Abstract
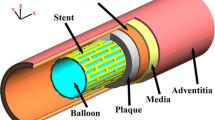
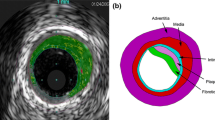
Carotid artery stenting presents challenges of in-stent restenosis and late thrombosis, which are caused primarily by alterations in the mechanical environment of the artery after stent implantation. The present study constructed patient-specific carotid arterial bifurcation models with lipid pools and calcified components based on magnetic resonance imaging. We numerically analyzed the effects of multicomponent plaques on the distributions of von Mises stresses (VMSs) in the patient-specific models after stenting. The results showed that when a stent was deployed, the large soft lipid pool in atherosclerotic plaques cushioned the host artery and reduced the stress within the arterial wall; however, this resulted in a sharp increase of VMS in the fibrous cap. When compared with the lipid pool, the presence of the calcified components led to slightly increased stresses on the luminal surface. However, when a calcification was located close to the luminal surface of the host artery and the stenosis, the local VMS was elevated. Overall, compared with calcified components, large lipid pools severely damaged the host artery after stenting. Furthermore, damage due to the calcified component may depend on location.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentzon, J.F., Otsuka, F., Virmani, R., et al.: Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture. Circ. Res. 114, 1852–1866 (2014)
von Birgelen, C., Mintz, G.S., Eggebrecht, H., et al.: Preintervention arterial remodeling affects vessel stretch and plaque extrusion during coronary stent deployment as demonstrated by three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound. Am. J. Cardiol. 92, 130–135 (2003)
Chen, Z.S., Fan, Z.M., Zhang, X.W.: The interactions between bloodstream and vascular structure on aortic dissecting aneurysmal model: A numerical study. Acta Mech. Sin. 29, 462–468 (2013)
Morlacchi, S., Colleoni, S.G., Cardenes, R.C., et al.: Patient-specific simulations of stenting procedures in coronary bifurcations: Two clinical cases. Med. Eng. Phys. 35, 1272–1281 (2013)
Sonoda, S., Muraoka, Y., Kashiyama, K., et al.: Coronary arterial remodeling and peristent plaque change after drug-eluting stent implantation: comparison between zotarolimus-eluting stents and paclitaxel-eluting stents. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 59, E147–E147 (2012)
Walsh, M.T., Cunnane, E.M., Mulvihill, J.J., et al.: Uniaxial tensile testing approaches for characterisation of atherosclerotic plaques. J. Biomech. 47, 793–804 (2014)
Teng, Z.Z., Zhang, Y.X., Huang, Y., et al.: Material properties of components in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques: A uniaxial extension study. Acta Biomater. 10, 5055–5063 (2014)
Chai, C.K., Speelman, L., Oomens, C.W.J., et al.: Compressive mechanical properties of atherosclerotic plaques-indentation test to characterise the local anisotropic behaviour. J. Biomech. 47, 784–792 (2014)
Tang, D.L., Yang, C., Zheng, J., et al.: 3D MRI-based multicomponent FSI models for atherosclerotic plaques. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32, 947–960 (2004)
Carnelli, D., Pennati, G., Villa, T., et al.: Mechanical properties of open-cell, self-expandable shape memory alloy carotid stents. Artif. Organs 35, 74–80 (2011)
Pericevic, I., Lally, C., Toner, D., et al.: The influence of plaque composition on underlying arterial wall stress during stent expansion: The case for lesion-specific stents. Med. Eng. Phys. 31, 428–433 (2009)
Gastaldi, D., Morlacchi, S., Nichetti, R., et al.: Modelling of the provisional side-branch stenting approach for the treatment of atherosclerotic coronary bifurcations: effects of stent positioning. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 9, 551–561 (2010)
Liang, D.K., Yang, D.Z., Qi, M., et al.: Finite element analysis of the implantation of a balloon-expandable stent in a stenosed artery. Int. J. Cardiol. 104, 314–318 (2005)
Wong, K.K.L., Thavornpattanapong, P., Cheung, S.C.P.: Effect of calcification on the mechanical stability of plaque based on a three-dimensional carotid bifurcation model. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 12, 1–18 (2012)
Gao, H., Long, Q.: Effects of varied lipid core volume and fibrous cap thickness on stress distribution in carotid arterial plaques. J. Biomech. 41, 3053–3059 (2008)
Tang, D.L., Yang, C., Zheng, J., et al.: Image-based modeling and precision medicine: patient-specific carotid and coronary plaque assessment and predictions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60, 643–651 (2013)
Teng, Z.Z., He, J., Sadat, U., et al.: How does juxtaluminal calcium affect critical mechanical conditions in carotid atherosclerotic plaque? An exploratory study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61, 35–40 (2014)
Gray, W.A., Yadav, J.S., Verta, P., et al.: The CAPTURE registry: Predictors of outcomes in carotid artery stenting with embolic protection for high surgical risk patients in the early post-approval setting. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 70, 1025–1033 (2007)
Tsutsumi, M., Kodama, T., Aikawa, H., et al.: Fragmentation of calcified plaque after carotid artery stenting in heavily calcified circumferential stenosis. Neuroradiology 52, 831–836 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11332003, 11421202, 61190123, 31200703, 11472031); Special Fund for Excellent Doctoral Degree Dissertation of Beijing (Grant 20131000601); the 111 Project (Grant B13003); the Innovation Foundation of BUAA for Ph.D. graduates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, ZM., Liu, X., Du, CF. et al. Plaque components affect wall stress in stented human carotid artery: A numerical study. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 1149–1154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-016-0572-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-016-0572-4