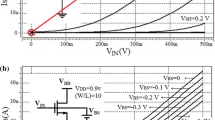
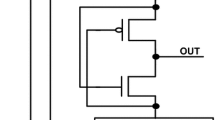
Abstract
A new circuit-level methodology called input controlled leakage restrainer transistor (ICLRT) compatible with single threshold CMOS technology is proposed in this paper, to further discount the leakage and short-circuit powers. To implement this idea a PMOS ICLRT is placed on top of the PUN and an NMOS ICLRT is located at the bottom of the PDN for any path from the supply voltage and the ground to output. The ICLRTs can be deliberately applied to the main sources of leakage and short-circuit currents to reduce total power dissipation. To test the proposed technique, ICLRTs are applied to four 4-2 CMOS compressors. The efficiency of the proposed methodology is evaluated using SPICE simulations in 22-nm BSIM4 (level-54 parameters) CMOS technology. Simulation results with 0.9-V power supply revealed that the power consumption of the 4-2 CMOS compressors based on ICLRT technique is reduced 59.62–74.28% and also power-delay product (PDP) is diminished 32–46.78% relative to corresponding original designs.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sanchez-Sinencio, E., & Andreou, A. G. (1999). Low-voltage/low-power integrated circuits. IEEE Press.
Narendra, S. G., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2006). Leakage in nanometer CMOS technologies. Springer.
Shigemitsu, S., et al. (1997). A 1-V high-speed MTCMOS circuit scheme for power-down application circuits. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 32(6), 861–869.
Wei, L., Chen, Z., Roy, K., Johnson, M. C., Ye, Y., & De, V. K. (1999). Design and optimization of dual-threshold circuits for low-voltage low-power applications. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 7(1), 16–24.
Zhang, K., et al. (2005). SRAM design on 65-nm CMOS technology with dynamic sleep transistor for leakage reduction. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(4), 895–901.
Sathanur, A., Benini, L., Macii, A., Macii, E., & Poncino, M. (2011). Row-based power-gating: A novel sleep transistor insertion methodology for leakage power optimization in nanometer CMOS circuits. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 19(3), 469–482.
Mishra, J. K., Srivastava, H., Misra, P. K., & Goswami, M. (2019). Analytical modelling and design of 9T SRAM cell with leakage control technique. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 101, 31–43.
Kuroda, T., et al. (1996). A 0.9-V, 150MHz, 10-mW, 4 mm2, 2-D discrete cosine transform core processor with variable threshold-voltage (VT) scheme. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31(11), 1770–1779.
Cserveny, S., Sumanen, L., Masgonty, J.-M., & Piguet, Ch. (2005). Locally switched and limited source-body bias and other leakage reduction techniques for a low-power embedded SRAM. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 52(10), 636–640.
Abdollahi, A., Fallah, F., & Pedram, M. (2004). Leakage current reduction in CMOS VLSI circuits by input vector control. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 12(2), 140–154.
Yuan, L., & Qu, G. (2006). A combined gate replacement and input vector control approach for leakage current reduction. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 14(2), 173–182.
Hanchate, N., & Ranganathan, N. (2004). LECTOR: A technique for leakage reduction in CMOS circuits. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 12(2), 196–205.
Bajpai, P., Pandey, N., Gupta, K., & Panda, J. (2019). LECTOR incorporated differential cascode voltage swing logic (L-DCVSL). Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 100, 221–234.
Srikanth, K., & Dhireesha, K. (2008). GALEOR: Leakage reduction for CMOS circuit. In Proceedings of 15th IEEE international conference on electronics circuits and systems (pp. 574–577).
Cerqueira, J. P., Li, J., & Seok, M. (2018). A fW- and kHz-class feed-forward leakage self-suppression logic requiring no external sleep signal to enter the leakage suppression mode. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters, 1(6), 150–153.
Sharma, V. K., Pattanaik, M., & Raj, B. (2013). ONOFIC approach: Low power high speed nanoscale VLSI circuits design. International Journal of Electronics, 101(1), 61–73.
Thapliyal, H., Mohammad, A., Kumar, S. D., & Sharifi, F. (2017). Energy-efficient magnetic 4-2 compressor. Microelectronics Journal, 67, 1–9.
Akbari, O., Kamal, M., Afzali-Kusha, A., & Pedram, M. (2017). Dual-quality 4:2 compressors for utilizing in dynamic accuracy configurable multipliers. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 25(4), 1352–1361.
Aliparast, P., et al. (2011). A very high-speed CMOS 4-2 compressor using fully differential current-mode circuit techniques. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 66, 235–243.
Chang, C.-H., Gu, J., & Zhang, M. (2004). Ultra low-voltage low-power CMOS 4–2 and 5–2 compressors for fast arithmetic circuits. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 51(10), 1985–1997.
Pishvaie, A., Jaberipur, Gh., & Jahanian, A. (2012). Improved CMOS (4;2) compressor designs for parallel multipliers. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 38, 1703–1716.
Pishvaie, A., Jaberipur, Gh., & Jahanian, A. (2014). High-performance CMOS (4:2) compressors. International Journal of Electronics, 101(11), 1511–1525.
Maryan, M. M., Amini-Valashani, M., & Azhari, S. J. (2021). A new circuit-level technique for leakage and short-circuit power reduction of static logic gates in 22-nm CMOS technology. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 40, 3536–3560.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maryan, M.M., Azhari, S.J. & Amini-Valashani, M. A circuit-level methodology for leakage power reduction of high-efficient compressors in 22-nm CMOS technology. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 110, 569–581 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01983-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01983-z