Abstract
A novel actinobacterium, designated strain BN506T, was isolated from soil collected from Tuz (Salt) Lake, Konya, Turkey, and was characterised to determine its taxonomic position. The isolate was found to have morphological and chemotaxonomic properties associated with members of the genus Streptomonospora. The isolate was found to grow optimally at 37 °C and in the presence of 10 % (w/v) NaCl but not in the absence of NaCl. Phylogenetic analyses based on an almost-complete 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that isolate is closely related to members of the genus Streptomonospora and forms a distinct phyletic line in the Streptomonospora phylogenetic tree. Strain BN506T is closely related to Streptomonospora halophila YIM 91355T (98.1 % sequence similarity). Sequence similarities with other type strains of the genus Streptomyces were lower than 98.0 %. The cell wall of the novel strain was found to contain meso-diaminopimelic acid. Whole cell hydrolysates were found to contain galactose, glucose and ribose. The predominant menaquinone was identified as MK-10(H8) (57.0 %). The polar lipids detected were identified as diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine. The major fatty acids were found to be anteiso-C17:0, iso-C16:0 and 10 methyl C18:0. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, DNA–DNA relatedness, phenotypic characteristics and chemotaxonomic data, strain BN506T was identified as a member of a novel species of the genus Streptomonospora, for which the name Streptomonospora tuzyakensis sp. nov. (type strain BN506T = DSM 45930T = KCTC 29210T) is proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai M, Zhi XY, Tang SK, Zhang YQ, Xu LH, Li WJ (2008) Streptomonospora halophila sp. nov., a halophilic actinomycete isolated from a hypersaline soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1556–1560
Cai M, Tang SK, Chen YG, Li Y, Zhang YQ, Li WJ (2009) Streptomonospora amylolytica sp. nov. and Streptomonospora flavalba sp. nov., two novel halophilic actinomycetes isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2471–2475
Chun J, Goodfellow M (1995) A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardia with 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:240–245
Cui XL, Mao PH, Zeng M, Li WJ, Zhang LP, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2001) Streptomonospora salina gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Nocardiopsaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:357–363
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogeny: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1977) On the problem of discovering the most parsimonious tree. Am Nat 111:223–257
Hamedi J, Mohammadipanah F, Ventosa A (2013) Systematic and biotechnological aspects of halophilic and halotolerant actinomycetes. Extremophiles 17:1–13
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schlefier KH (1983) Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Jones KL (1949) Fresh isolates of actinomycetes in which the presence of sporogenous aerial mycelia is a fluctuating characteristic. J Bacteriol 57:141–145
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism, vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Kämpfer P, Kroppenstedt RM (1996) Numerical analysis of fatty acid patterns of coryneform bacteria and related taxa. Can J Microbiol 42:989–1005
Kelly KL (1964) Inter-Society Color Council-National Bureau of Standards color name charts illustrated with centroid colors. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Lam KS (2006) Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:245–251
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier H (1970) Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 20:435–443
Li WJ, Xu P, Zhang LP, Tang SK, Cui XL, Mao PH, Xu LH, Schumann P, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2003) Streptomonospora alba sp. nov., a novel halophilic actinomycete, and emended description of the genus Streptomonospora Cui et al. 2001. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1421–1425
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from micro-organisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Meklat A, Bouras N, Riba A, Zitouni A, Mathieu F, Rohde M, Schumann P, Spröer C, Klenk HP, Sabaou N (2014) Streptomonospora algeriensis sp. nov., a halophilic actinomycete isolated from soil in Algeria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 106:287–292
Nash P, Krent MM (1991) Culture media. In: Ballows A, Hauser WJ, Herrmann KL, Isenberg HD, Shadomy HJ (eds) Manual of clinical microbiology, 5th edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 1268–1270
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method. A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. Technical note 101. Microbial ID, Newark
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey NL (1997) Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:479–491
Staneck JL, Roberts GD (1974) Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol 28:226–231
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trueper HG (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee of reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington EMH, Sneath PHA, Sackin MJ (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129:1743–1813
Zamanian S, Shahidi Bonjar GH, Saadoun I (2005) First report of antibacterial properties of a new strain of Streptomyces plicatus (strain 101) against Erwinia carotovora from Iran. Biotechnology 4:114–120
Zhang DF, Pan HQ, He J, Zhang XM, Zhang YG, Klenk HP, Hu JC, Li WJ (2013) Description of Streptomonospora sediminis sp. nov. and Streptomonospora nanhaiensis sp. nov., and reclassification of Nocardiopsis arabia Hozzein and Goodfellow 2008 as Streptomonospora arabica comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Streptomonospora. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4447–4455
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Ondokuz Mayis University (OMU), project no. PYO. FEN. 1901.11.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Streptomonospora tuzyakensis BN506T(=DSM 45930T = KCTC 29210T) is KC959224.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10482_2015_607_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
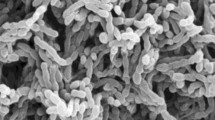
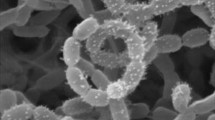
Scanning electron micrograph of strain BN506T grow on ISP 2 (Shirling and Gottlieb 1966) medium with 10 % NaCl for 30 days at 37 °C showing spore chains (a) and single spore (b). Bars, 1 μm. (JPEG 32 kb)
10482_2015_607_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Molybdophosporic acid stained two-dimensional TLC of polar lipids from strain BN506T. DPG: diphosphatidylglycerol, PG: phosphatidylglycerol, PC: phosphatidylcholine, GL: 1-3 three unidentified glycolipids, PL: unidentified phospholipid. (TIFF 2271 kb)
10482_2015_607_MOESM3_ESM.doc
Maximum parsimony tree based on almost complete 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the position of strain BN506T amongst its phylogenetic neighbours. Streptosporangium album DSM 43023T was used as an outgroup. Numbers at the nodes indicate the levels of bootstrap support (%); only values ≥ 50 % are shown. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Maximum likelihood tree based on almost complete 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the position of strain. BN506T amongst its phylogenetic neighbours. Streptosporangium album DSM 43023T was used as an outgroup. Numbers at the nodes indicate the levels of bootstrap support (%); only values ≥ 50 % are shown. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Bar, 0.01 substitutions per site. (DOC 106 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatar, D., Guven, K., Inan, K. et al. Streptomonospora tuzyakensis sp. nov., a halophilic actinomycete isolated from saline soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109, 35–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0607-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0607-z