Abstract
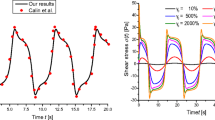
In the present paper, a structure-based viscoelastic model is employed to characterize and predict the viscoelastic properties of a wormlike micellar solution at 20 °C. Considering the effect of shear rate on linear viscoelastic property, a structural parameter f is obtained. Meanwhile, another structural parameter ζ is determined when the effects of time and shear rate are considered simultaneously. Both structural parameters are calculated by using linear interpolation method. The startup experiment can be described well by the model. The prediction on the shear stress in the ramping-up region of the hysteresis loop experiment shows an apparent relation between the rheological behaviors in the startup experiment and those in the hysteresis loop experiment. For the hysteresis loop experiment with 30 s time interval, the defect of the calculation in 0.001–0.01 s−1 is due to the lack of the ramping-down history effect. In addition, the model can improve completeness of perimental data used for characterizing rheological property.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-01133-8
References
Zhao, Y., Haward, S.J., Shen, A.Q.: Rheological characterizations of wormlike micellar solutions containing cationic surfactant and anionic hydrotropic salt. J. Rheol. 59, 1229–1259 (2015)
Dai, S., Tao, M., Lu, H.: CO2-switchable wormlike micelles based on a switchable ionic liquid and tetradecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 42, 475–484 (2021)
Dutta, S., Graham, M.D.: Mechanistic constitutive model for wormlike micelle solutions with flow induced structure formation. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 251, 97–106 (2018)
He, G., Liu, Y., Deng, X., et al.: Constitutive modeling of viscoelastic-viscoplastic behavior of short fiber reinforced polymers coupled with anisotropic damage and moisture effects. Acta Mech. Sin. 35, 495–506 (2019)
Johnson, M., Segalman, D.: A model for viscoelastic fluid behavior which allows non-affine deformation. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2, 255–270 (1977)
Fielding, S.M.: Linear instability of planar shear banded flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 134501 (2005)
Olmsted, P.D.: Perspectives on shear banding in complex fluids. Rheol. Acta 47, 283–300 (2008)
Giesekus, H.A.: Simple constitutive equation for polymer fluids based on the concept of the deformation dependent tensorial mobility. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 11, 69–109 (1982)
Germann, N., Gurnon, A.K., Zhou, L., et al.: Validation of constitutive modeling of shear banding, threadlike wormlike micellar, fluids. J. Rheol. 60, 983–999 (2016)
Vasquez, P.A., McKinley, G.H., Cook, L.P.: A network scission model for wormlike micellar solutions. I: Model formulation and homogeneous flow predictions. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 144, 122–139 (2007)
Pipe, C.J., Kim, N.J., Vasquez, P.A., et al.: Wormlike micellar solutions. II: Comparison between experimental data and scission model predictions. J. Rheol. 54, 881–914 (2010)
Zhou, L., McKinley, G.H., Cook, L.P.: Wormlike micellar solutions: III VCM model predictions in steady and transient shearing flows. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 211, 70–83 (2014)
Germann, N., Cook, L.P., Beris, A.N.: Nonequilibrium thermodynamic modeling of the structure and rheology of concentrated wormlike micellar solutions. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 196, 51–57 (2013)
Gaudino, D., Costanzo, S., Ianniruberto, G., et al.: Linear wormlike micelles behave similarly to entangled linear polymers in fast shear flows. J. Rheol. 64, 879–888 (2020)
Becu, L., Manneville, S., Colin, A.: Spatiotemporal dynamics of wormlike micelles under shear. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 18301 (2004)
Guettari, M., Naceur, I.B., Kassab, G., et al.: Temperature and concentration induced complex behavior in ternary microemulsion. Appl. Rheol. 23, 44966 (2013)
Chen, X.: Inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin with CTAB in aqueous solution. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 24, 484–488 (2011)
Xiong, J., Fang, B., Lu, Y., et al.: Rheology and high-temperature stability of novel viscoelastic gemini micelle solutions. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 39, 1324–1327 (2018)
Shibaev, A.V., Molchanov, V.S., Philippova, O.E.: Rheological behavior of oil-swollen wormlike surfactant micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 15938–15946 (2015)
Georgieva, G.S., Anachkov, S.E., Lieberwirth, I., et al.: Synergistic growth of giant wormlike micelles in ternary mixed surfactant solutions: effect of octanoic acid. Langmuir 32, 12885–12893 (2016)
Zhang, W., Mao, J., Yang, X., et al.: Study of a novel gemini viscoelastic surfactant with high performance in clean fracturing fluid application. Polymers 10, 1215 (2018)
Huang, S.: Structural viscoelasticity of a water-soluble polysaccharide extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 120, 1601–1609 (2018)
Bernstein, B., Kearsley, E.A., Zapas, L.J.: A study of stress relaxation with finite strain. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 7, 391–410 (1963)
Wagner, M.H.: Analysis of time-dependent non-linear stress-growth data for shear and elongational flow of a low-density branched polyethylene melt. Rheol. Acta 15, 136–142 (1976)
Osaki, K.: Non-linear viscoelasticity of polymer solutions. In: Klason, C., Kubat, J. (eds) Proceedings of the VIIth International Congress on Rheology. Gothenburg, Sweden, August 23–27, pp. 104–109 (1976)
Laun, H.M.: Description of the non-linear shear behaviour of a low density polyethylene melt by means of an experimentally determined strain dependent memory function. Rheol. Acta 17, 1–15 (1978)
Papanastasiou, A.C., Scriven, L.E., Macosko, C.W.: An integral constitutive equation for mixed flows: viscoelastic characterization. J. Rheol. 27, 387–410 (1983)
Bird, R.B., Armstrong, R.C., Hassager, O.: Dynamics of Polymeric Fluids Fluid Mechanic, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1987)
Laun, H.M., Schmidt, G.: Rheotens tests and viscoelastic simulations related to high-speed spinning of polyamide 6. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 222, 45–55 (2015)
Huang, S.: Viscoelastic characterization of the mucus from the skin of loach. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 33, 1–9 (2021)
Cox, W.P., Merz, E.H.: Correlation of dynamic and steady flow viscosities. J. Polym. Sci. 28, 619–622 (1958)
Sharma, V., McKinley, G.H.: An intriguing empirical rule for computing the first normal stress difference from steady shear viscosity data for concentrated polymer solutions and melts. Rheol. Acta 51, 487–495 (2012)
Osaki, K., Tamura, M., Kurata, M., et al.: Complex modulus of concentrated polymer solutions in steady shear. J. Phys. Chem. 69, 4183–4191 (1965)
Macdonald, I., Bird, R.B.: Complex modulus of concentrated polymer solutions in steady shear. J. Phys. Chem. 70, 2068–2069 (1966)
Kim, S.H., Mewis, J., Clasen, C., et al.: Superposition rheometry of a wormlike micellar fluid. Rheol. Acta 52, 727–740 (2013)
Curtis, D.J., Davies, A.R.: On shear-rate dependent relaxation spectra in superposition rheometry: a basis for quantitative comparison/interconversion of orthogonal and parallel superposition moduli. J. Non-Newton Fluid Mech. 274, 104198 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Executive Editor: Chao Sun.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S. Viscoelastic characterization and prediction of a wormlike micellar solution. Acta Mech. Sin. 37, 1648–1658 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-01120-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-01120-z