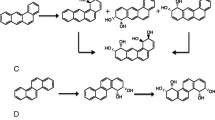
Abstract
The genes of two ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases (RHDs) of Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434 were cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The relative values of the RHD specificity constants were estimated for six polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) based on the kinetics of PAH mixture conversion by the recombinant strains. The substrate specificity profiles of the enzymes were found to be very different. Dioxygenase ArhA was the most specific to acenaphthylene and showed a low specificity to fluoranthene. Dioxygenase PhnA was the most specific to anthracene and phenanthrene and showed a considerable specificity to fluoranthene. Knockout derivatives of Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434 lacking ArhA, PhnA, and both dioxygenases were constructed. PAH degradation by the single-knockout mutants was in agreement with the substrate specificity of the RHD remaining intact. Double-knockout mutant lacking both enzymes was unable to oxidize PAHs. A mutant form of dioxygenase ArhA with altered substrate specificity was described.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baboshin MA, Golovleva LA (2011a) Multisubstrate kinetics of PAH mixture biodegradation: analysis in the double-logarithmic plot. Biodegradation 22:13–23
Baboshin MA, Golovleva LA (2011b) Characterization of hydrophobic organic contaminant biodegradation by COD analysis. Int Biodeterior Biodegr 65:883–889
Baboshin MA, Akimov VN, Baskunov BP, Born TL, Khan SU, Golovleva LA (2008) Conversion of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434. Biodegradation 19:567–576
Chen W, Kuo T (1993) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of gram-negative bacterial genomic DNA. Nucleic Acid Res 21:2260
Demaneche S, Meyer C, Micoud J, Louwagie M, Willison JC, Jouanneau Y (2004) Identification and functional analysis of two aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from a Sphingomonas strain that degrades various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6714–6725
Desai AM, Autenrieth RL, Dimitriou-Christidis P, McDonald TJ (2008) Biodegradation kinetics of select polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) mixtures by Sphingomonas paucimobilis EPA505. Biodegradation 19:223–233
Dimitriou-Christidis P, Autenrieth RL (2007) Kinetics of biodegradation of binary and ternary mixtures of PAHs. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:788–800
Dimitriou-Christidis P, Autenrieth RL, McDonald TJ, Desai AM (2007) Measurement of biodegradability parameters for single unsubstituted and methylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in liquid bacterial suspensions. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:922–932
Gibson DT, Parales RE (2000) Aromatic hydrocarbon dioxygenases in environmental biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:236–243
Guha S, Peters CA, Jaffé PR (1999) Multisubstrate biodegradation kinetics of naphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrene mixtures. Biotechnol Bioeng 65:491–499
Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP (1998) A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77–86
Ivashina TV, Fedorova EE, Ashina NP, Kalinchuk NA, Druzhinina TN, Shashkov AS, Shibaev VN, Ksenzenko VN (2010) Mutation in the pssM gene encoding ketal pyruvate transferase leads to disruption of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae–Pisum sativum symbiosis. J Appl Microbiol 109:731–742
Jouanneau Y, Meyer C, Jakoncic J, Stojanoff V, Gaillard J (2006) Characterization of a naphthalene dioxygenase endowed with an exceptionally broad substrate specificity toward polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochemistry 45:12380–12391
Kasai Y, Shindo K, Harayama S, Misawa N (2003) Molecular characterization and substrate preference of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon dioxygenase from Cycloclasticus sp. strain A5. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6688–6697
Kim S-J, Kweon O, Freeman JP, Jones RC, Adjei MD, Jhoo J-W, Edmondson RD, Cerniglia CE (2006) Molecular cloning and expression of genes encoding a novel dioxygenase involved in low- and high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1045–1054
Knightes CD, Peters CA (2006) Multisubstrate biodegradation kinetics for binary and complex mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1746–1756
Krivobok S, Kuony S, Meyer C, Louwagie M, Willison JC, Jouanneau Y (2003) Identification of pyrene-induced proteins in Mycobacterium sp. strain 6PY1: evidence for two ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases. J Bacteriol 185:3828–3841
Kweon O, Kim S-J, Freeman JP, Song J, Baek S, Cerniglia CE (2010) Substrate specificity and structural characteristics of the novel Rieske nonheme iron aromatic ring-hydroxylating oxygenases NidAB and NidA3B3 from Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1. mBio 1:e00135-10
Lotfabad SK, Gray MR (2002) Kinetics of biodegradation mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:361–366
Martin F, Malagnoux L, Violet F, Jakoncic J, Jouanneau Y (2013) Diversity and catalytic potential of PAH-specific ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from a hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5125–5135
Notredame C, Higgins DG, Heringa J (2000) T-Coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J Mol Biol 302:205–217
Parales R (2003) The role of active-site residues in naphthalene dioxygenase. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:271–278
Pinyakong O, Habe H, Omori T (2003) The unique aromatic catabolic genes in sphingomonads degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). J Gen Appl Microbiol 49:1–19
Pinyakong O, Habe H, Kouzuma A, Nojiri H, Yamane H, Omori T (2004) Isolation and characterization of genes encoding polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon dioxygenase from acenaphthene and acenaphthylene degrading Sphingomonas sp. strain A4. FEMS Microbiol Lett 238:297–305
Resnick SM, Lee K, Gibson DT (1996) Diverse reactions catalyzed by naphthalene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB 9816. J Ind Microbiol 17:438–457
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schuler L, Jouanneau Y, Chadhain SMN, Meyer C, Pouli M, Zylstra GJ, Hols P, Agathos SN (2009) Characterization of a ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase from phenanthrene-degrading Sphingomonas sp. strain LH128 able to oxidize benz[a]anthracene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:465–475
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784–791
Singleton DR, Hu J, Aitken MD (2012) Heterologous expression of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase genes from a novel pyrene-degrading betaproteobacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:3552–3559
Stringfellow WT, Aitken MD (1995) Competitive metabolism of naphthalene, methylnaphthalene and fluorene by phenanthrene-degrading pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:357–362
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1997) Construction of evolutionary distance trees with TREECON. Comput Applic Biosci 13:227–230
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Yu CL, Liu W, Ferraro DJ, Brown EN, Parales JV, Ramaswamy S, Zylstra GJ, Gibson DT, Parales RE (2007) Purification, characterization, and crystallization of the components of a biphenyl dioxygenase system from Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:311–324
Zhou HW, Guo CL, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2006) Genetic diversity of dioxygenase genes in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from mangrove sediments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 262:148–157
Acknowledgments
The reported study was partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR), Research Project No. 11-04-00831-a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baboshin, M., Ivashina, T., Chernykh, A. et al. Comparison of the substrate specificity of two ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434 to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biodegradation 25, 693–703 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9692-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9692-3