) Kinetics of heavy metal inhibition of 1,2-dichloroethane biodegradation in co-contaminated water. J Basic Microbiol 55:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201200776
Babel S, Dacera DDM (2006) Heavy metal removal from contaminated sludge for land application: a review. Waste Manage 26:988–1004
Benomar S et al (2015) Nutritional stress induces exchange of cell material and energetic coupling between bacterial species. Nat Commun 6:6283
Bernhardt D, Diekmann H (1991) Degradation of dioxane, tetrahydrofuran and other cyclic ethers by an environmental Rhodococcus strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:120–123
Boon E, Meehan CJ, Whidden C, Wong DH-J, Langille MG, Beiko RG (2014) Interactions in the microbiome: communities of organisms and communities of genes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:90–118
Chaturvedi AD, Pal D, Penta S, Kumar A (2015) Ecotoxic heavy metals transformation by bacteria and fungi in aquatic ecosystem. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1595–1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1911-5
Chen K-C, Wu J-Y, Liou D-J, Hwang S-CJ (2003) Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. J Biotechnol 101:57–68
Chen J-M, Zhou Y-Y, Chen D-Z, Jin X-J (2010) A newly isolated strain capable of effectively degrading tetrahydrofuran and its performance in a continuous flow system. Bioresour Technol 101:6461–6467
Daye K, Groff J, Kirpekar A, Mazumder R (2003) High efficiency degradation of tetrahydrofuran (THF) using a membrane bioreactor: identification of THF-degrading cultures of Pseudonocardia sp. strain M1 and Rhodococcus ruber isolate M2. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:705–714
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Foster KR, Bell T (2012) Competition, not cooperation, dominates interactions among culturable microbial species. Curr Biol 22:1845–1850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.08.005
Gamer A, Jaeckh R, Leibold E, Kaufmann W, Gembardt C, Bahnemann R, Van Ravenzwaay B (2002) Investigations on cell proliferation and enzyme induction in male rat kidney and female mouse liver caused by tetrahydrofuran. Toxicol Sci 70:140–149
He Z, Xiao H, Tang L, Min H, Lu Z (2013) Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by a stable bacterial consortium, HD-1, enriched from activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 128:526–532
Hermida SA et al (2006) 2′-Deoxyguanosine, 2′-deoxycytidine, and 2′-deoxyadenosine adducts resulting from the reaction of tetrahydrofuran with DNA bases. Chem Res Toxicol 19:927–936
Hug LA, Beiko RG, Rowe AR, Richardson RE, Edwards EA (2012) Comparative metagenomics of three Dehalococcoides-containing enrichment cultures: the role of the non-dechlorinating community. BMC Genomics 13:327
Ikehata K, Wang-Staley L, Qu X, Li Y (2016) Treatment of groundwater contaminated with 1, 4-dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, and chlorinated volatile organic compounds using advanced oxidation processes. Ozone Sci Eng 38:413–424
Isaacson C, Mohr TK, Field JA (2006) Quantitative determination of 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran in groundwater by solid phase extraction GC/MS/MS. Environ Sci Technol 40:7305–7311
Kılıç NK, Nielsen JL, Yüce M, Dönmez G (2007) Characterization of a simple bacterial consortium for effective treatment of wastewaters with reactive dyes and Cr(VI). Chemosphere 67:826–831
Kim D-J, Choi J-W, Choi N-C, Mahendran B, Lee C-E (2005) Modeling of growth kinetics for Pseudomonas spp. during benzene degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:456–462
Kim Y-M, Jeon J-R, Murugesan K, Kim E-J, Chang Y-S (2009) Biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane and transformation of related cyclic compounds by a newly isolated Mycobacterium sp. PH-06. Biodegradation 20:511
King E, Painter H (1983) Assessment of biodegradability of chemicals in water by manometric respirometry. Comm Eur Communities EUR 8631:31
Kohlweyer U, Thiemer B, Schräder T, Andreesen JR (2000) Tetrahydrofuran degradation by a newly isolated culture of Pseudonocardia sp. strain K1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 186:301–306
Lan RS, Smith CA, Hyman MR (2013) Oxidation of cyclic ethers by alkane-grown Mycobacterium vaccae JOB5. Remediat J 23:23–42
Larkin MJ, Kulakov LA, Allen CC (2006) Biodegradation by members of the genus Rhodococcus: biochemistry, physiology, and genetic adaptation. Adv Appl Microbiol 59:1–29
Lee K, Park J-W, Ahn I-S (2003) Effect of additional carbon source on naphthalene biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida G7. J Hazard Mater 105:157–167
Liu Z, He Z, Huang H, Ran X, Oluwafunmilayo AO, Lu Z (2017) pH Stress-induced cooperation between Rhodococcus ruber YYL and Bacillus cereus MLY1 in biodegradation of tetrahydrofuran. Front Microbiol 8:2297
Luo J, Hein C, Mücklich F, Solioz M (2017) Killing of bacteria by copper, cadmium, and silver surfaces reveals relevant physicochemical parameters. Biointerphases 12:020301. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.4980127
Maidak BL, Olsen GJ, Larsen N, Overbeek R, McCaughey MJ, Woese CR (1997) The RDP (ribosomal database project). Nucleic Acids Res 25:109–110
Malley LA, Christoph GR, Stadler JC, Hansen JF, Biesemeier JA, Jasti SL (2001) Acute and subchronic neurotoxicological evaluation of tetrahydrofuran by inhalation in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 24:201–219
Martínková L, Uhnáková B, Pátek M, Nešvera J, Křen V (2009) Biodegradation potential of the genus Rhodococcus. Environ Int 35:162–177
Masuda H, McClay K, Steffan RJ, Zylstra GJ (2012) Biodegradation of tetrahydrofuran and 1, 4-dioxane by soluble diiron monooxygenase in Pseudonocardia sp. strain ENV478. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 22:312–316
McCutcheon JP, von Dohlen CD (2011) An interdependent metabolic patchwork in the nested symbiosis of mealybugs. Curr Biol 21:1366–1372
Metsger L, Bittner S (2000) Autocatalytic oxidation of ethers with sodium bromate. Tetrahedron 56:1905–1910
Moody DE (1991) The effect of tetrahydrofuran on biological systems: does a hepatotoxic potential exist? Drug Chem Toxicol 14:319–342
Oh ST, Kim JR, Premier GC, Lee TH, Kim C, Sloan WT (2010) Sustainable wastewater treatment: how might microbial fuel cells contribute. Biotechnol Adv 28:871–881
Parales R, Adamus J, White N, May H (1994) Degradation of 1, 4-dioxane by an actinomycete in pure culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4527–4530
Phelan VV, Liu W-T, Pogliano K, Dorrestein PC (2012) Microbial metabolic exchange—the chemotype-to-phenotype link. Nat Chem Biol 8:26
Saratale R, Saratale G, Kalyani D, Chang J-S, Govindwar S (2009) Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of textile azo dye Scarlet R by using developed microbial consortium-GR. Bioresour Technol 100:2493–2500
Sathishkumar M, Binupriya AR, Baik SH, Yun SE (2008) Biodegradation of crude oil by individual bacterial strains and a mixed bacterial consortium isolated from hydrocarbon contaminated areas. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 36:92–96
Sei K, Miyagaki K, Kakinoki T, Fukugasako K, Inoue D, Ike M (2013) Isolation and characterization of bacterial strains that have high ability to degrade 1, 4-dioxane as a sole carbon and energy source. Biodegradation 24:665–674
Skinner K, Cuiffetti L, Hyman M (2009) Metabolism and cometabolism of cyclic ethers by a filamentous fungus, a Graphium sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5514–5522
Sprocati AR, Alisi C, Segre L, Tasso F, Galletti M, Cremisini C (2006) Investigating heavy metal resistance, bioaccumulation and metabolic profile of a metallophile microbial consortium native to an abandoned mine. Sci Total Environ 366:649–658
Stolyar S, Van Dien S, Hillesland KL, Pinel N, Lie TJ, Leigh JA, Stahl DA (2007) Metabolic modeling of a mutualistic microbial community. Mol Syst Biol 3:92
Sun B, Ko K, Ramsay JA (2011) Biodegradation of 1, 4-dioxane by a Flavobacterium. Biodegradation 22:651–659
Tajima T, Hayashida N, Matsumura R, Omura A, Nakashimada Y, Kato J (2012) Isolation and characterization of tetrahydrofuran-degrading Rhodococcus aetherivorans strain M8. Process Biochem 47:1665–1669
Thavamani P, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2015) Metal-tolerant PAH-degrading bacteria: development of suitable test medium and effect of cadmium and its availability on PAH biodegradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8957–8968
Thijs S, Weyens N, Sillen W, Gkorezis P, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2014) Potential for plant growth promotion by a consortium of stress-tolerant 2, 4-dinitrotoluene-degrading bacteria: isolation and characterization of a military soil. Microb Biotechnol 7:294–306
Wanapaisan P et al (2018) Synergistic degradation of pyrene by five culturable bacteria in a mangrove sediment-derived bacterial consortium. J Hazard Mater 342:561–570
Wang Y et al (2017) Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by bacterial consortium LV-1 enriched from river sludge. PLoS ONE 12:e0178213
Xu Y, Chen X (2002) Recovering tetrahydrofuran from waste pharmaceutical liquor using new separation methods. Chem Eng (China) 30:17–19
Yao Y, Lv Z, Min H, Lv Z, Jiao H (2009) Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel Rhodococcus sp. strain in biodegradation of tetrahydrofuran and its medium optimization using sequential statistics-based experimental designs. Bioresour Technol 100:2762–2769
Yao Y et al (2010) Assessment of toxicity of tetrahydrofuran on the microbial community in activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 101:5213–5221
Yao Y, Lu Z, Min H, Gao H, Zhu F (2012) The effect of tetrahydrofuran on the enzymatic activity and microbial community in activated sludge from a sequencing batch reactor. Ecotoxicology 21:56–65
Yu L, Cheng JM (2015) Effect of heavy metals Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn on enzyme activity and microbial biomass carbon in brown soil. Adv Mater Res 1073–1076:726–730
Zagrodnik R, Łaniecki M (2017) The effect of pH on cooperation between dark-and photo-fermentative bacteria in a co-culture process for hydrogen production from starch. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:2878–2888
Zelezniak A, Andrejev S, Ponomarova O, Mende DR, Bork P, Patil KR (2015) Metabolic dependencies drive species co-occurrence in diverse microbial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:6449–6454
Zhang L, Hu J, Zhu R, Zhou Q, Chen J (2013) Degradation of paracetamol by pure bacterial cultures and their microbial consortium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:3687–3698
Zhao H, Liu Q, Wang Y, Han Z, Chen Z, Mu Y (2018a) Biochar enhanced biological nitrobenzene reduction with a mixed culture in anaerobic systems: short-term and long-term assessments. Chem Eng J 351:912–921
Zhao L et al (2018b) Co-contaminant effects on 1,4-dioxane biodegradation in packed soil column flow-through systems. Environ Pollut 243:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.018
Zhou K, Qiao K, Edgar S, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Distributing a metabolic pathway among a microbial consortium enhances production of natural products. Nat Biotechnol 33:377
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41630637 and 41721001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Yu, H., Qi, M. et al. Enrichment and characterization of a highly efficient tetrahydrofuran-degrading bacterial culture. Biodegradation 30, 467–479 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-019-09888-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-019-09888-5