Abstract
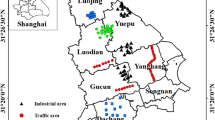
As an accumulation of solid organic and inorganic pollutant particles on outdoor ground surfaces, road dust is an important carrier of heavy metal contaminants and can be a valuable medium for characterizing urban environmental quality. Because the dusts can be an important source of atmospheric particles and take impact on human health, the aim of this study described in detail the mineralogical characteristics, morphology, and heavy metal content of road dust from Xuanwei and Fuyuan, locations with high lung cancer incidence. Our results show that the average concentrations of heavy metals in road dust were higher than their background values. Higher concentrations of heavy metals were found in the magnetic fractions (MFs) than in the non-magnetic fractions (NMFs). Magnetic measurements revealed high magnetic susceptibility values in the road dust samples, and the dominant magnetic carrier was magnetite. The magnetic grains were predominantly pseudo-single domain, multi-domain, and coarse-grained stable single domains (coarse SSD) in size. SEM/XRD analysis identified two groups of magnetic particles: spherules and angular/aggregate particles. Hazard index (HI) values for adults exposure to road dust samples, including MF, Bulk, and NMF, in both areas were lower or close to safe levels, while HI values for childhood exposure to magnetic fractions in both areas were very close or higher than safe levels. Cancer risks from road dust exposure in both areas were in the acceptable value range.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2007). Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman, Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29(1), 1–10.
Arslan, H. (2001). Heavy metals in street dust in Bursa, Turkey. Journal of Trace and Microprobe Techniques, 19(3), 439–445.
Birch, G. F., & Olmos, M. A. (2008). Sediment-bound heavy metals as indicators of human influence and biological risk in coastal water bodies. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 65(8), 1407–1413.
Bourliva, A., Papadopoulou, L., & Aidona, E. (2016). Study of road dust magnetic phases as the main carrier of potentially harmful trace elements. Science of the Total Environment, 553, 380–391.
Bućko, M. S., Magiera, T., Johanson, B., Petrovský, E., & Pesonen, L. J. (2011). Identification of magnetic particulates in road dust accumulated on roadside snow using magnetic, geochemical and micro-morphological analyses. Environmental Pollution, 159(5), 1266–1276.
Bućko, M. S., Magiera, T., Pesonen, L. J., & Janus, B. (2010). Magnetic, geochemical, and microstructural characteristics of road dust on roadsides with different traffic volumes—Case study from Finland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 209(1–4), 295–306.
Dankers, P. (1981). Relationship between median destructive field and remanent coercive forces for dispersed natural magnetite, titanomagnetite and hematite. Geophysical Journal International, 64(2), 447–461.
Dearing, J. A. (1994). Environmental magnetic susceptibility using the Bartington MS2 system (pp. 52–55). England: Chi Publishing.
Dearing, J. A., Hay, K. L., Baban, S. M. J., Huddleston, A. S., Wellington, E. M. H., & Loveland, P. J. (1996). Magnetic susceptibility of soil: An evaluation of conflicting theories using a national data set. Geophysical Journal International, 127(3), 728–734.
Dunlop, D., & Ozdemir, O. (1997). Rock magnetism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
EPA U. S. (1989). Risk assessment guidance for superfund—Human health evaluation manual (Part A) (Vol. I). Interim final.
EPA U.S. (2001). Supplemental guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites. Peer Review Draft, OSWER, 9355, 4–24.
Evans, M. E., & Heller, F. (2003). Environmental magnetism: Principles and applications of enviromagnetics. London: Academic Press.
Ferreira-Baptista, L., & Miguel, E. D. (2005). Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 39(25), 4501–4512.
Gautam, P., Blaha, U., & Appel, E. (2005). Magnetic susceptibility of dust-loaded leaves as a proxy of traffic-related heavy metal pollution in Kathmandu city, Nepal. Atmospheric Environment, 39(12), 2201–2211.
Goddu, S. R., Appel, E., Jordanova, D., & Wehland, F. (2004). Magnetic properties of road dust from Visakhapatnam (India)—Relationship to industrial pollution and road traffic. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 29(13), 985–995.
Godish, T., & Fu, J. S. (2003). Air quality (4th ed.). London: Lewis Pub.
Han, Y., Du, P., Cao, J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355(1–3), 176–186.
Hoffmann, V., Knab, M., & Appel, E. (1999). Magnetic susceptibility mapping of roadside pollution. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 66(1), 313–326.
Hu, X.-F., Su, Y., Ye, R., Li, X., & Zhang, G. (2007). Magnetic properties of the urban soils in Shanghai and their environmental implications. CATENA, 70(3), 428–436.
Kim, W., Doh, S.-J., Park, Y.-H., & Yun, S.-T. (2007). Two-year magnetic monitoring in conjunction with geochemical and electron microscopic data of roadside dust in Seoul, Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 41(35), 7627–7641.
Lecoanet, H., Leveque, F., & Ambrosi, J. P. (2003). Combination of magnetic parameters: An efficient way to discriminate soil-contamination sources (south France). Environmental Pollution, 122(2), 229–234.
Li, H., Qian, X., Hu, W., Wang, Y., & Gao, H. (2013a). Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China. Science of the Total Environment, 456, 212–221.
Li, J., Tang, R., & Yin, G. (2004). An investigation on incidence of lung cancer in Fuyuan county, Yunnan province. Bull Chin Cancer, 13, 286–289.
Li, R., Pan, C., Chen, J., Jiang, Y., & Ding, G. (2012). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for urban topsoil and dust in Tongling City. China Environmental Science, 32(12), 2261–2270.
Liu, Q., Roberts, A. P., Larrasoaña, J. C., Banerjee, S. K., Guyodo, Y., Tauxe, L., et al. (2012). Environmental magnetism: Principles and applications. Reviews of Geophysics, 50(4), 197–215.
Liu, E., Yan, T., Birch, G., & Zhu, Y. (2014). Pollution and health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban road dust in Nanjing, a mega-city of China. Science of the Total Environment, 476, 522–531.
Li, W., Wang, Y., Collett, J., Chen, J., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., et al. (2013b). Microscopic evaluation of trace metals in cloud droplets in an acid precipitation region. Environmental Science and Technology, 47, 4172–4180.
Loska, K., Cebula, J., Pelczar, J., Wiechuła, D., & Kwapuliński, J. (1997). Use of enrichment, and contamination factors together with geoaccumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik water reservoir in Poland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 93(1–4), 347–365.
Lu, S., Tan, Z., Liu, P., Zhao, H., Liu, D., Yu, S., et al. (2017). Single particle aerosol mass spectrometry of coal combustion particles associated with high lung cancer rates in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, China. Chemosphere, 186, 278–286.
Lu, S., Yi, F., Hao, X., Yu, S., Ren, J., Wu, M., et al. (2014). Physicochemical properties and ability to generate free radicals of ambient coarse, fine, and ultrafine particles in the atmosphere of Xuanwei, China, an area of high lung cancer incidence. Atmospheric Environment, 97, 519–528.
Lu, X., Li, L., Wang, L., Lei, K., Huang, J., & Zhai, Y. (2009a). Contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in roadway dust from Baoji. China Atmospheric Environment, 43(15), 2489–2496.
Lu, X., Li, L., Wang, L., Lei, K., Huang, J., & Zhai, Y. (2009b). Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2), 1058–1062.
Lu, X., Wang, L., Li, L., Lei, K., Huang, L., & Kang, D. (2010). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1), 744–749.
Lv, J., Zhang, W., & Xu, R. (2013). Investigation of radon and heavy metals in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, high lung cancer incidence areas in China. Journal of Environmental Health, 76(4), 32.
Magiera, T., Jabłońska, M., Strzyszcz, Z., & Rachwal, M. (2011). Morphological and mineralogical forms of technogenic magnetic particles in industrial dusts. Atmospheric Environment, 45(25), 4281–4290.
Magiera, T., Parzentny, H., Róg, L., Chybiorz, R., & Wawer, M. (2015). Spatial variation of soil magnetic susceptibility in relation to different emission sources in southern Poland. Geoderma, 255, 94–103.
Maher, B. A. (1988). Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites. Geophysical Journal International, 94(1), 83–96.
Maher, B., & Thompson, R. (1999). Quaternary climates, environments and magnetism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Manasreh, W. A. (2010). Assessment of trace metals in street dust of mutah city, Kurak, Jordan. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 5(1), 5–12.
Moreno, T., Karanasiou, A., Amato, F., Lucarelli, F., Nava, S., Calzolai, G., et al. (2013). Daily and hourly sourcing of metallic and mineral dust in urban air contaminated by traffic and coal-burning emissions. Atmospheric Environment, 68, 33–44.
Morton-Bermea, O., Hernandez, E., Martinez-Pichardo, E., Soler-Arechalde, A., Santa-Cruz, R. L., Gonzalez-Hernandez, G., et al. (2009). Mexico City topsoils: Heavy metals vs. magnetic susceptibility. Geoderma, 151(3), 121–125.
Qiao, Q., Zhang, C., Huang, B., & Piper, J. D. (2011). Evaluating the environmental quality impact of the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games: Magnetic monitoring of street dust in Beijing Olympic Park. Geophysical Journal International, 187(3), 1222–1236.
Reimann, C., & Caritat, P. (2000). Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(24), 5084–5091.
Salo, H., Bućko, M. S., Vaahtovuo, E., Limo, J., Mäkinen, J., & Pesonen, L. J. (2012). Biomonitoring of air pollution in SW Finland by magnetic and chemical measurements of moss bags and lichens. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 115, 69–81.
Spiteri, C., Kalinski, V., Rösler, W., Hoffmann, V., Appel, E., & Team, M. (2005). Magnetic screening of a pollution hotspot in the Lausitz area, Eastern Germany: Correlation analysis between magnetic proxies and heavy metal contamination in soils. Environmental Geology, 49(1), 1–9.
Sutherland, R. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Sutherland, R. A., & Tolosa, C. (2000). Multi-element analysis of road-deposited sediment in an urban drainage basin, Honolulu, Hawaii. Environmental Pollution, 110(3), 483–495.
Tanner, P. A., Ma, H. L., & Yu, P. K. (2008). Fingerprinting metals in urban street dust of Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(19), 7111–7117.
Thompson, R., & Oldfield, F. (1986). Environmental magnetism. Crows Nest: Allen & Unwin.
US EPA. (1996). Soil screening guidance: Technical background document|Superfund. Washington, D.C.: US EPA.
Wang, G., Oldfield, F., Xia, D., Chen, F., Liu, X., & Zhang, W. (2012). Magnetic properties and correlation with heavy metals in urban street dust: A case study from the city of Lanzhou, China. Atmospheric Environment, 46, 289–298.
Wang, Z., Liu, S. Q., Chen, X. M., & Lin, C. Y. (2008). Estimates of the exposed dermal surface area of Chinese in view of human health risk assessment. Journal of Safety and Environment, 8(4), 152–156.
Wei, B., Jiang, F., Li, X., & Mu, S. (2010). Heavy metal induced ecological risk in the city of Urumqi, NW China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1), 33–45.
Xia, D., Wang, B., Yu, Y., Jia, J., Nie, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2014). Combination of magnetic parameters and heavy metals to discriminate soil-contamination sources in Yinchuan—A typical oasis city of Northwestern China. Science of the Total Environment, 485, 83–92.
Yang, T., Liu, Q., Chan, L., & Cao, G. (2007). Magnetic investigation of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoils around the East Lake, Wuhan, China. Geophysical Journal International, 171(2), 603–612.
Yang, T., Liu, Q., Li, H., Zeng, Q., & Chan, L. (2010). Anthropogenic magnetic particles and heavy metals in the road dust: Magnetic identification and its implications. Atmospheric Environment, 44(9), 1175–1185.
Yuen, J., Olin, P. H., Lim, H., Benner, S. G., Sutherland, R., & Ziegler, A. (2012). Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in road deposited sediments in residential and light industrial neighborhoods of Singapore. Journal of Environmental Management, 101, 151–163.
Zhang, W., Jiang, H., Dong, C., Yan, Q., Yu, L., & Yu, Y. (2011). Magnetic and geochemical characterization of iron pollution in subway dusts in Shanghai, China. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(6). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GC003524.
Zhang, W., Lü, S., Liu, D., Liu, P., Yonmochi, S., Wang, X., et al. (2015). Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the street dusts in Xuanwei and their health risk assessment. Environmental Sciences, 36(5), 1810–1817. (in Chinese).
Zhu, Z., Han, Z., Bi, X., & Yang, W. (2012). The relationship between magnetic parameters and heavy metal contents of indoor dust in e-waste recycling impacted area, Southeast China. Science of the Total Environment, 433, 302–308.
Zhu, Z., Li, Z., Bi, X., Han, Z., & Yu, G. (2013a). Response of magnetic properties to heavy metal pollution in dust from three industrial cities in China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 246–247, 189–198.
Zhu, Z., Sun, G., Bi, X., Li, Z., & Yu, G. (2013b). Identification of trace metal pollution in urban dust from kindergartens using magnetic, geochemical and lead isotopic analyses. Atmospheric Environment, 77, 9–15.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Grant Nos. 21477073, 41273127), International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC-JSPS (41511140096), and the Program for Innovative Research Team in the University (No. IRT13078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Z., Lu, S., Zhao, H. et al. Magnetic, geochemical characterization and health risk assessment of road dust in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, China. Environ Geochem Health 40, 1541–1555 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0070-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0070-7