Abstract
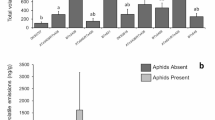
We studied the influence of synthetic (E)-2-hexenal on the abundance of Telenominae aiming to attract parasitoids and enhance stink bug egg parasitism in treated areas. We conducted experiments in 2006, 2007 and 2008 soybean seasons with two short-term (one week) and one long-term (seven weeks) experiment, respectively. We evaluated the abundance of parasitoids with yellow sticky traps and estimated the incidence and intensity of parasitism with sentinel eggs of Euschistus heros Fabricius (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) or with tulle bags, enclosing laboratory pregnant E. heros as an egg source. In short-term experiments, there was increased abundance of Trissolcus spp. (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae: Telenominae) in treated areas, associated with greater intensity of parasitism. In long-term experiments, treatment with (E)-2-hexenal did not influence the abundance of Telenominae or parasitism levels, but increased egg predation. Applications of (E)-2-hexenal can be used to increase recruitment of Trissolcus spp. in the early flowering stages of soybean and also to attract other natural enemies, but do not increase egg parasitism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich JR (1988) Chemical ecology of the Heteroptera. Annu Rev Entomol 33:211–238
Aldrich JR, Rosi MC, Bin F (1995) Behavioral correlates for minor volatile compounds from stink bugs (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). J Chem Ecol 21:1907–1920
Baker R, Borges M, Cooke NG, Herbert RH (1987) Identification and synthesis of (Z)-(1′S,3′R,4′S)(–)-2-(3′,4′-Epoxy-4′-methylcyclohexyl)-6-methylhepta-2,5-diene, the sex pheromone of the southern green stinkbug, Nezara viridula (L.). J Chem Soc Chem Comm 6:414–416
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2013) lme4: linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4. R package version 1.0-5
Borges M, Aldrich JR (1994) Estudos de semioquímicos para o manejo de Telenominae, insetos benéficos. Ann Soc Entomol Brasil 23:575–577
Borges M, Costa MLM, Sujii ER, Cavalcanti MDG, Redigolo GF, Resck IS, Vilela EF (1999) Semiochemical and physical stimuli involved in host recognition by Telenomus podisi (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) toward Euschistus heros (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Physiol Entomol 24:227–233
Borges M, Colazza S, Ramirez-Lucas P, Chauhan KR, Moraes MCB, Aldrich JR (2003) Kairomonal effect of walking traces from Euschistus heros (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on two strains of Telenomus podisi (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Physiol Entomol 28:349–355
Colazza S, Salerno G, Wajnberg E (1999) Volatile and contact chemicals released by Nezara viridula (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) have a kairomonal effect on the egg parasitoid Trissolcus basalis (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Biol Control 16:310–317
Colazza S, McElfresh JS, Millar JG (2004) Identification of volatile synomones, induced by Nezara viridula feeding and oviposition on bean spp., that attract the egg parasitoid Trissolcus basalis. J Chem Ecol 30:945–964
Colazza S, Cusumano A, Lo Giudice D, Peri E (2014) Chemo-orientation responses in hymenopteran parasitoids induced by substrate-borne semiochemicals. BioControl 59:1–17
Conti E, Salerno G, Bin F, Williams HJ, Vinson SB (2003) Chemical cues from Murgantia histrionica eliciting host location and recognition in the egg parasitoid Trissolcus brochymenae. J Chem Ecol 29:115–130
Cook SM, Khan ZR, Pickett JA (2007) The use of push-pull strategies in integrated pest management. Annu Rev Entomol 52:375–400
Corrêa-Ferreira BS (2002) Trissolcus basalis para o controle de percevejos da soja. In: Parra JRP, Botelho PSM, Corrêa-Ferreira BS, Bento JMS (eds) Controle biológico no Brasil: Parasitóides e Predadores. Manole, São Paulo, Brazil, pp 449–476
Corrêa-Ferreira BS, Moscardi F (1995) Seasonal occurrence and host spectrum of egg parasitoids associated with soybean stink bugs. Biol Control 5:196–202
Corrêa-Ferreira BS, Moscardi F (1996) Biological control of soybean stink bugs by inoculative releases of Trissolcus basalis. Entomol Exp Appl 79:1–7
Costa MLM, Borges M, Vilela EF (1998) Biologia reprodutiva de Euschistus heros (F.) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 27:559–568
Crawley MJ (2012) The R book, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, UK
Cronin JT, Strong DR (1990) Density-independent parasitism among host patches by Anagrus delicatus (Hymenoptera, Mymaridae) - experimental manipulation of hosts. J Anim Ecol 59:1019–1026
de Aquino MFS, Dias AM, Borges M, Moraes MCB, Laumann RA (2012) Influence of visual cues on host-searching and learning behaviour of the egg parasitoids Telenomus podisi and Trissolcus basalis. Entomol Exp Appl 145:162–174
Demidenko E (2013) Mixed models: theory and applications with R, 2nd edn. Wiley, New Jersey, USA
Dudareva N, Negre F, Nagegowda DA, Orlova I (2006) Plant volatiles: recent advances and future perspectives. Crit Rev Plant Sci 25:417–440
Embrapa (2010) Tecnologias de Produção de Soja - Região Central do Brasil 2011. Embrapa Soja, Embrapa Cerrados, Embrapa Agropecuária Oeste, Londrina, Brazil
Fatouros NE, Dicke M, Mumm R, Meiners T, Hilker M (2008) Foraging behavior of egg parasitoids exploiting chemical information. Behav Ecol 19:677–689
Galecki A, Burzykowski T (2013) Linear mixed-effects models using R: a step-by-step approach. Springer, New York, USA
Hare JD (2011) Ecological role of volatiles produced by plants in response to damage by herbivorous insects. Annu Rev Entomol 56:161–180
Hassell MP (1985) Insect natural enemies as regulating factors. Ecology 54:323–334
Hassell MP, Waage JK (1984) Host-parasitoid population interactions. Annu Rev Entomol 29:89–114
Hilker M, McNeil JN (2008) Chemical and behavioral ecology in insect parasitoids: how to behave optimally in a complex odorous environment. In: Wajnberg E, Bernstein C, van Alphen J (eds) Behavioural ecology of insect parasitoids: from theoretical approaches to field applications. Wiley-Blackwell, London, UK, pp 92–112
Ishiwatari T (1974) Studies on the scent of stink bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). I. Alarm pheromone activity. Appl Entomol Zool 9:153–158
Ishiwatari T (1976) Studies on the scent of stink bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). II. Aggregation pheromone activity. Appl Entomol Zool 11:38–44
James DG (2003) Synthetic herbivore induced plant volatiles as field attractants for beneficial insects. Environ Entomol 32:977–982
James DG (2005) Further field evaluation of synthetic herbivore induced plant volatiles as attractants for beneficial insects. J Chem Ecol 31:481–495
Jones VP, Steffan SA, Wiman NG, Horton DR, Miliczky E, Zhang QH, Baker CC (2011) Evaluation of herbivore-induced plant volatiles for monitoring green lacewings in Washington apple orchards. Biol Control 56:98–105
Kaplan I (2012) Attracting carnivorous arthropods with plant volatiles: the future of biocontrol or playing with fire? Biol Control 60:77–89
Khan ZR, Midega CAO, Amudavi DM, Hassanali A, Pickett JA (2008) On-farm evaluation of the ‘push–pull’ technology for the control of stemborers and striga weed on maize in western Kenya. Field Crop Res 106:224–233
Khan Z, Midega C, Pittchar J, Pickett J, Bruce T (2011) Push–pull technology: a conservation agriculture approach for integrated management of insect pests, weeds and soil health in Africa UK government’s Foresight Food and Farming Futures project. Int J Agr Sustain 9:162–170
Laumann RA, Moraes MCB, Pareja M, Alarcão GC, Botelho AC, Maia ANH, Leonardecz-Neto E, Borges M (2008) Comparative biology and functional response of Trissolcus spp. (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) and implications for stink-bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) biological control. Biol Control 44:32–41
Laumann RA, Aquino MFS, Moraes MCB, Pareja M, Borges M (2009) Response of the egg parasitoids Trissolcus basalis and Telenomus podisi to compounds from defensive secretions of stink bugs. J Chem Ecol 35:8–19
Laumann RA, Cokl A, Lopes APS, Ferreira JBC, Moraes MCB, Borges M (2011) Silent singers are not safe: selective response of a parasitoid to substrate-borne vibratory signals of stink bugs. Anim Behav 82:1175–1183
Lee JC (2010) Effect of methyl salicylate-based lures on beneficial and pest arthropods in strawberry. Environ Entomol 39:653–660
Lockwood JA, Story RN (1985) Bifunctional pheromone in the first instar of the southern green stink bug, Nezara viridula (L.) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): its characterization and interaction with other stimuli. Ann Entomol Soc Am 78:474–479
Lockwood JA, Story RN (1987) Defensive secretion of the southern green stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) as an alarm pheromone. Ann Entomol Soc Am 80:686–691
Mattiacci L, Vinson SB, Williams HJ, Aldrich JR, Bin F (1993) A long-range attractant kairomone for egg parasitoid Trissolcus basalis, isolated from defensive secretion of its host, Nezara viridula. J Chem Ecol 19:1167–1181
McPherson JE, McPherson R (2000) Stink bugs of economic importance in America North of Mexico. CRC Press LLC, Florida, USA
Meats A, Pando MC (2002) Ratio-dependent parasitism with Trissolcus basalis (Wollaston) (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) on egg rafts of Nezara viridula (Linnaeus) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): effect of experimental variables and compatibility of ‘ratio’ and ‘Holling’ models. Aust J Entomol 41:243–252
Medeiros MA, Schimidt FGV, Loiácono M, Carvalho VF (1997) Parasitismo e predação em ovos de Euschistus heros (Fab.) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) no Distrito Federal, Brasil. An Soc Entomol Bras 26:397–401
Medeiros MA, Loiácono M, Borges M, Schmidt FGV (1998) Incidência natural de parasitóides em ovos de percevejos (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) encontrados na soja no Distrito Federal. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 33:1431–1435
Michereff MFF, Laumann RA, Borges M, Michereff M, Diniz IR, Neto ALF, Moraes MCB (2011) Volatiles mediating a plant-herbivore-natural enemy interaction in resistant and susceptible soybean cultivars. J Chem Ecol 37:273–285
Moraes MCB, Pareja M, Laumann RA, Borges M (2008a) The chemical volatiles (semiochemicals) produced by Neotropical stink bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Neotrop Entomol 37:489–505
Moraes MCB, Pareja M, Laumann RA, Hoffmann-Campo CB, Borges M (2008b) Response of the parasitoid Telenomus podisi to induced volatiles from soybean damaged by stink bug herbivory and oviposition. J Plant Interact 3:111–118
Moraes MCB, Borges M, Laumann RA (2013) The application of chemical cues in arthropod pest management for arable crops. In: Wajnberg E, Colazza S (eds) Chemical ecology of insect parasitoids. Wiley-Blackwell, London, pp 225–244
Panizzi AR (1997) Wild hosts of pentatomids: ecological significance and role in their pest status on crops. Annu Rev Entomol 42:99–122
Pareja M, Borges M, Laumann RA, Moraes MCB (2007) Inter- and intraspecific variation in defensive compounds produced by five neotropical stink bug species (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Insect Physiol 53:639–648
Peres WAA (2004) Aspectos bioecológicos e táticas de manejo dos percevejos Nezara viridula (Linnaeus), Euschistus heros (Fabricius) e Piezodorus guildinii (Westwood) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) em cultivo orgânico de soja. Departamento de Entomologia, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil 160 pp
Pires CSS, Sujii ER, Borges M, Schmidt FGV, Zarbin PHG, Azevedo VCR, Lacerda AL, Pantaleão D (2001) Ação cairomonal de componentes do feromônio de alarme do percevejo verde pequeno da soja, Piezodorus guildinii, sobre o parasitóide de ovos Telenomus podisi. Embrapa Recursos Genéticos e Biotecnologia, Brasília, Brazil
Price PW, Bouton CE, Gross P, McPheron BA, Thompson JN, Weis AE (1980) Interactions among three trophic levels: Influence of plants on interactions between insect herbivores and natural enemies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:41–65
Quinn GP, Keough MJ (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
R Development Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria
Ritchie SW, Hanway JJ, Thompson HE (1988) How a soybean plant develops. Iowa State University of Science and Technology, Ames, USA
Silva CC, Moraes MCB, Laumann RA, Borges M (2006) Sensory response of the egg parasitoid Telenomus podisi to stimuli from the bug Euschistus heros. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 41:1093–1098
Simpson M, Gurr GM, Simmons AT, Wratten SD, James DG, Leeson G, Nicol HI (2011a) Insect attraction to synthetic herbivore-induced plant volatile-treated field crops. Agr Forest Entomol 13:45–57
Simpson M, Gurr GM, Simmons AT, Wratten SD, James DG, Leeson G, Nicol HI, Orre-Gordon GUS (2011b) Attract and reward: combining chemical ecology and habitat manipulation to enhance biological control in field crops. J Appl Ecol 48:580–590
Stiling PD (1987) The frequency of density dependence in insect host-parasitoid systems. Ecology 68:844–856
Straub CS, Finke DL, Snyder WE (2008) Are the conservation of natural enemy biodiversity and biological control compatible goals? Biol Control 45:225–237
Sujii ER, Costa MLM, Pires CSS, Colazza S, Borges M (2002) Inter and intra-guild interactions in egg parasitoid species of the soybean stink bug complex. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 37:1541–1549
Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS (2013) Using multivariate statistics, 6th edn. Allyn & Bacon, Needham, USA
Tillman PG (2010) Parasitism and predation of stink bug (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) eggs in Georgia corn fields. Environ Entomol 39:1184–1194
Vet LEM, Dicke M (1992) Ecology of infochemical use by natural enemies in a tritrophic context. Annu Rev Entomol 37:141–172
Vieira CR, Moraes MCB, Borges M, Sujii ER, Laumann RA (2013) cis-Jasmone indirect action on egg parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) and its application in biological control of soybean stink bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Biol Control 64:75–82
Vinson SB, Bin F, Vet LEM (1998) Critical issues in host selection by insect parasitoids. Biol Control 11:77–78
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Walker NJ, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effect models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York, USA
Acknowledgments
We thank Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – CNPq (process # 480501/2008-4), Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária – Embrapa (process # 03.07.5.100) and Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa do Distrito Federal – FAPDF (process # 193.000.469/2008) for funding. We thank Guarino Colli and James Pitts for comments and suggestions on earlier versions of the manuscript and Hélio Moreira dos Santos for his help with fieldwork. CRV thanks CNPq for providing a dissertation fellowship (process #131208/2008-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stefano Colazza
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieira, C.R., Blassioli -Moraes, M.C., Borges, M. et al. Field evaluation of (E)-2-hexenal efficacy for behavioral manipulation of egg parasitoids in soybean. BioControl 59, 525–537 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-014-9592-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-014-9592-9