Abstract
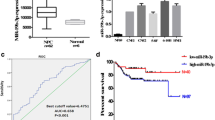
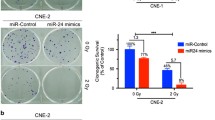
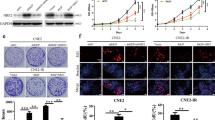
Radiotherapy resistance is a major cause of treatment failure and leads to poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Evidences indicate that microRNA (miRNAs) are closely associated with radiotherapy for NPC. In this study, we found that the expression level of miR-92b-3p was significantly higher in radiotherapy-sensitive NPC patients than in radiotherapy-resistant patients. High expression of miR-92b-3p was associated with good prognosis in patients with NPC, and high expression of FHL2 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with NPC. It was predicted that miR-92b-3p could directly target and bind FHL2. Overexpression of miR-92b-3p significantly inhibited FHL2 expression at the mRNA as well as protein levels, while inhibition of miR-92b-3p expression significantly upregulated FHL2 expression. Overexpression of miR-92b-3p significantly reduced proliferation and colony formation in NPC cells. Inhibition of miR-92b-3p attenuated the sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiotherapy, while simultaneous inhibition of miR-92b-3p and FHL2 increased the sensitivity of NPC to radiotherapy. Our findings highlighted that miR-92b-3p is closely associated with radiotherapy sensitivity and prognosis in NPC patients and may improve the sensitivity of NPC to radiotherapy by targeting FHL2.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data generated during analyzing in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bossi P, Chan AT, Licitra L, Trama A, Orlandi E, Hui EP, Halamkova J, Mattheis S, Baujat B, Hardillo J, Smeele L, van Herpen C, Castro A, Machiels JP, Euracan, (2021) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(dagger). Ann Oncol 32(4):452–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.12.007
Cao CY, Mok SW, Cheng VW, Tsui SK (2015) The FHL2 regulation in the transcriptional circuitry of human cancers. Gene 572(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.07.043
Cserhalmi M, Papp A, Brandus B, Uzonyi B, Jozsi M (2019) Regulation of regulators: role of the complement factor H-related proteins. Semin Immunol 45:101341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2019.101341
Guan S, Wei J, Huang L, Wu L (2020) Chemotherapy and chemo-resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Med Chem 207:112758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112758
Huang Z, Li Q, Luo K, Zhang Q, Geng J, Zhou X, Xu Y, Qian M, Zhang JA, Ji L, Wu J (2019) miR-340-FHL2 axis inhibits cell growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis 10(5):372. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1604-3
Jiang J, Tang Q, Gong J, Jiang W, Chen Y, Zhou Q, Aldeen A, Wang S, Li C, Lv W, Du T, Wang X, Long X, Feng X (2022) Radiosensitizer EXO-miR-197-3p Inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and radioresistance by regulating the AKT/mTOR axis and HSPA5-mediated autophagy. Int J Biol Sci 18(5):1878–1895. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.69934
Jin X, Jiao X, Jiao J, Zhang T, Cui B (2018) Increased expression of FHL2 promotes tumorigenesis in cervical cancer and is correlated with poor prognosis. Gene 669:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.087
Killock D (2023) Recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: hyperfractionation of IMRT improves outcomes. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-023-00753-2
Lee AWM, Ng WT, Chan JYW, Corry J, Makitie A, Mendenhall WM, Rinaldo A, Rodrigo JP, Saba NF, Strojan P, Suarez C, Vermorken JB, Yom SS, Ferlito A (2019) Management of locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev 79:101890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.101890
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME (2018) MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141(4):1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Lu J, Liu QH, Wang F, Tan JJ, Deng YQ, Peng XH, Liu X, Zhang B, Xu X, Li XP (2018) Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):147. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0814-3
Qu JQ, Yi HM, Ye X, Zhu JF, Yi H, Li LN, Xiao T, Yuan L, Li JY, Wang YY, Feng J, He QY, Lu SS, Xiao ZQ (2015) MiRNA-203 reduces nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by targeting IL8/AKT signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 14(11):2653–2664. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0461
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Shathasivam T, Kislinger T, Gramolini AO (2010) Genes, proteins and complexes: the multifaceted nature of FHL family proteins in diverse tissues. J Cell Mol Med 14(12):2702–2720. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01176.x
Verset L, Feys L, Trepant AL, De Wever O, Demetter P (2016) FHL2: a scaffold protein of carcinogenesis, tumour-stroma interactions and treatment response. Histol Histopathol 31(5):469–478. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-11-709
Xue YL, Meng XQ, Ma LJ, Yuan Z (2016) Plumbagin exhibits an anti-proliferative effect in human osteosarcoma cells by downregulating FHL2 and interfering with Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Oncol Lett 12(2):1095–1100. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4725
Yan H, Bu P (2021) Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem 65(4):625–639. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20200032
Yuan Y, Liao H, Pu Q, Ke X, Hu X, Ma Y, Luo X, Jiang Q, Gong Y, Wu M, Liu L, Zhu W (2020) miR-410 induces both epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance through activation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):85. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0182-2
Zhang C, Fang X, Li W, Shi Q, Wu L, Chen X, Huang Z, Wu P, Wang Z, Liao Z (2014) Influence of recombinant lentiviral vector encoding miR-15a/16-1 in biological features of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2Z cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 29(10):422–427. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2013.1596
Zhou R, Li S, Liu J, Wu H, Yao G, Sun Y, Chen ZJ, Li W, Du Y (2020) Up-regulated FHL2 inhibits ovulation through interacting with androgen receptor and ERK1/2 in polycystic ovary syndrome. EBioMedicine 52:102635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102635
Zhu Q, Zhang Q, Gu M, Zhang K, Xia T, Zhang S, Chen W, Yin H, Yao H, Fan Y, Pan S, Xie H, Liu H, Cheng T, Zhang P, Zhang T, You B, You Y (2021) MIR106A-5p upregulation suppresses autophagy and accelerates malignant phenotype in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Autophagy 17(7):1667–1683. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1781368
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by the Hunan Provincial Department of Education Project (Grant No. 20B537).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CZ, SND, LZ wrote the main manuscript text and JJ prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, C., Duan, S., Zhao, L. et al. Hsa-miR-92b-3p Targeting FHL2 to Enhance Radiosensitivity of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10741-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10741-5