Abstract
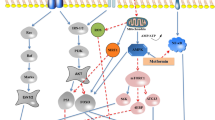
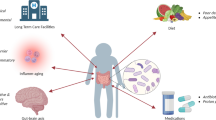
Longevity is mainly conditioned by genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors. Different genetic modifications seem to be positively associated to longevity, including SNPs in SIRT1, APOE, FOXO3A, ACE, ATM, NOS1 and NOS2 gene. Epigenetic changes as DNA hyper- and hypo-methylation influence significantly human longevity by activating/deactivating different genes involved in physiological mechanisms. Several studies have confirmed that centenarians have a lower DNA methylation content compared to young subjects, which showed more homogeneously methylated DNA region. Also the up-regulation of miR-21 seems to be more associated with longevity in different populations of long-lived subjects, suggesting its role as potential epigenetic biomarkers. A non-pharmacological treatment that seems to contrast age-related diseases and promote longevity is represented by dietary intervention. It has been evaluated the effects of dietary restriction of both single nutrients or total calories to extend lifespan. However, in daily practice it is very difficult to guarantee adherence/compliance of the subjects to dietary restriction and at the same time avoid dangerous nutritional deficiencies. As consequence, the attention has focused on a variety of substances both drugs and natural compounds able to mime the beneficial effects of caloric restriction, including resveratrol, quercetin, rapamycin, metformin and 2-deoxy-d-glucose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abete P, Ferrara N, Cacciatore F, Sagnelli E, Manzi M, Carnovale V, Calabrese C, de Santis D, Testa G, Longobardi G, Napoli C, Rengo F (2001) High level of physical activity preserves the cardioprotective effect of preinfarction angina in elderly patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 38:1357–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01560-1
Abete P, Cacciatore F, Ferrara N, Calabrese C, de Santis D, Testa G, Galizia G, Del Vecchio S, Leosco D, Condorelli M, Napoli C, Rengo F (2003) Body mass index and preinfarction angina in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Clin Nutr 78:796–801. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/78.4.796
Albani D, Mazzuco S, Polito L, Batelli S, Biella G, Ongaro F, Gustafson DR, Antuono P, Gajo G, Durante E, Caberlotto L, Zanardo A, Siculi M, Gallucci M, Forloni G (2011) Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor polymorphism rs2229765 and circulating interleukin-6 level affect male longevity in a population-based prospective study (Treviso Longeva–TRELONG). Aging Male 14:257–264. https://doi.org/10.3109/13685538.2011.607521
Anisimov VN, Berstein LM, Egormin PA, Piskunova TS, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Tyndyk ML, Yurova MV, Kovalenko IG, Poroshina TE, Semenchenko AV (2008) Metformin slows down aging and extends life span of female SHR mice. Cell Cycle. 7:2769–2773. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.17.6625
Anselmi CV, Malovini A, Roncarati R, Novelli V, Villa F, Condorelli G, Bellazzi R, Puca AA (2009) Association of the FOXO3A locus with extreme longevity in a southern Italian centenarian study. Rejuvenation Res 12:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2008.0827
Arai Y, Martin-Ruiz CM, Takayama M, Abe Y, Takebayashi T, Koyasu S, Suematsu M, Hirose N, von Zglinicki T (2015) Inflammation, but not telomere length, predicts successful ageing at extreme old age: a longitudinal study of semi-supercentenarians. EBioMedicine 2:1549–1558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.07.029
Arai Y, Sasaki T, Hirose N (2017) Demographic, phenotypic, and genetic characteristics of centenarians in Okinawa and Honshu, Japan: part 2 Honshu, Japan. Mech Ageing Dev 165:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2017.02.005
Ard JD, Gower B, Hunter G, Ritchie CS, Roth DL, Goss A, Wingo BC, Bodner EV, Brown CJ, Bryan D, Buys DR, Haas MC, Keita AD, Flagg LA, Williams CP, Locher JL (2017) Effects of calorie restriction in obese older adults: the CROSSROADS randomized controlled trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 73:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glw237
Balasubramanian P, Longo VD (2016) Growth factors, aging and age-related diseases. Growth Horm IGF Res 28:66–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ghir.2016.01.001
Balestrieri ML, Rienzo M, Felice F, Rossiello R, Grimaldi V, Milone L, Casamassimi A, Servillo L, Farzati B, Giovane A, Napoli C (2008) High glucose downregulates endothelial progenitor cell number via SIRT1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:936–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.03.004
Balzano F, Deiana M, Dei Giudici S, Oggiano A, Pasella S, Pinna S, Mannu A, Deiana N, Porcu B, Masala AGE, Pileri PV, Scognamillo F, Pala C, Zinellu A, Carru C, Deiana L (2017) MicroRNA expression analysis of centenarians and rheumatoid arthritis patients reveals a common expression pattern. Int J Med Sci 14:622–628. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.18972
Bandyopadhyay D, Okan NA, Bales E, Nascimento L, Cole PA, Medrano EE (2002) Down-regulation of p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase activates a senescence checkpoint in human melanocytes. Cancer Res 62:6231–6239
Bao JM, Song XL, Hong YQ, Zhu HL, Li C, Zhang T, Chen W, Zhao SC, Chen Q (2014) Association between FOXO3A gene polymorphisms and human longevity: a meta-analysis. Asian J Androl 16:446–452. https://doi.org/10.4103/1008-682X.123673
Barzilai N, Gabriely I, Gabriely M, Iankowitz N, Sorkin JD (2001) Offspring of centenarians have a favorable lipid profile. J Am Geriatr Soc 49:76–79. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1532-5415.2001.49013.x
Beekman M, Blanché H, Perola M, Hervonen A, Bezrukov V, Sikora E, Flachsbart F, Christiansen L, De Craen AJ, Kirkwood TB, Rea IM, Poulain M, Robine JM, Valensin S, Stazi MA, Passarino G, Deiana L, Gonos ES, Paternoster L, Sørensen TI, Tan Q, Helmer Q, van den Akker EB, Deelen J, Martella F, Cordell HJ, Ayers KL, Vaupel JW, Törnwall O, Johnson TE, Schreiber S, Lathrop M, Skytthe A, Westendorp RG, Christensen K, Gampe J, Nebel A, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Slagboom PE, Franceschi C, GEHA consortium (2013) Genome-wide linkage analysis for human longevity: genetics of healthy aging study. Aging Cell 12:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12039
Bell JT, Tsai PC, Yang TP, Pidsley R, Nisbet J, Glass D, Mangino M, Zhai G, Zhang F, Valdes A, Shin SY, Dempster EL, Murray RM, Grundberg E, Hedman AK, Nica A, Small KS, MuTHER Consortium, Dermitzakis ET, McCarthy MI, Mill J, Spector TD, Deloukas P (2012) Epigenome-wide scans identify differentially methylated regions for age and age-related phenotypes in a healthy ageing population. PLoS Genet 8:e1002629. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002629
Blanché H, Cabanne L, Sahbatou M, Thomas G (2001) A study of French centenarians: are ACE and APOE associated with longevity? C R Acad Sci III 324:129–135
Bollati V, Schwartz J, Wright R, Litonjua A, Tarantini L, Suh H, Sparrow D, Vokonas P, Baccarelli A (2009) Decline in genomic DNA methylation through aging in a cohort of elderly subjects. Mech Ageing Dev 130:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2008.12.003
Boots AW, Wilms LC, Swennen EL, Kleinjans JC, Bast A, Haenen GR (2008) In vitro and ex vivo anti-inflammatory activity of quercetin in healthy volunteers. Nutrition 24:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2008.03.023
Borrás C, Serna E, Gambini J, Inglés M, Vina J (2017) Centenarians maintain miRNA biogenesis pathway while it is impaired in octogenarians. Mech Ageing Dev 168:54–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2017.07.003
Brandts L, van den Brandt PA (2018) Sex-specific associations between smoking habits and reaching longevity: Netherlands cohort study. Geriatr Gerontol Int 18:1249–1258. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.13468
Brasnyó P, Molnár GA, Mohás M, Markó L, Laczy B, Cseh J, Mikolás E, Szijártó IA, Mérei A, Halmai R, Mészáros LG, Sümegi B, Wittmann I (2011) Resveratrol improves insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress and activates the Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic patients. Br J Nutr 106:383–389. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114511000316
Bultman SJ (2017) Interplay between diet, gut microbiota, epigenetic events, and colorectal cancer. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201500902
Cangemi R, Friedmann AJ, Holloszy JO, Fontana L (2010) Long-term effects of calorie restriction on serum sex-hormone concentrations in men. Aging Cell 9:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00553.x
Cellini E, Nacmias B, Olivieri F, Ortenzi L, Tedde A, Bagnoli S, Petruzzi C, Franceschi C, Sorbi S (2005) Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) I405 V polymorphism and longevity in Italian centenarians. Mech Ageing Dev 126:826–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2005.01.009
Chen T, Dong B, Lu Z, Tian B, Zhang J, Zhou J, Wu H, Zhang Y, Wu J, Lin P, Zhang J, Xu H, Mo X (2010) A functional single nucleotide polymorphism in promoter of ATM is associated with longevity. Mech Ageing Dev 131:636–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2010.08.009
Ciccarone F, Malavolta M, Calabrese R, Guastafierro T, Bacalini MG, Reale A, Franceschi C, Capri M, Hervonen A, Hurme M, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Koller B, Bernhardt J, Schön C, Slagboom PE, Toussaint O, Sikora E, Gonos ES, Breusing N, Grune T, Jansen E, Dollé M, Moreno-Villanueva M, Sindlinger T, Bürkle A, Zampieri M, Caiafa P (2016) Age-dependent expression of DNMT1 and DNMT3B in PBMCs from a large European population enrolled in the MARK-AGE study. Aging Cell 15:755–765. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12485
Clemente JC, Ursell LK, Parfrey LW, Knight R (2012) The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148:1258–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035
Das SK, Gilhooly CH, Golden JK, Pittas AG, Fuss PJ, Cheatham RA, Tyler S, Tsay M, McCrory MA, Lichtenstein AH, Dallal GE, Dutta C, Bhapkar MV, Delany JP, Saltzman E, Roberts SB (2007) Long-term effects of 2 energy-restricted diets differing in glycemic load on dietary adherence, body composition, and metabolism in CALERIE: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 85:1023–1030. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.4.1023
Das SK, Roberts SB, Bhapkar MV, Villareal DT, Fontana L, Martin CK, Racette SB, Fuss PJ, Kraus WE, Wong WW, Saltzman E, Pieper CF, Fielding RA, Schwartz AV, Ravussin E, Redman LM (2017) Body-composition changes in the comprehensive assessment of long-term effects of reducing intake of energy (CALERIE)-2 study: a 2-year randomized controlled trial of calorie restriction in nonobese humans. Am J Clin Nutr 105:913–927. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.116.137232
De Marte ML, Enesco HE (1986) Influence of low tryptophan diet on survival and organ growth in mice. Mech Ageing Dev 36:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-6374(86)90017-5
Deelen J, Beekman M, Uh HW, Broer L, Ayers KL, Tan Q, Kamatani Y, Bennet AM, Tamm R, Trompet S, Guðbjartsson DF, Flachsbart F, Rose G, Viktorin A, Fischer K, Nygaard M, Cordell HJ, Crocco P, van den Akker EB, Böhringer S, Helmer Q, Nelson CP, Saunders GI, Alver M, Andersen-Ranberg K, Breen ME, van der Breggen R, Caliebe A, Capri M, Cevenini E, Collerton JC, Dato S, Davies K, Ford I, Gampe J, Garagnani P, de Geus EJ, Harrow J, van Heemst D, Heijmans BT, Heinsen FA, Hottenga JJ, Hofman A, Jeune B, Jonsson PV, Lathrop M, Lechner D, Martin-Ruiz C, Mcnerlan SE, Mihailov E, Montesanto A, Mooijaart SP, Murphy A, Nohr EA, Paternoster L, Postmus I, Rivadeneira F, Ross OA, Salvioli S, Sattar N, Schreiber S, Stefánsson H, Stott DJ, Tiemeier H, Uitterlinden AG, Westendorp RG, Willemsen G, Samani NJ, Galan P, Sørensen TI, Boomsma DI, Jukema JW, Rea IM, Passarino G, de Craen AJ, Christensen K, Nebel A, Stefánsson K, Metspalu A, Magnusson P, Blanché H, Christiansen L, Kirkwood TB, van Duijn CM, Franceschi C, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Slagboom PE (2014) Genome-wide association meta-analysis of human longevity identifies a novel locus conferring survival beyond 90 years of age. Hum Mol Genet 23:4420–4432. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu139
Demirovic D, Rattan SI (2011) Curcumin induces stress response and hermetically modulates wound healing ability of human skin fibroblasts undergoing ageing in vitro. Biogerontology 12:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-011-9326-7
Dibble CC, Manning BD (2013) Signal integration by mTORC1 coordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic output. Nat Cell Biol 15:555–564. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2763
Díez JJ, Iglesias P (2003) The role of the novel adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin in human disease. Eur J Endocrinol 148:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.0.1480293
Donlon TA, Morris BJ, Chen R, Masaki KH, Allsopp RC, Willcox DC, Tiirikainen M, Willcox BJ (2018) Analysis of polymorphisms in 59 potential candidate genes for association with human longevity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 73:1459–1464. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glx247
ElSharawy A, Keller A, Flachsbart F, Wendschlag A, Jacobs G, Kefer N, Brefort T, Leidinger P, Backes C, Meese E, Schreiber S, Rosenstiel P, Franke A, Nebel A (2012) Genome-wide miRNA signatures of human longevity. Aging Cell 11:607–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00824.x
Feng J, Xiang L, Wan G, Qi K, Sun L, Huang Z, Zheng C, Lv Z, Hu C, Yang Z (2011) Is APOE ε3 a favourable factor for the longevity: an association study in Chinese population. J Genet 90:343–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0075-9
Ferri E, Gussago C, Casati M, Mari D, Rossi PD, Ciccone S, Cesari M, Arosio B (2019) Apolipoprotein E gene in physiological and pathological aging. Mech Ageing Dev 178:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2019.01.005
Fiuza-Luces C, Ruiz JR, Rodríguez-Romo G, Santiago C, Gómez-Gallego F, Cano-Nieto A, Garatachea N, Rodríguez-Moreno I, Morán M, Lucia A (2011) Is the ACE I/D polymorphism associated with extreme longevity? A study on a Spanish cohort. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 12:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320310391505
Flachsbart F, Caliebe A, Kleindorp R, Blanché H, von Eller-Eberstein H, Nikolaus S, Schreiber S, Nebel A (2009) Association of FOXO3A variation with human longevity confirmed in German centenarians. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2700–2705. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809594106
Florath I, Butterbach K, Müller H, Bewerunge-Hudler M, Brenner H (2014) Cross-sectional and longitudinal changes in DNA methylation with age: an epigenome-wide analysis revealing over 60 novel age-associated CpG sites. Hum Mol Genet 23:1186–1201. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt531
Fontana L, Hu FB (2014) Optimal body weight for health and longevity: bridging basic, clinical, and population research. Aging Cell 13:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12207
Fontana L, Meyer TE, Klein S, Holloszy JO (2004) Long-term calorie restriction is highly effective in reducing the risk for atherosclerosis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6659–6663. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308291101
Fontana L, Villareal DT, Das SK, Smith SR, Meydani SN, Pittas AG, Klein S, Bhapkar M, Rochon J, Ravussin E, Holloszy JO, CALERIE Study Group (2016) Effects of 2-year calorie restriction on circulating levels of IGF-1, IGF-binding proteins and cortisol in nonobese men and women: a randomized clinical trial. Aging Cell 15:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12400
Fritz KS (2013) Chemical acetylation and deacetylation. Methods Mol Biol 1077:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-637-5_13
Garatachea N, Emanuele E, Calero M, Fuku N, Arai Y, Abe Y, Murakami H, Miyachi M, Yvert T, Verde Z, Zea MA, Venturini L, Santiago C, Santos-Lozano A, Rodríguez-Romo G, Ricevuti G, Hirose N, Rábano A, Lucia A (2014) ApoE gene and exceptional longevity: Insights from three independent cohorts. Exp Gerontol 53:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2014.02.004
Ge Y, Liu H, Qiu X, Ma G, Wang H, Du M, Wang M, Zhao Q, Tao G, Chu H, Zhang Z (2018) Genetic variants in PI3 K/Akt/mTOR pathway genes contribute to gastric cancer risk. Gene 670:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.093
Gentilini D, Mari D, Castaldi D, Remondini D, Ogliari G, Ostan R, Bucci L, Sirchia SM, Tabano S, Cavagnini F, Monti D, Franceschi C, Di Blasio AM, Vitale G (2013) Role of epigenetics in human aging and longevity: genome-wide DNA methylation profile in centenarians and centenarians’ offspring. Age (Dordr) 35:1961–1973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9463-1
Giovannini S, Onder G, Liperoti R, Russo A, Carter C, Capoluongo E, Pahor M, Bernabei R, Landi F (2011) Interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha as predictors of mortality in frail, community-living elderly individuals. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:1679–1685. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03570.x
Gombar S, Jung HJ, Dong F, Calder B, Atzmon G, Barzilai N, Tian XL, Pothof J, Hoeijmakers JH, Campisi J, Vijg J, Suh Y (2012) Comprehensive microRNA profiling in B-cells of human centenarians by massively parallel sequencing. BMC Genomics 13:353. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-353
Guarente L (2011) Franklin H epstein lecture: sirtuins, aging, and medicine. N Engl J Med 364:2235–2244. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1100831
Gyurus E, Kaposztas Z, Kahan BD (2011) Sirolimus therapy predisposes to new-onset diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation: a long-term analysis of various treatment regimens. Transplant Proc 43:1583–1592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.05.001
Hannum G, Guinney J, Zhao L, Zhang L, Hughes G, Sadda S, Klotzle B, Bibikova M, Fan JB, Gao Y, Deconde R, Chen M, Rajapakse I, Friend S, Ideker T, Zhang K (2013) Genome-wide methylation profiles reveal quantitative views of human aging rates. Mol Cell 49:359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.016
Heyn H, Li N, Ferreira HJ, Moran S, Pisano DG, Gomez A, Diez J, Sanchez-Mut JV, Setien F, Carmona FJ, Puca AA, Sayols S, Pujana MA, Serra-Musach J, Iglesias-Platas I, Formiga F, Fernandez AF, Fraga MF, Heath SC, Valencia A, Gut IG, Wang J, Esteller M (2012) Distinct DNA methylomes of newborns and centenarians. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:10522–10527. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1120658109
Hjelmborg JVB, Iachine I, Skytthe A, Vaupel JW, McGue M, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, Pedersen NL, Christensen K (2006) Genetic influence on human lifespan and longevity. Hum Genet 119:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0144-y
Horstman AM, Dillon EL, Urban RJ, Sheffield-Moore M (2012) The role of androgens and estrogens on healthy aging and longevity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67:1140–1152. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls068
Hou X, Rooklin D, Fang H, Zhang Y (2016) Resveratrol serves as a protein-substrate interaction stabilizer in human SIRT1 activation. Sci Rep 6:38186. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38186
Huidobro C, Fernandez AF, Fraga MF (2013) Aging epigenetics: causes and consequences. Mol Aspects Med 34:765–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.06.006
Ignarro LJ, Balestrieri ML, Napoli C (2007) Nutrition, physical activity, and cardiovascular disease: an update. Cardiovasc Res 73:326–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.06.030
Ingram DK, Roth GS (2011) Glycolytic inhibition as a strategy for developing calorie restriction mimetics. Exp Gerontol 46:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2010.12.001
Jacobsen R, Martinussen T, Christiansen L, Jeune B, Andersen-Ranberg K, Vaupel JW, Christensen K (2010) Increased effect of the ApoE gene on survival at advanced age in healthy and long-lived Danes: two nationwide cohort studies. Aging Cell 9:1004–1009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00626.x
Karbowska J, Kochan Z (2012) Fat-reducing effects of dehydroepiandrosterone involve upregulation of ATGL and HSL expression, and stimulation of lipolysis in adipose tissue. Steroids 77:1359–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2012.08.002
Khabour OF, Barnawi JM (2010) Association of longevity with IL-10-1082 G/A and TNF-alpha-308 G/A polymorphisms. Int J Immunogenet 37:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-313X.2010.00925.x
Kilic U, Gok O, Erenberk U, Dundaroz MR, Torun E, Kucukardali Y, Elibol-Can B, Uysal O, Dundar T (2015) A remarkable age-related increase in SIRT1 protein expression against oxidative stress in elderly: SIRT1 gene variants and longevity in human. PLoS ONE 10:e0117954. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117954
Kim NH, Lee J, Kim TJ, Kim NH, Choi KM, Baik SH, Choi DS, Pop-Busui R, Park Y, Kim SG (2015) Body mass index and mortality in the general population and in subjects with chronic disease in Korea: a nationwide cohort study (2002–2010). PLoS ONE 10:e0139924. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139924
Kujala UM (2018) Is physical activity a cause of longevity? It is not as straightforward as some would believe. A critical analysis. Br J Sports Med 52:914–918. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-098639
Kumar NT, Liestøl K, Løberg EM, Reims HM, Brorson SH, Maehlen J (2012) The apolipoprotein E polymorphism and cardiovascular diseases—an autopsy study. Cardiovasc Pathol 21:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2012.02.005
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149:274–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
Lardenoije R, Iatrou A, Kenis G, Kompotis K, Steinbusch HW, Mastroeni D, Coleman P, Lemere CA, Hof PR, van den Hove DL, Rutten BP (2015) The epigenetics of aging and neurodegeneration. Prog Neurobiol 131:21–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.05.002
Lazarus J, Mather KA, Thalamuthu A, Kwok JB (2015) Genetic factors and epigenetic mechanisms of longevity: current perspectives. Epigenomics 7:1339–1349. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi.15.80
Le Rhun E, Bertrand N, Dumont A, Tresch E, Le Deley MC, Mailliez A, Preusser M, Weller M, Revillion F, Bonneterre J (2017) Identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms of the PI3 K-AKT-mTOR pathway as a risk factor of central nervous system metastasis in metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 87:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.10.006
Levine ME, Suarez JA, Brandhorst S, Balasubramanian P, Cheng CW, Madia F, Fontana L, Mirisola MG, Guevara-Aguirre J, Wan J, Passarino G, Kennedy BK, Wei M, Cohen P, Crimmins EM, Longo VD (2014) Low protein intake is associated with a major reduction in IGF-1, cancer, and overall mortality in the 65 and younger but not older population. Cell Metab 19:407–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.02.006
Li Q, Huang P, He QC, Lin QZ, Wu J, Yin RX (2014) Association between the CETP polymorphisms and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, carotid atherosclerosis, longevity, and the efficacy of statin therapy. Neurobiol Aging 35:1513.e13–1513.e23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.12.032
Li Y, Choi WJ, Wei W, Song S, Zhang Q, Liu J, Wang RK (2018) Aging-associated changes in cerebral vasculature and blood flow as determined by quantitative optical coherence tomography angiography. Neurobiol Aging 70:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.06.017
Lin R, Yan D, Zhang Y, Liao X, Gong G, Hu J, Fu Y, Cai W (2016) Common variants in SIRT1 and human longevity in a Chinese population. BMC Med Genet 17:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-016-0293-3
Liu CC, Liu CC, Kanekiyo T, Xu H, Bu G (2013) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat Rev Neurol 9:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.263
Liu Z, Zhong G, Li S, Deng W, Zhang Y, Qian D, Jin L, Wang X (2015) Use of serum albumin and activities of daily living to predict mortality in long-lived individuals over 95 years of age: a population-based study. Age (Dordr) 37:9809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-015-9809-6
Liu Z, Huang J, Qian D, Chen F, Xu J, Li S, Jin L, Wang X (2016) Does low body mass index matter? Relationship between body mass index and subjective well-being among long-lived women over 95 years of age. J Nutr Health Aging 20:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0556-2
Lv YB, Yin ZX, Chei CL, Qian HZ, Kraus VB, Zhang J, Brasher MS, Shi XM, Matchar DB, Zeng Y (2015) Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol was inversely associated with 3-year all-cause mortality among Chinese oldest old: data from the Chinese longitudinal healthy longevity survey. Atherosclerosis 239:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.01.002
Lv YB, Mao C, Gao X, Yin ZX, Kraus VB, Yuan JQ, Zhang J, Luo JS, Zeng Y, Shi XM (2019) Triglycerides paradox among the oldest old: “the lower the better?”. J Am Geriatr Soc 67:741–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.15733
Maggio M, Cattabiani C, Lauretani F, Bandinelli S, De Vita F, Dall’Aglio E, Corsonello A, Lattanzio F, Paolisso G, Ferrucci L, Ceda GP (2013) Insulin-like growth factor-1 bioactivity plays a prosurvival role in older participants. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68:1342–1350. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glt045
Marttila S, Kananen L, Häyrynen S, Jylhävä J, Nevalainen T, Hervonen A, Jylhä M, Nykter M, Hurme M (2015) Ageing-associated changes in the human DNA methylome: genomic locations and effects on gene expression. BMC Genomics 16:179. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1381-z
Mattson MP (2008) Hormesis defined. Ageing Res Rev 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2007.08.007
Meazza C, Vitale G, Pagani S, Castaldi D, Ogliari G, Mari D, Laarej K, Tinelli C, Bozzola M (2011) Common adipokine features of neonates and centenarians. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 24:953–957. https://doi.org/10.1515/JPEM.2011.373
Meydani SN, Das SK, Pieper CF, Lewis MR, Klein S, Dixit VD, Gupta AK, Villareal DT, Bhapkar M, Huang M, Fuss PJ, Roberts SB, Holloszy JO, Fontana L (2016) Long-term moderate calorie restriction inhibits inflammation without impairing cell-mediated immunity: a randomized controlled trial in non-obese humans. Aging (Albany NY) 8:1416–1431. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100994
Miller RA, Buehner G, Chang Y, Harper JM, Sigler R, Smith-Wheelock M (2005) Methionine-deficient diet extends mouse lifespan, slows immune and lens aging, alters glucose, T4, IGF-I and insulin levels, and increases hepatocyte MIF levels and stress resistance. Aging Cell 4:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2005.00152.x
Miller KM, Tjeertes JV, Coates J, Legube G, Polo SE, Britton S, Jackson SP (2010) Human HDAC1 and HDAC2 function in the DNA-damage response to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1144–1151. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1899
Mirzaei H, Suarez JA, Longo VD (2014) Protein and amino acid restriction, aging and disease: from yeast to humans. Trends Endocrinol Metab 25:558–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2014.07.002
Montesanto A, Crocco P, Tallaro F, Pisani F, Mazzei B, Mari V, Corsonello A, Lattanzio F, Passarino G, Rose G (2013) Common polymorphisms in nitric oxide synthase (NOS) genes influence quality of aging and longevity in humans. Biogerontology 14:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9421-z
Moore AZ, Hernandez DG, Tanaka T, Pilling LC, Nalls MA, Bandinelli S, Singleton AB, Ferrucci L (2016) Change in epigenome-wide DNA methylation over 9 years and subsequent mortality: results from the InCHIANTI study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 71:1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glv118
Moreira EA, Most M, Howard J, Ravussin E (2011) Dietary adherence to long-term controlled feeding in a calorie-restriction study in overweight men and women. Nutr Clin Pract 26:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533611405992
Morris BJ (2013) Seven sirtuins for seven deadly diseases of aging. Free Radic Biol Med 56:133–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.10.525
Morris BJ, Donlon TA, He Q, Grove JS, Masaki KH, Elliott A, Willcox DC, Allsopp R, Willcox BJ (2015) Genetic analysis of TOR complex gene variation with human longevity: a nested case-control study of American men of Japanese ancestry. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 70:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu021
Morselli E, Maiuri MC, Markaki M, Megalou E, Pasparaki A, Palikaras K, Criollo A, Galluzzi L, Malik SA, Vitale I, Michaud M, Madeo F, Tavernarakis N, Kroemer G (2010) Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuin-1-dependent induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis 1:e10. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2009.8
Most J, Tosti V, Redman LM, Fontana L (2017) Calorie restriction in humans: an update. Ageing Res Rev 39:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.08.005
Napoli C, Crudele V, Soricelli A, Al-Omran M, Vitale N, Infante T, Mancini FP (2012) Primary prevention of atherosclerosis: a clinical challenge for the reversal of epigenetic mechanisms? Circulation 125:2363–2373. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.085787
Napoli C, Benincasa G, Loscalzo J (2019) Epigenetic inheritance underlying pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 39(4):653–664
Nebel A, Kleindorp R, Caliebe A, Nothnagel M, Blanché H, Junge O, Wittig M, Ellinghaus D, Flachsbart F, Wichmann HE, Meitinger T, Nikolaus S, Franke A, Krawczak M, Lathrop M, Schreiber S (2011) A genome-wide association study confirms APOE as the major gene influencing survival in long-lived individuals. Mech Ageing Dev 132:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2011.06.008
Nijiati M, Saidaming A, Qiao J, Cheng Z, Qiu C, Sun Y (2013) GNB3, eNOS, and mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms correlate to natural longevity in a Xinjiang Uygur population. PLoS ONE 8:e81806. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081806
Nisoli E, Clementi E, Paolucci C, Cozzi V, Tonello C, Sciorati C, Bracale R, Valerio A, Francolini M, Moncada S, Carruba MO (2003) Mitochondrial biogenesis in mammals: the role of endogenous nitric oxide. Science 299:896–899. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1079368
Olivieri F, Spazzafumo L, Santini G, Lazzarini R, Albertini MC, Rippo MR, Galeazzi R, Abbatecola AM, Marcheselli F, Monti D, Ostan R, Cevenini E, Antonicelli R, Franceschi C, Procopio AD (2012) Age-related differences in the expression of circulating microRNAs: miR-21 as a new circulating marker of inflammaging. Mech Ageing Dev 133:675–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2012.09.004
Pareja-Galeano H, Santos-Lozano A, Sanchis-Gomar F, Fiuza-Luces C, Garatachea N, Gálvez BG, Lucia A, Emanuele E (2017) Circulating leptin and adiponectin concentrations in healthy exceptional longevity. Mech Ageing Dev 162:129–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.02.014
Passtoors WM, Beekman M, Deelen J, van der Breggen R, Maier AB, Guigas B, Derhovanessian E, van Heemst D, de Craen AJ, Gunn DA, Pawelec G, Slagboom PE (2013) Gene expression analysis of mTOR pathway: association with human longevity. Aging Cell 12:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12015
Peña-Romero AC, Navas-Carrillo D, Marín F, Orenes-Piñero E (2018) The future of nutrition: nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics in obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:3030–3041. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1349731
Piaceri I, Bagnoli S, Tedde A, Sorbi S, Nacmias B (2013) Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) genetic variant in Italian centenarians. Neurol Sci 34:573–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1188-5
Piskovatska V, Stefanyshyn N, Storey KB, Vaiserman AM, Lushchak O (2019a) Metformin as a geroprotector: experimental and clinical evidence. Biogerontology 20:33–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-018-9773-5
Piskovatska V, Strilbytska O, Koliada A, Vaiserman A, Lushchak O (2019b) Health benefits of anti-aging drugs. Subcell Biochem 91:339–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3681-2_13
Psahoulia FH, Moumtzi S, Roberts ML, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, Pintzas A (2007) Quercetin mediates preferential degradation of oncogenic Ras and causes autophagy in Ha-RAS-transformed human colon cells. Carcinogenesis 28:1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgl232
Puzianowska-Kuźnicka M, Owczarz M, Wieczorowska-Tobis K, Nadrowski P, Chudek J, Slusarczyk P, Skalska A, Jonas M, Franek E, Mossakowska M (2016) Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein, successful aging, and mortality: the PolSenior study. Immun Ageing 13:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12979-016-0076-x
Rahilly-Tierney CR, Spiro A 3rd, Vokonas P, Gaziano JM (2011) Relation between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and survival to age 85 years in men (from the VA normative aging study). Am J Cardiol 107:1173–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.12.015
Rattan SI (2010) Targeting the age-related occurrence, removal, and accumulation of molecular damage by hormesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1197:28–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05193.x
Rattan SI (2014) Aging is not a disease: implications for intervention. Aging Dis 5:196–202. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2014.0500196
Rattan SI, Demirovic D (2009) Hormesis can and does work in humans. Dose Response 8:58–63. https://doi.org/10.2203/dose-response.09-041.Rattan
Revelas M, Thalamuthu A, Oldmeadow C, Evans TJ, Armstrong NJ, Kwok JB, Brodaty H, Schofield PR, Scott RJ, Sachdev PS, Attia JR, Mather KA (2018) Review and meta-analysis of genetic polymorphisms associated with exceptional human longevity. Mech Ageing Dev 175:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2018.06.002
Rochon J, Bales CW, Ravussin E, Redman LM, Holloszy JO, Racette SB, Roberts SB, Das SK, Romashkan S, Galan KM, Hadley EC, Kraus WE, CALERIE Study Group (2011) Design and conduct of the CALERIE study: comprehensive assessment of the long-term effects of reducing intake of energy. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 66:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glq168
Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL (2014) 20 years of leptin: role of leptin in energy homeostasis in humans. J Endocrinol 223:T83–T96. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-14-0358
Ruby JG, Wright KM, Rand KA, Kermany A, Noto K, Curtis D, Varner N, Garrigan D, Slinkov D, Dorfman I, Granka JM, Byrnes J, Myres N, Ball C (2018) Estimates of the heritability of human longevity are substantially inflated due to assortative mating. Genetics 210:1109–1124. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.118.301613
Ruth MR, Port AM, Shah M, Bourland AC, Istfan NW, Nelson KP, Gokce N, Apovian CM (2013) Consuming a hypocaloric high fat low carbohydrate diet for 12 weeks lowers C-reactive protein, and raises serum adiponectin and high density lipoprotein-cholesterol in obese subjects. Metabolism 62:1779–1787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.07.006
Sanders YY, Liu H, Zhang X, Hecker L, Bernard K, Desai L, Liu G, Thannickal VJ (2013) Histone modifications in senescence-associated resistance to apoptosis by oxidative stress. Redox Biol 1:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2012.11.004
Santos-Lozano A, Santamarina A, Pareja-Galeano H, Sanchis-Gomar F, Fiuza-Luces C, Cristi-Montero C, Bernal-Pino A, Lucia A, Garatachea N (2016) The genetics of exceptional longevity: insights from centenarians. Maturitas 90:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.05.006
Schiano C, Vietri MT, Grimaldi V, Picascia A, De Pascale MR, Napoli C (2015) Epigenetic-related therapeutic challenges in cardiovascular disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2015.02.005
Scognamiglio M, Costa D, Sorriento A, Napoli C (2019) Current therapy and nutraceuticals for the treatment of patients with dyslipidemias. Curr Pharm Des 25:85–95. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666190130101108
Seidelmann SB, Claggett B, Cheng S, Henglin M, Shah A, Steffen LM, Folsom AR, Rimm EB, Willett WC, Solomon SD (2018) Dietary carbohydrate intake and mortality: a prospective cohort study and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 3:e419–e428. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(18)30135-X
Seripa D, Franceschi M, Matera MG, Panza F, Kehoe PG, Gravina C, Orsitto G, Solfrizzi V, Di Minno G, Dallapiccola B, Pilotto A (2006) Sex differences in the association of apolipoprotein E and angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms with healthy aging and longevity: a population-based study from Southern Italy. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61:918–923. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/61.9.918
Serna E, Gambini J, Borras C, Abdelaziz KM, Belenguer A, Sanchis P, Avellana JA, Rodriguez-Mañas L, Viña J (2012) Centenarians, but not octogenarians, up-regulate the expression of microRNAs. Sci Rep 2:961. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00961
Shah S, McRae AF, Marioni RE, Harris SE, Gibson J, Henders AK, Redmond P, Cox SR, Pattie A, Corley J, Murphy L, Martin NG, Montgomery GW, Starr JM, Wray NR, Deary IJ, Visscher PM (2014) Genetic and environmental exposures constrain epigenetic drift over the human life course. Genome Res 24:1725–1733. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.176933.114
Skytthe A, Pedersen NL, Kaprio J, Stazi MA, Hjelmborg JV, Iachine I, Vaupel JW, Christensen K (2003) Longevity studies in GenomEUtwin. Twin Res 6:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1375/136905203770326457
Slawson DL, Fitzgerald N, Morgan KT (2013) Position of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: the role of nutrition in health promotion and chronic disease prevention. J Acad Nutr Diet 113:972–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2013.05.005
Soare A, Cangemi R, Omodei D, Holloszy JO, Fontana L (2011) Long-term calorie restriction, but not endurance exercise, lowers core body temperature in humans. Aging (Albany NY) 3:374–379. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100280
Soerensen M, Dato S, Tan Q, Thinggaard M, Kleindorp R, Beekman M, Jacobsen R, Suchiman HE, de Craen AJ, Westendorp RG, Schreiber S, Stevnsner T, Bohr VA, Slagboom PE, Nebel A, Vaupel JW, Christensen K, McGue M, Christiansen L (2012) Human longevity and variation in GH/IGF-1/insulin signaling, DNA damage signaling and repair and pro/antioxidant pathway genes: cross sectional and longitudinal studies. Exp Gerontol 47:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2012.02.010
Solymár M, Ivic I, Pótó L, Hegyi P, Garami A, Hartmann P, Pétervári E, Czopf L, Hussain A, Gyöngyi Z, Sarlós P, Simon M, Mátrai P, Bérczi B, Balaskó M (2018) Metformin induces significant reduction of body weight, total cholesterol and LDL levels in the elderly—a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 13:e0207947. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207947
Stenholm S, Head J, Aalto V, Kivimäki M, Kawachi I, Zins M, Goldberg M, Platts LG, Zaninotto P, Magnusson Hanson LL, Westerlund H, Vahtera J (2017) Body mass index as a predictor of healthy and disease-free life expectancy between ages 50 and 75: a multicohort study. Int J Obes (Lond) 41:769–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2017.29
Sun L, Lin J, Du H, Hu C, Huang Z, Lv Z, Zheng C, Shi X, Zhang Y, Yang Z (2014) Gender-specific DNA methylome analysis of a Han Chinese longevity population. Biomed Res Int 2014:396727. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/396727
Tan Q, Christiansen L, Bathum L, Li S, Kruse TA, Christensen K (2006) Genetic association analysis of human longevity in cohort studies of elderly subjects: an example of the PON1 gene in the Danish 1905 birth cohort. Genetics 172:1821–1828. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.105.050914
Tan Q, Heijmans BT, Hjelmborg JV, Soerensen M, Christensen K, Christiansen L (2016) Epigenetic drift in the aging genome: a ten-year follow-up in an elderly twin cohort. Int J Epidemiol 45:1146–1158. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyw132
Tay J, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Thompson CH, Noakes M, Buckley JD, Wittert GA, Yancy WS Jr, Brinkworth GD (2015) Comparison of low- and high-carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes management: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr 102:780–790. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.112581
Vaiserman A, Lushchak O (2017) Implementation of longevity-promoting supplements and medications in public health practice: achievements, challenges and future perspectives. J Transl Med 15:160. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1259-8
Vaiserman AM, Lushchak OV, Koliada AK (2016) Anti-aging pharmacology: promises and pitfalls. Ageing Res Rev 31:9–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.08.004
Vaiserman A, Koliada A, Lushchak O (2018) Developmental programming of aging trajectory. Ageing Res Rev 47:105–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.07.007
van der Spoel E, Rozing MP, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Slagboom PE, Beekman M, de Craen AJ, Westendorp RG, van Heemst D (2015) Association analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 axis parameters with survival and functional status in nonagenarians of the Leiden longevity study. Aging (Albany NY) 7:956–963. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100841
Villareal DT, Fontana L, Weiss EP, Racette SB, Steger-May K, Schechtman KB, Klein S, Holloszy JO (2006) Bone mineral density response to caloric restriction-induced weight loss or exercise-induced weight loss: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med 166:2502–2510. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.22.2502
Villareal DT, Kotyk JJ, Armamento-Villareal RC, Kenguva V, Seaman P, Shahar A, Wald MJ, Kleerekoper M, Fontana L (2011) Reduced bone mineral density is not associated with significantly reduced bone quality in men and women practicing long-term calorie restriction with adequate nutrition. Aging Cell 10:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00643.x
Wang Q, Liang B, Shirwany NA, Zou MH (2011) 2-Deoxy-d-glucose treatment of endothelial cells induces autophagy by reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase. PLoS ONE 6:e17234. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017234
Wei M, Brandhorst S, Shelehchi M, Mirzaei H, Cheng CW, Budniak J, Groshen S, Mack WJ, Guen E, Di Biase S, Cohen P, Morgan TE, Dorff T, Hong K, Michalsen A, Laviano A, Longo VD (2017) Fasting-mimicking diet and markers/risk factors for aging, diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aai8700
Willcox BJ, Willcox DC (2014) Caloric restriction, caloric restriction mimetics, and healthy aging in Okinawa: controversies and clinical implications. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 17:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000019
Willcox BJ, Yano K, Chen R, Willcox DC, Rodriguez BL, Masaki KH, Donlon T, Tanaka B, Curb JD (2004) How much should we eat? The association between energy intake and mortality in a 36-year follow-up study of Japanese-American men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 59:789–795. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/59.8.B789
Willcox DC, Willcox BJ, Todoriki H, Curb JD, Suzuki M (2006) Caloric restriction and human longevity: what can we learn from the Okinawans? Biogerontology 7:173–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-006-9008-z
Willcox BJ, Willcox DC, Todoriki H, Fujiyoshi A, Yano K, He Q, Curb JD, Suzuki M (2007) Caloric restriction, the traditional Okinawan diet, and healthy aging: the diet of the world’s longest-lived people and its potential impact on morbidity and life span. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1114:434–455. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1396.037
Willcox BJ, Donlon TA, He Q, Chen R, Grove JS, Yano K, Masaki KH, Willcox DC, Rodriguez B, Curb JD (2008) FOXO3A genotype is strongly associated with human longevity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13987–13992. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809594106
Willcox BJ, Willcox DC, Suzuki M (2017) Demographic, phenotypic, and genetic characteristics of centenarians in Okinawa and Japan: part 1—centenarians in Okinawa. Mech Ageing Dev 165:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.11.001
Willis-Martinez D, Richards HW, Timchenko NA, Medrano EE (2010) Role of HDAC1 in senescence, aging, and cancer. Exp Gerontol 45:279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2009.10.001
Xiao FH, He YH, Li QG, Wu H, Luo LH, Kong QP (2015) A genome-wide scan reveals important roles of DNA methylation in human longevity by regulating age-related disease genes. PLoS ONE 10:e0120388. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120388
You FJ, Shen DM (2016) Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphisms and the risk of heart disease: an updated meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res 15:15017194. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15017194
Ziaee V, Razaei M, Ahmadinejad Z, Shaikh H, Yousefi R, Yarmohammadi L, Bozorgi F, Behjati MJ (2006) The changes of metabolic profile and weight during Ramadan fasting. Singapore Med J 47:409–414
Zullo A, Sommese L, Nicoletti G, Donatelli F, Mancini FP, Napoli C (2017) Epigenetics and type 1 diabetes: mechanisms and translational applications. Transl Res 185:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2017.05.002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, D., Scognamiglio, M., Fiorito, C. et al. Genetic background, epigenetic factors and dietary interventions which influence human longevity. Biogerontology 20, 605–626 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-019-09824-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-019-09824-3