Abstract
Objective
An electroporation procedure for the species was investigated to develop an efficient transformation method for the basidiomycetous fungus Pseudozyma hubeiensis SY62, a strong biosurfactant-producing host.
Results
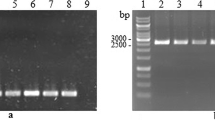
A plasmid, pUXV1emgfp including green fluorescence protein as a reporter gene, was constructed to determine the transformation and expression of foreign genes. Optimal electroporation conditions achieved 44.8 transformants μg−1 plasmid competency (intact cells) without protoplast treatment. Lithium acetate treatments increased the efficiency to approx. Twice that of control experiments. Almost all transformants demonstrated green fluorescence expressed in the transformant cells.
Conclusion
The optimal method, successfully applied to several related species, yields sufficient transformant colonies to engineer the host strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avis TJ, Cheng YL, Zhao YY, Bolduc S, Neveu B, Anguenot R, Labbé C, Belxile F, Bélanger RR (2005) The potential of Pseudozyma yeastlike epiphytes for the production of heterologous recombinant proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:304–311
Banks GR (1983) Transformation of Ustilago maydis by a plasmid containing yeast 2-micron DNA. Curr Genet 7:73–77
Bej AK, Perlin MH (1989) A high efficiency transformation system for the basidiomycete Ustilago violacea employing hygromycin resistance and lithium acetate treatment. Gene 80:171–176
Delome E (1989) Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by electroporation. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2242–2246
Imura T, Yanagishita H, Ohira J, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2005) Thermodynamically stable vesicle formation from glycolipid biosurfactant sponge phase. Colloids Surf B 43:114–121
Imura T, Hikosaka Y, Worakitkanchanakul W, Sakai H, Abe M, Konishi M, Minamikawa H, Kitamoto D (2007) Aqueous-phase behabior of natural glycolipid biosurfactants mannosylerythritol lipid A: sponge, cubic, and lamella phases. Langmuir 23:1659–1663
Inoh Y, Furuno T, Nirashima N, Kitamoto D, Nakanishi M (2013) Synergistic effect of a biosurfactant and protamine on gene transfection efficiency. Eur J Pham Sci 49:1–9
Isoda H, Shinmoto H, Kitamoto D, Matsumura M, Nakahara T (1997) Differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL60 by microbial extracellular glycolipids. Lipids 32:263–271
Ito S, Imura T, Fukuoka T, Morita T, Sakai H, Abe M, Kitamoto D (2007) Kinetic studies on the interactions between glycolipid biosurfactants assembled monolayers and various classes of immunogloblins using surface plasmon resonance. Colloid Surf B 58:165–171
Kinal H, Jianshi T, Bruenn JA (1991) An expression vector for the phytophathogenic fungus, Ustilago maydis. Gene 98:129–134
Kitamoto D, Yanagishita H, Shimbo T, Nakane T, Kamisawa C, Nakahara T (1993) Surface active properties and antimicrobial activities of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants produced by Candida anatarctica. J Biotechnol 29:91–96
Konishi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007a) A yeast glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, shows high binding affinity towards lectins on a self-assembled monolayer system. Biotechnol Lett 29:473–480
Konishi M, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007b) Production of different types of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants by the newly isolated yeast strain belonging to the genus Pseudozyma. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:37–46
Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Nagahama T, Morita T, Imura T, Kitamoto D, Hatada Y (2010) Biosurfactant-producing yeast isolated from Calyptogena soyoae (deep-sea cold-seep clam) in the deep sea. J Biosci Bioeng 110:169–175
Konishi M, Nagahama T, Fukuoka T, Morita T, Imura T, Kitamoto D, Hatada Y (2011) Yeast extract stimulates production of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, by Pseudozyma hubeiensis SY62. J Biosci Bioeng 111:702–705
Konishi M, Hatada Y, Horiuchi J (2013) Draft genome sequence of the basidiomycetous yeast-like fungus Pseudozyma hubeiensis SY62, which produces an abundant of the biosurfactant mannosylerythritol lipids. Genome Announc 1:e00409–e00413
Manivasakam P, Schiestl RH (1993) High efficiency transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 21:4414–4415
Marchand G, Fortier E, Neveu B, Bolduc S, Belzile F, Bèkabger RR (2007) Alternative methods for genetic transfection of Pseudozyma antarctica, a basidiomycetous yeast-like fungus. J Micobiol Methods 70:519–527
Morita T, Habe H, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Kitamoto D (2007) Convenient transformation of anamorphic basidiomycetous yeasts belonging to genus Pseudozyma induced by electroporation. J Biosci Bioeng 104:517–520
Morita T, Kitagawa M, Yamamoto S, Sogabe A, Imura T, Fukuoka T, Kitamoto D (2010) Glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, repair the damaged hair. J Oleo Sci 59:267–272
Thomson JR, Register E, Curotto J, Kurtz M, Kelly R (1998) An improved protocol for the preparation of yeast cells for transformation by electroporation. Yeast 14:565–571
Wakamatsu Y, Zhao X, Jin C, Day N, Shibahara M, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Murata T, Yokoyama KK (2001) Mannosylerythritol lipid induces characteristics of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells through an ERK-related signal cascade. Eur J Biochem 268:374–383
Wang Q-M, Jia J-H, Bai F-Y (2006) Pseudozyma hubeiensis sp. nov. and Pseudozyma shanxiensis sp. nov. ustilaginomycetous anamorphic yeast species from plant leaves. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:289–293
Wu S, Letchworth GJ (2004) High efficiency transformation by electroporation of Pichia pastries pretereated with lithium acetate and dithiothreitol. Biotechniques 36:152–154
Yamamoto S, Morita T, Fukuoka T, Imura T, Yanagidani S, Sogabe A, Kitamoto D, Kitagawa M (2012) The moisturizing effects of glycolipid biosurfactants, mannosylerythritol lipids, on human skin. J Oleo Sci 61:407–412
Zhao XX, Murata T, Ohno S, Day N, Song J, Nomura N, Nakahara T, Yokoyama KK (2001) Protein kinase C alpha plays a critical role in mannosylerythritol lipid-induced differentiation of melanoma B16 cells. J Biol Chem 276:39903–39910
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 24681013. We thank to JAMSTEC for kindly providing Pseudozyma hubeiensis SY62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konishi, M., Yoshida, Y., Ikarashi, M. et al. Efficient and simple electro-transformation of intact cells for the basidiomycetous fungus Pseudozyma hubeiensis . Biotechnol Lett 37, 1679–1685 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1837-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1837-x