Abstract
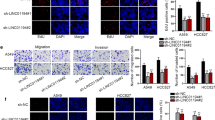
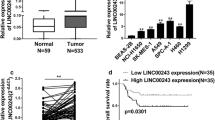
Recently, long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is proved to play critical roles in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression. However, the detailed effects of LINC01426 in NSCLC and its functional mechanism remain unknown. The expression of LINC01426, microRNA-143-3p (miR-143-3p), and Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 28 (USP28) was assessed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The colony-forming ability was determined by colony-forming assay. 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) staining assay was performed to evaluate cell proliferation. The migrated and invaded abilities of cells were measured by transwell assays. Flow cytometry was used to examine cell apoptosis. The protein expression was analyzed by Western blot analysis. The glycolysis ability was analyzed by commercial kits. Dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay, and RNA pull-down assay were used to confirm relationship among LINC01426, miR-143-3p, and USP28. A xenograft experiment was conducted to explore the effects of LINC01426 inhibition in vivo. Our results confirmed that LINC01426 and USP28 expression were increased, while miR-143-3p expression was decreased in NSCLC tissues and cells. Further functional experiments demonstrated that LINC01426 inhibition markedly impaired cell proliferation, migration, invasion, autophagy, and glycolysis while induced apoptosis in NSCLC cells, and LINC01426 derived malignant behaviors of NSCLC cells by sponging miR-143-3p. Additionally, LINC01426 regulated USP28 expression by sponging miR-143-3p. USP28 overexpression partly overturned the inhibitory effect of miR-143-3p on NSCLC progression. Consistently, silencing of LINC01426 significantly inhibited the growth of NSCLC tumor in vivo. LINC01426 accelerated the malignant progression of NSCLC. Mechanistically, LINC01426 acted as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-143-3p to upregulate USP28 expression.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Please contact the correspondence author for the data request.
References
Akhade VS, Pal D, Kanduri C (2017) Long nonacoding RNA: genome organization and mechanism of action. Adv Exp Med Biol 1008:47–74
Cao J, Tang Z, Su Z (2020) Long non-coding RNA LINC01426 facilitates glioblastoma progression via sponging miR-345-3p and upregulation of VAMP8. Cancer Cell Int 20:327
Dai J, Wang B, Zhao Y, Zuo X, Cui H, Chen X et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA LINC01426 sequesters microRNA-519d-5p to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression by increasing ETS1 expression. Cancer Manag Res 12:12697–12708
Devrim T, Atac F, Devrim AK, Balci M (2020) The concomitant use of USP28 and p53 to predict the progression of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Pathol Res Pract 216:152774
Diefenbacher ME, Popov N, Blake SM, Schulein-Volk C, Nye E, Spencer-Dene B et al (2014) The deubiquitinase USP28 controls intestinal homeostasis and promotes colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest 124:3407–3418
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553:446–454
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL et al (2017) Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 389:299–311
Jiang Y, Zhang H, Li W, Yan Y, Yao X, Gu W (2021) LINC01426 contributes to clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by modulating CTBP1/miR-423-5p/FOXM1 axis via interacting with IGF2BP1. J Cell Physiol 236:427–439
Li J, Wang J, Chen Y, Yang L, Chen S (2017) A prognostic 4-gene expression signature for squamous cell lung carcinoma. J Cell Physiol 232:3702–3713
Li P, Huang Z, Wang J, Chen W, Huang J (2019a) Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 28 enhances STAT3 signaling and promotes cell growth in non-small-cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther 12:1603–1611
Li F, Han H, Sun Q, Liu K, Lin N, Xu C et al (2019b) USP28 regulates deubiquitination of histone H2A and cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res 379:11–18
Nasim F, Sabath BF, Eapen GA (2019) Lung cancer. Med Clin North Am 103:463–473
Peng WX, Koirala P, Mo YY (2017) LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36:5661–5667
Prieto-Garcia C, Hartmann O, Reissland M, Braun F, Fischer T, Walz S et al (2020) Maintaining protein stability of Np63 via USP28 is required by squamous cancer cells. EMBO Mol Med 12:e11101
Pu M, Chen J, Tao Z, Miao L, Qi X, Wang Y et al (2019) Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:441–451
Ren K, Li Y, Lu H, Li Z, Han X (2017) miR-3940-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting cyclin D1 and ubiquitin specific peptidase-28. Transl Oncol 10:80–89
Sahami-Fard MH, Kheirandish S, Sheikhha MH (2019) Expression levels of miR-143-3p and -424-5p in colorectal cancer and their clinical significance. Cancer Biomark 24:291–297
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH (2019) An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol 234:5451–5465
Shi H, Shen H, Xu J, Zhao S, Yao S, Jiang N (2018) MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res 10:866–874
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:7–34
Sun W, Zu Y, Fu X, Deng Y (2017) Knockdown of lncRNA-XIST enhances the chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells via suppression of autophagy. Oncol Rep 38:3347–3354
Tian B, Han X, Li G, Jiang H, Qi J, Li J et al (2020) A long intergenic non-coding RNA, LINC01426, promotes cancer progression via AZGP1 and predicts poor prognosis in patients with LUAD. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 18:765–780
Wang SJ, Wang H, Zhao CD, Li R (2018a) Long noncoding RNA LINC01426 promotes glioma progression through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and serves as a prognostic biomarker. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:6358–6368
Wang X, Liu Z, Zhang L, Yang Z, Chen X, Luo J et al (2018b) Targeting deubiquitinase USP28 for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis 9:186
Weili Z, Zhikun L, Jianmin W, Qingbao T (2019) Knockdown of USP28 enhances the radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells via the c-Myc/hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha pathway. J Cell Biochem 120:201–212
Xia C, Yang Y, Kong F, Kong Q, Shan C (2018) MiR-143-3p inhibits the proliferation, cell migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by modulating the expression of MAPK7. Biochimie 147:98–104
Xu Y, Wang J, Qiu M, Xu L, Li M, Jiang F et al (2015) Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol 36:1643–1651
Yamanaka S, Sato Y, Oikawa D, Goto E, Fukai S, Tokunaga F et al (2020) Subquinocin, a small molecule inhibitor of CYLD and USP-family deubiquitinating enzymes, promotes NF-kappaB signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 524:1–7
Yang Y, Li S, Cao J, Li Y, Hu H, Wu Z (2019) RRM2 regulated by LINC00667/miR-143-3p signal is responsible for non-small cell lung cancer cell progression. OncoTargets Ther 12:9927–9939
Yang J, Jia Y, Wang B, Yang S, Du K, Luo Y et al (2020) Circular RNA TUBA1C accelerates the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by sponging miR-143-3p. Cell Signal 74:109693
Zhang L, Xu B, Qiang Y, Huang H, Wang C, Li D et al (2015) Overexpression of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 promoted non-small cell lung cancer growth. J Cell Mol Med 19:799–805
Zhao LJ, Zhang T, Feng XJ, Chang J, Suo FZ, Ma JL et al (2018) USP28 contributes to the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28040
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL was responsible for drafting the manuscript. WL, PS, HF, and GN: Contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. WL, CL, and YH: Contributed in the data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Written informed consent was obtained from patients with approval by the Institutional Review Board in The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University (No. 202080584).
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Si, P., Fang, H. et al. Long Non-coding RNA LINC01426 Contributes to the Malignant Behaviors of NSCLC Via Acting As a Sponge for miR-143-3p. Biochem Genet 60, 2570–2586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10234-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10234-3