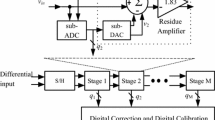
Abstract
This paper presents a new digital background calibration method to correct MDAC errors. The novelty of this research is to use Newton–Raphson algorithm in order to reduce the number of divisions as well as power in digital domain. This is achieved by combining the conventional slope mismatch averaging and linear approximation technique to compute the correction coefficient in fast iterative method. To validate the accuracy of the proposed method, the digital part of the calibration scheme is implemented on FPGA. The superiorities of the proposed method are fast convergence time, less power consumption, and less digital complexity in compared to previous studies. These benefits are due to using split structure along with Newton–Raphson method. Several simulations of a 12-bit 100MS/s pipelined ADC indicate that SNDR/SFDR is improved from 30/33 dB to 70/79 dB after calibration. Calibration process is achieved in approximately 2000 clock cycles. The proposed ADC achieves a FoM of 0.03-pJ/conversion-step and consumes an analog power of 6.7 mW.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jalali-Farahani, B., & Meruva, A. (2009). A 14-b 32 MS/s pipelined ADC with fast convergence comprehensive background calibration. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process,61(1), 65–74.
Jia, H., & Lv, Y. (2016). A calibration technique based on sub-stages’ weights of pipelined ADC. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process,89(1), 223–229.
Larsson, A., Silva-Martinez, J., & Soenen, E. (2014). A 360 fJ/conversion-step, 14-bit, 100 MS/s, digitally background calibrated pipelined ADC in 130-nm CMOS. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process,81(1), 153–164.
Chen, Z.-H., Wu, H., Zhang, H., Wei, J.-H., Su, X., Xue, Y., et al. (2019). A 14-bit 250-MS/s charge-domain pipelined ADC with mix-signal foreground calibration. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process,101(2), 283–295.
Li, J., & Moon, U.-K. (2003). Background calibration techniques for multistage pipelined ADCs with digital redundancy. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Analog Digital Signal Process,50(9), 531–538.
Adel, H., Louerat, M.-M., & Sabut, M. (2012). Fast split background calibration for pipelined ADCs enabled by slope mismatch averaging technique. Electronics Letters,48(6), 318–320.
Mafi, H. R., & Sodagar, A. M. (2013). A background calibration in pipelined ADCs. AEU-Int J Electron Commun,67(8), 729–732.
Shi, L., Zhao, W., Wu, J., & Chen, C. (2012). Digital background calibration techniques for pipelined ADC based on comparator dithering. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Exp Briefs,59(4), 239–243.
Siragusa, E., & Galton, I. (2000). Gain error correction technique for pipelined analogue-to-digital converters. Electronics Letters,36(7), 1.
Ming, J., & Lewis, S. H. (2001). An 8-bit 80-Msample/s pipelined analog-to-digital converter with background calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,36(10), 1489–1497.
Panigada, A., & Galton, I. (2006). Digital background correction of harmonic distortion in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regular Pap,53(9), 1885–1895.
Mafi, H., Mohammadi, R., & Shamsi, H. (2015). A statistics-based digital background calibration technique for pipelined ADCs. Integr VLSI J,51, 149–157.
McNeill, J. A., Coln, M. C., Brown, D. R., & Larivee, B. J. (2009). Digital background-calibration algorithm for “Split ADC” architecture. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regular Pap,56(2), 294–306.
Ahmed, I., & Johns, D. A. (2008). An 11-Bit 45 MS/s pipelined ADC with rapid calibration of DAC errors in a multibit pipeline stage. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,43(7), 1626–1637.
Montazerolghaem, M. A., Moosazadeh, T., & Yavari, M. (2015). A predetermined LMS digital background calibration technique for pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs,62(9), 841–845.
Zia, E., Farshidi, E., & Kosarian, A. (2019). A split-based digital background calibration of pipelined analog-to-digital converters by cubic spline interpolation filtering. Circuits, Syst Signal Process,38(10), 1–18.
Shen D-L, Lee T-C (2005) A linear-approximation technique for digitally-calibrated pipelined A/D converters. In: 2005 IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, IEEE, pp 1382–1385
Sahoo, B. D., & Razavi, B. (2013). A 10-b 1-GHz 33-mW CMOS ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,48(6), 1442–1452.
Sahoo, B. D., & Razavi, B. (2009). A 12-bit 200-MHz cmos adc. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits,44(9), 2366–2380.
Fatemi-Behbahani, E., Farshidi, E., & Ansari-Asl, K. (2016). Analysis of chaotic behavior in pipelined analog to digital converters. AEU-Int J Electron Commun,70(3), 301–310.
Gautschi, W. (1997). Numerical analysis. New York: Springer.
Chang, D.-Y. (2004). Design techniques for a pipelined ADC without using a front-end sample-and-hold amplifier. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regular Pap,51(11), 2123–2132.
Moosazadeh, T., & Yavari, M. (2014). A pseudo-differential MDAC with a gain-boosting inverter for pipelined ADCs. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process,79(2), 255–266.
Sumanen L, Waltari M, Hakkarainen V, Halonen K (2002) CMOS dynamic comparators for pipeline A/D converters. In: 2002 IEEE international symposium and proceedings on circuits and systems (Cat. No. 02CH37353), vol 5, IEEE, p V
Gholami, P., & Yavari, M. (2018). Digital background calibration with histogram of decision points in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II: Exp Briefs,65(1), 16–20.
Mafi, H., Yargholi, M., & Yavari, M. (2018). Statistics-based digital background calibration of residue amplifier nonlinearity in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I: Regular Pap,99, 1–13.
Zeinali, B., Moosazadeh, T., Yavari, M., & Rodriguez-Vazquez, A. (2013). Equalization-based digital background calibration technique for pipelined ADCs. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst,22(2), 322–333.
Walden, R. H. (1999). Analog-to-digital converter survey and analysis. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,17(4), 539–550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zia, E., Farshidi, E. & Kosarian, A. Digital calibration of pipelined ADC using Newton–Raphson algorithm. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 104, 61–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01659-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01659-0