Abstract
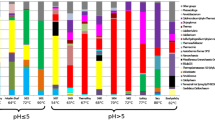
Microbial communities of four acidic thermal pools in the Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka, Russia, were studied using amplification and pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene fragments. The sites differed in temperature and pH: 1805 (60 °C, pH 3.7), 1810 (90 °C, pH 4.1), 1818 (80 °C, pH 3.5), and 1807 (86 °C, pH 5.6). Archaea of the order Sulfolobales were present among the dominant groups in all four pools. Acidilobales dominated in pool 1818 but were a minor fraction at the higher temperature in pool 1810. Uncultivated Archaea of the Hot Thaumarchaeota-related clade were present in significant quantities in pools 1805 and 1807, but they were not abundant in pools 1810 and 1818, where high temperatures were combined with low pH. Nanoarchaeota were present in all pools, but were more abundant in pools 1810 and 1818. A similar abundance pattern was observed for Halobacteriales. Thermophilic Bacteria were less diverse and were mostly represented by aerobic hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizers of the phylum Aquificae and sulfur-oxidising Proteobacteria of the genus Acidithiobacillus. Thus we showed that extremely acidic hot pools contain diverse microbial communities comprising different metabolic groups of prokaryotes, including putative lithoautotrophs using energy sources of volcanic origin, and various facultative and obligate heterotrophs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA (2004) Studies of thermophilic microorganisms at the Institute of Microbiology, Russian Academy of Sciences. Mikrobiologiia 73(5):644–658
Burgess EA, Unrine JM, Mills GL, Romanek CS, Wiegel J (2012) Comparative geochemical and microbiological characterization of two thermal pools in the Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka, Russia. Microb Ecol 63:471–489
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Casanueva A, Galada N, Baker GC, Grant WD, Heaphy S, Jones B, Yanhe M, Ventosa A, Blamey J, Cowan DA (2008) Nanoarchaeal 16S rRNA gene sequences are widely dispersed in hyperthermophilic and mesophilic halophilic environments. Extremophiles 12:651–656
Chernyh NA, Mardanov AV, Gumerov VM, Miroshnichenko ML, Lebedinsky AV, Merkel AY, Crowe D, Pimenov NV, Rusanov II, Ravin NV, Moran MA, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA (2015) Microbial life in Bourlyashchy, the hottest thermal pool of Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka. Extremophiles 19:1157–1171
Clingenpeel S, Kan J, Macur RE, Woyke T, Lovalvo D, Varley J, Inskeep WP, Nealson K, McDermott TR (2013) Yellowstone lake nanoarchaeota. Front Microbiol 4:274
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200
Eme L, Reigstad LJ, Spang A, Lanzén A, Weinmaier T, Rattei T, Schleper C, Brochier-Armanet C (2013) Metagenomics of Kamchatkan hot spring filaments reveal two new major (hyper)thermophilic lineages related to Thaumarchaeota. Res Microbiol 164:425–438
Flores GE, Campbell JH, Kirshtein JD, Meneghin J, Podar M, Steinberg JI, Seewald JS, Tivey MK, Voytek MA, Yang ZK, Reysenbach AL (2011) Microbial community structure of hydrothermal deposits from geochemically different vent fields along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Environ Microbiol 13:2158–2171
Gumerov VM, Mardanov AV, Beletsky AV, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Ravin NV (2011) Molecular analysis of microbial diversity in the Zavarzin spring, Uzon Caldera Kamchatka. Mikrobiologiia 80(2):258–265
Hohn M, Hedlund BP, Huber H (2002) Detection of 16S rDNA sequences representing the novel phylum “Nanoarchaeota”: indication for a wide distribution in high temperature biotopes. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:551–554
Hou W, Wang S, Dong H, Jiang H, Briggs BR, Peacock JP, Huang Q, Huang L, Wu G, Zhi X, Li W, Dodsworth JA, Hedlund BP, Zhang C, Hartnett HE, Dijkstra P, Hungate BA (2013) A comprehensive census of microbial diversity in hot springs of Tengchong, Yunnan Province China using 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 8(1):e53350
Huber H, Hohn MJ, Rachel R, Fuchs T, Wimmer VC, Stetter KO (2002) A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nano-sized hyperthermophilic symbiont. Nature 417:63–67
Inskeep WP, Jay ZJ, Herrgard MJ, Kozubal MA, Rusch DB, Tringe SG, Macur RE, Jennings Rd, Boyd ES, Spear JR, Roberto FF (2013) Phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenome sequence from high temperature archaeal habitats demonstrate linkages between metabolic potential and geochemistry. Front Microbiol 4:95
Islam T, Jensen S, Reigstad LJ, Larsen O, Birkeland NK (2008) Methane oxidation at 55 degrees C and pH 2 by a thermoacidophilic bacterium belonging to the Verrucomicrobia phylum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:300–304
Itoh T, Suzuki K, Nakase T (2002) Vulcanisaeta distributa gen. nov., sp. nov., and Vulcanisaeta souniana sp. nov., novel hyperthermophilic, rodshaped crenarchaeotes isolated from hot springs in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1097–1104
Jay ZJ, Rusch DB, Tringe SG, Bailey C, Jennings RM, Inskeep WP (2014) Predominant Acidilobus-like populations from geothermal environments in Yellowstone national park exhibit similar metabolic potential in different hypoxic microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(1):294–305
Kletzin A (2007) General characteristics and important model organisms. In: Cavicchioli R (ed) Archaea: molecular and cellular biology. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Mardanov AV, Svetlitchnyi VA, Beletsky AV, Prokofeva MI, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Ravin NV, Skryabin KG (2010) The genome sequence of the crenarchaeon Acidilobus saccharovorans supports a new order, Acidilobales, and suggests an important ecological role in terrestrial acidic hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5652–5657
Mardanov AV, Gumerov VM, Beletsky AV, Perevalova AA, Karpov GA, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Ravin NV (2011a) Uncultured archaea dominate in the thermal groundwater of Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka. Extremophiles 15:365–372
Mardanov AV, Gumerov VM, Beletsky AV, Prokofeva MI, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Ravin NV, Skryabin KG (2011b) Complete genome sequence of the thermoacidophilic crenarchaeon Thermoproteus uzoniensis 768-20. J Bacteriol 193:3156–3157
Merkel AY, Pimenov NV, Rusanov II, Slobodkin AI, Slobodkina GB, Tarnovetckii IY, Frolov EN, Dubin AV, Perevalova AA, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA (2017) Microbial diversity and autotrophic activity in Kamchatka hot springs. Extremophiles 21(2):307–317
Miller RG (1974) The jackknife—a review. Biometrika 61(1):1–15
Munson-McGee JH, Field EK, Bateson M, Rooney C, Stepanauskas R, Young MJ (2015) Nanoarchaeota, their sulfolobales host, and Nanoarchaeota virus distribution across Yellowstone National Park Hot Springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:7860–7868
Perevalova AA, Kolganova TV, Birkeland N-K, Schleper C, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Lebedinsky AV (2008) Distribution of Crenarchaeota representatives in terrestrial hot springs of Russia and Iceland. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7620–7628
Perevalova AA, Bidzhieva SK, Kublanov IV, Hinrichs KU, Liu XL, Mardanov AV, Lebedinsky AV, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA (2010) Fervidicoccus fontis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel anaerobic thermophilic crenarchaeote from hot springs in Kamchatka, and proposal of Fervidicoccaceae fam. nov. and Fervidicoccales ord. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2082–2088
Podar M, Makarova KS, Graham DE, Wolf YI, Koonin EV, Reysenbach AL (2013) Insights into archaeal evolution and symbiosis from the genomes of a nanoarchaeon and its inferred crenarchaeal host from Obsidian Pool, Yellowstone National Park. Biol Direct 8:9
Prokofeva MI, Kostrikina NA, Kolganova TV, Tourova TP, Lysenko AM, Lebedinsky AV, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA (2009) Isolation of the anaerobic thermoacidophilic crenarchaeote Acidilobus saccharovorans sp. nov. and proposal of Acidilobales ord. nov., including Acidilobaceae fam. nov. and Caldisphaeraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3116–3122
Reigstad LJ, Jorgensen SL, Schleper C (2010) Diversity and abundance of Korarchaeota in terrestrial hot springs of Iceland and Kamchatka. ISME J 4:346–356
Reysenbach AL, Ehringer M, Hershberger K (2000) Microbial diversity at 83 degrees C in Calcite Springs, Yellowstone National Park: another environment where the Aquificales and “Korarchaeota” coexist. Extremophiles 4:61–67
Rozanov AS, Bryanskaya AV, Malup TK, Meshcheryakova IA, Lazareva EV, Taran OP, Ivanisenko TV, Ivanisenko VA, Zhmodik SM, Kolchanov NA, Peltek SE (2014) Molecular analysis of the benthos microbial community in Zavarzin thermal spring (Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka, Russia). BMC Genomics 15:2–15
Sayeh R, Birrien JL, Alain K, Barbier G, Hamdi M, Prieur D (2010) Microbial diversity in Tunisian geothermal springs as detected by molecular and culture-based approaches. Extremophiles 14:501–514
Sharp CE, Brady AL, Sharp GH, Grasby SE, Stott MB, Dunfield PF (2014) Humboldt’s spa: microbial diversity is controlled by temperature in geothermal environments. ISME J 8(6):1166–1174
Spear JR, Walker JJ, McCollom TM, Pace N (2005) Hydrogen and bioenergetics in the Yellowstone geothermal ecosystem. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2555–2560
Takacs-Verbach C, Inskeep WP, Jay ZJ, Herrgard MJ, Rusch DB, Tringe SG, Kozubal MA, Hamamura N, Macur RE, Fouke BW, Reysenbach AL, McDermott TR, Jennings Rd, Hengartner NW, Xie G (2013) Metagenome sequence analysis of filamentous microbial communities obtained from geochemically distinct geothermal channels reveals specialization of three Aquificales lineages. Front Microbiol 4:84
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Valdes J, Quatrini R, Hallberg K, Dopson M, Valenzuela PDT, Holmes DS (2009) Draft genome sequence of the extremely acidophilic bacterium Acidithiobacillus caldus ATCC 51756 reveals metabolic versatility in the genus Acidithiobacillus. J Bacteriol 191:5877–5878
Waters E, Hohn MJ, Ahel I, Graham DE, Adams MD, Barnstead M, Beeson KY, Bibbs L, Bolanos R, Keller M, Kretz K, Lin X, Mathur E, Ni J, Podar M, Richardson T, Sutton GG, Simon M, Soll D, Stetter KO, Short JM, Noordewier M (2003) The genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans: insights into early archaeal evolution and derived parasitism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12984–12988
Wurch L, Giannone RG, Belisle BS, Swift C, Utturkar S, Hettich RL, Reysenbach AL, Podar M (2016) Genomics-informed isolation and characterization of a symbiotic Nanoarchaeota system from a terrestrial geothermal environment. Nat Commun 7:12115
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation [Grant Number 14-14-01016]. The work of AVM and VMG was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research [Grant Number 11-04-00671] and the Program “Molecular and Cellular Biology” of the Russian Academy of Sciences [project of AVM]. We are grateful to the Editor, Dr. Brian P. Hedlund, and three anonymous reviewers for their appropriate and constructive suggestions and for their proposed corrections to improve the manuscript. We thank Dr. Elizaveta Bonch-Osmolovskaya, her colleagues from the Winorgadsky Institute of Microbiology RAS (Moscow, Russia), and the staff of the Kronotsky Nature Reserve for their assistance in field studies in the Uzon Caldera. This work was performed using the scientific equipment of the Core Research Facility “Bioengineering”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mardanov, A.V., Gumerov, V.M., Beletsky, A.V. et al. Microbial diversity in acidic thermal pools in the Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 111, 35–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0924-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0924-5