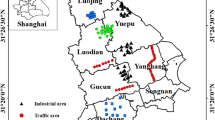
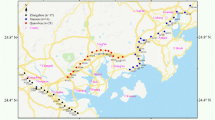
Abstract
Pollution by magnetic particles is a rising environmental issue with possible adverse health effects such as the Alzheimer's disease. Magnetic particles in urban dust originate from traffic-related activities, industrial products and detrital minerals, yet distribution of magnetic particles in cities is poorly known. Here, we measured magnetic properties of surface roadside dust and topsoils by low-frequency magnetic susceptibility (χLF), saturation isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM), anhysteretic remanent magnetization (χARM) and advanced rock-magnetic methods. Results show that χLF, SIRM and χARM of roadside dust are much higher than topsoil values. Roadside dusts had much lower percent frequency-dependent susceptibility of 1.83 ± 0.12% than topsoil of 2.96 ± 0.14%. Findings also demonstrate a minor contribution of fine pedogenic grains to the elevated χLF. The high values of dust χLF, SIRM and χARM are explained by the contribution of local, exogenous magnetite-like materials.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera A, Morales JJ, Goguitchaichvili A, García-Oliva F, Armendariz-Arnez C, Quintana P, Bautista F (2020) Spatial distribution of magnetic material in urban road dust classified by land use and type of road in San Luis Potosí, Mexico. Air Qual Atmos Health 13:951–963
Bourliva A, Papadopoulou L, Aidona E (2016) Study of road dust magnetic phases as the main carrier of potentially harmful trace elements. Sci Total Environ 553:380–391
Cabanova K, Hrabovska K, Matejkova P, Dedkova K, Tomasek V, Dvorackova J, Kukutschova J (2019) Settled iron-based road dust and its characteristics and possible association with detection in human tissues. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:2950–2959
Cao L, Appel E, Hu S, Yin G, Lin H, Rösler W (2015) Magnetic response to air pollution recorded by soil and dust-loaded leaves in a changing industrial environment. Atmos Environ 119:304–313
Dearing J (1999) Environmental magnetic susceptibility: using the Bartington MS2 system. Chi Publishing, England
Dlháň Ľ, Kopáni M, Boča R (2019) Magnetic properties of iron oxides present in the human brain. Polyhedron 157:505–510
Dytłow S, Winkler A, Górka-Kostrubiec B, Sagnotti L (2019) Magnetic, geochemical and granulometric properties of street dust from Warsaw (Poland). J Appl Geophys 169:58–73
Harrison RJ, Feinberg JM (2008) FORCinel: An improved algorithm for calculating first-order reversal curve distributions using locally weighted regression smoothing. Geochem Geophy Geosy 9:008GC001987
Heslop D, Dekkers MJ, Kruiver PP, Oorschot IHM (2002) Analysis of isothermal remanent magnetization acquisition curves using the expectation–maximization algorithm. Geophys J Int 148:58–64
Jordanova D, Jordanova N, Petrov P (2014) Magnetic susceptibility of road deposited sediments at a national scale–relation to population size and urban pollution. Environ Pollut 189:239–251
Jordanova N, Jordanova D, Tcherkezova T, Georgieva B, Ishlyamski D (2021) Advanced mineral magnetic and geochemical investigations of road dusts for assessment of pollution in urban areas near the largest copper smelter in SE Europe. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148402
Kelepertzis E, Chrastný V, Botsou F, Sigala E, Kypritidou Z, Komárek M, Skordas K, Argyraki A (2021) Tracing the sources of bioaccessible metal(loid)s in urban environments: A multidisciplinary approach. Sci Total Environ 771:144827
Kruiver PP, Dekkers MJ, Heslop D (2001) Quantification of magnetic coercivity components by the analysis of acquisition curves of isothermal remanent magnetisation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 189:269–276
Leng X, Qian X, Yang M, Wang C, Li H, Wang J (2018) Leaf magnetic properties as a method for predicting heavy metal concentrations in PM2.5 using support vector machine: A case study in Nanjing. China Environ Pollut 242:922–930
Li H, Qian X, Wei H, Zhang R, Yang Y, Liu Z, Hu W, Gao H, Wang Y (2014) Magnetic properties as proxies for the evaluation of heavy metal contamination in urban street dusts of Nanjing, Southeast China. Geophy J Int 199:1354–1366
Liu H, Yan Y, Chang H, Chen H, Liang L, Liu X, Qiang X, Sun Y (2019) Magnetic signatures of natural and anthropogenic sources of urban dust aerosol. Atmos Chem Phys 19:731–745
Mahera BA, Ahmed IAM, Karloukovski V, MacLaren DA, Foulds PG, Allsop D, Mann DMA, Torres-Jardó nR, Calderon-Garciduenas L, (2016) Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America 113:10797–10801
Maity R, Venkateshwarlu M, Mondal S, Kapawar MR, Gain D, Paul P (2020) Magnetic and microscopic characterization of anthropogenically produced magnetic particles: a proxy for environmental pollution. Int J Environ Sci Te. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-13020-02902-x
Muñoz D, Aguilar B, Fuentealba R, Préndez M (2017) Environmental studies in two communes of Santiago de Chile by the analysis of magnetic properties of particulate matter deposited on leaves of roadside trees. Atmos Environ 152:617–627
O’Shea MJ, Vann DR, Hwang W, Gieré R (2020) A mineralogical and chemical investigation of road dust in Philadelphia, PA, USA. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:14883–14902
Qiao Q, Huang B, Zhang C, Piper JDA, Pan Y, Sun Y (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination of dustfall in northern China from integrated chemical and magnetic investigation. Atmos Environ 74:182–193
Ren Y, Wei X, Wang D, Luo Y, Song X, Wang Y, Yang Y, Hua L (2013) Linking landscape patterns with ecological functions: A case study examining the interaction between landscape heterogeneity and carbon stock of urban forests in Xiamen, China. Forest Ecol Manag 293:122–131
Reyes BA, Bautista F, Goguitchaichvili A, Morton O (2011) Magnetic monitoring of top soils of Merida (Southern Mexico). Stud Geophys Geod 55:377–388
Reyes BA, Bautista F, Goguitchaichvili A, Contreras JJM, Battu J, Owen PQ, Carvallo C (2013a) Rock-magnetic properties of topsoils and urban dust from Morelia (>800,000 inhabitants), Mexico: Implications for anthropogenic pollution monitoring in Mexico’s medium size cities. Geofís Int 52:121–133
Reyes BA, Mejía V, Goguitchaichvili A, Escobar J, Bayona G, Bautista F, Morales JC, Ihl TJ (2013b) Reconnaissance environmental magnetic study of urban soils, dust and leaves from Bogotá, Colombia. Stud Geophys Geod 57:741–754
Sandeep K, Shankar R, Balsam W (2017) Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of a tropical southern Indian lake sediment core: A window to environmental change. Episodes 40:47–56
Silva LS, Júnior JM, Barrón V, Gomes RP, Teixeira DDB, Siqueira DS, Vasconcelos V (2020) Spatial variability of iron oxides in soils from Brazilian sandstone and basalt. Catena 185:104258
Švédová B, Matýsek D, Raclavsk H, Kucbel M, Kantor P, Šafář M, Raclavský K (2020) Variation of the chemical composition of street dust in a highly industrialized city in the interval of ten years. J Environ Manage 267:110506
Szuszkiewicz M, Magiera T, Kapička A, Petrovský E, Grison H, Gołuchowska B (2015) Magnetic characteristics of industrial dust from different sources of emission: A case study of Poland. J Appl Geophys 116:84–92
Tan Z, Lu S, Zhao H, Kai X, Jiaxian P, Win MS, Yu S, Yonemochi S, Wang Q (2018) Magnetic, geochemical characterization and health risk assessment of road dust in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, China. Environ Geochem Health 40:1541–1555
Wang XS (2013) Mineralogical and chemical composition of magnetic fly ash fraction. Environ Earth Sci 71:1673–1681
Wang G, Oldfield F, Xia D, Chen F, Liu X, Zhang W (2011) Magnetic properties and correlation with heavy metals in urban street dust: A case study from the city of Lanzhou, China. Atmos Environ 46:289–298
Wang G, Chen J, Zhang W, Chen Y, Ren F, Fang A, Ma L (2019a) Relationship between magnetic properties and heavy metal contamination of street dust samples from Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:8958–8970
Wang G, Chen J, Zhang W, Ren F, Chen Y, Fang A, Ma L (2019b) Magnetic properties of street dust in Shanghai, China and its relationship to anthropogenic activities. Environ Pollut 255:113214
Wang L, Hu S, Ma M, Zhang Y, Wang X, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Cui B, Liu X (2019c) Magnetic characteristics of atmospheric dustfall in a subtropical monsoon climate zone of China and its environmental implications: A case study of Nanjing. Atmos Environ 212:231–238
Wang P, Xue J, Zhu Z (2021) Comparison of heavy metal bioaccessibility between street dust and beach sediment: particle size effect and environmental magnetism response. Sci Total Environ 777:146081
Warrier AK, Shankar R, Manjunatha BR, Harshavardhana BG (2014) Mineral magnetism of atmospheric dust over southwest coast of India: Impact of anthropogenic activities and implications to public health. J Appl Geophys 102:1–9
Yang D, Wang M, Liu J, Deng T, Yan C, Ding Z, Lu H (2020) Occurrence and characteristics of iron-bearing minerals in surface road dusts: a case study in the coastal areas of southern Fujian, China. J Soil Sediment 20:3406–3416
Zhang Y, Zhang S (2008) Magnetic properties of street dust and topsoil in Beijing and its environmental implications. Chinese Sci Bull 53:408–417
Zhang W, Jiang H, Dong C, Yan Q, Yu L, Yu Y (2011) Magnetic and geochemical characterization of iron pollution in subway dusts in Shanghai, China. Geochem Geophy Geosy 12:Q06Z25
Zhang C, Qiao Q, Appel E, Huang B (2012) Discriminating sources of anthropogenic heavy metals in urban street dusts using magnetic and chemical methods. J Geochem Explor 119–120:60–75
Zhao J, Zhang F, Xu Y, Chen J, Yin L, Shang X, Xu L (2011) Chemical characteristics of particulate matter during a heavy dust episode in a Coastal City, Xiamen, 2010. Pol J Environ Stud 11:300–309
Zhao G, Zhang R, Han Y, Lu B, Meng Y, Wang S, Wang N (2020) Identifying environmental pollution recorded in street dust using the magnetic method: a case study from central eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:34966–34977
Zhu Z, Sun G, Bi X, Li Z, Yu G (2013) Identification of trace metal pollution in urban dust from kindergartens using magnetic, geochemical and lead isotopic analyses. Atmos Environ 77:9–15
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Gui Da Zhuan Ji He Zi (2021) 14, National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1406603) and Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870483 and 31530008). The manuscript was greatly improved by Dr. Adam Roddy at Yale University. Dan Y is grateful to Dr. Weiguo Zhang at State Key Laboratory of Estuarine and Coastal Research, East China Normal University, for his help in magnetic measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D., Wu, J., Hong, H. et al. Traffic-related magnetic pollution in urban dust from the Xiamen Island, China. Environ Chem Lett 19, 3991–3997 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01270-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01270-3