Abstract
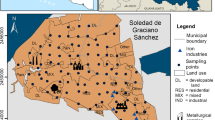
Settled road dust was examined to detect the presence of non-airborne submicron and nano-sized iron-based particles and to characterize these particles. Samples were collected from a road surface near a busy road junction in the city of Ostrava, Czech Republic, once a month from March to October. The eight collected samples were subjected to a combination of experimental techniques including elemental analysis, Raman microspectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, and magnetometry. The data thereby obtained confirmed the presence of non-agglomerated spherical nano-sized iron-based particles, with average sizes ranging from 2 down to 490 nm. There are several sources in road traffic which generate road dust particles, including exhaust and non-exhaust processes. Some of them (e.g., brake wear) produce iron as the dominant metallic element. Raman microspectroscopy revealed forms of iron (mainly as oxides, Fe2O3, and mixtures of Fe2O3 and Fe3O4). Moreover, Fe3O4 was also detected in samples of human tissues from the upper and lower respiratory tract. In view of the fact that no agglomeration of those particles was found by SEM, it is supposed that these particles may be easily resuspended and represent a risk to human health due to inhalation exposure, as proved by the detection of particles with similar morphology and phase composition in human tissues.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int 30:1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.04.004
Adamiec E (2017) Road environments: impact of metals on human health in heavily congested cities of Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:2–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070697
Ahmadzadeh M, Romero C, McCloy J (2018) Magnetic analysis of commercial hematite, magnetite, and their mixtures. AIP Adv 8:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5006474
Amato F, Flemming RC, Denier van der Gon HAC et al (2014) Urban air quality: the challenge of traffic non-exhaust emissions. J Hazard Mater 275:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.053
Apeagyei E, Spengler JD, Bank M (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos Environ 45:2310–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.11.015
Barbusiński K (2009) Fenton reaction – controversy concerning the chemistry. Ecol Chem Eng S 16:1–12
Bardelli F, Cattaruzza E, Gonella F, Rampazzo G, Valotto G (2011) Characterization of road dust collected in Traforo del San Bernardo highway tunnel: Fe and Mn speciation. Atmos Environ 45:6459–6468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.07.035
Bascom R, Bromberg PA, Costa DA et al (1996) Health effects of outdoor air pollution. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:3–50. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.153.1.8542133
Čábalová L, Čabanová K, Bielniková H (2015) Micro-and nanosized particles in nasal mucosa: a pilot study. Biomed Res Int 505986:1–7 https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/505986
Čabanová K, Bielniková H, Dvořáčková J (2015) Metal and carbon-based particles / clusters in the peripheral T - cell lymphoma in the lungs. NANOCON 2015 - Conference Proceedings. Tanger Ltd.: 553–557. ISBN: 978-808729463-5
Čabanová K, Bielniková H, Motyka O et al (2018) Detection of micron and submicron particles in human bronchogenic carcinomas. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.15842
Chen LC, Lippmann M (2015) Inhalation toxicology methods: the generation and characterization of exposure atmospheres and inhalational exposures. Curr Protoc Toxicol 63:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140856.tx2404s63
Chen Y, Shah N, Huggins FE, Huffman GP (2006) Microanalysis of ambient particles from Lexington, KY, by electron microscopy. Atmos Environ 40:651–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.09.036
Denby BR, Kupiainen KJ, Gustafsson M (2018) Review of road dust emissions - Chapter 9: 183–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811770-5.00009-1 in Amato F (2018) Non-exhaust emissions
Ghio AJ (2009) Disruption of iron homeostasis and lung disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.11.004
Gunawardana C, Goonetilleke A, Egodawatta P et al (2012) Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere 87:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.012
Hanesch M (2009) Raman spectroscopy of iron oxides and (oxy) hydroxides at low laser power and possible applications in environmental magnetic studies. Geophys J Int 177:941–948. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04122.x
Happo MS, Salonen RO, Hälinen AI, Jalava PI, Pennanen AS, Dormans JAMA, Gerlofs-Nijland ME, Cassee FR, Kosma VM, Sillanpää M, Hillamo R, Hirvonen MR (2010) Inflammation and tissue damage in mouse lung by single and repeated dosing of urban air coarse and fine particles collected from six European cities. Inhal Toxicol 22:402–416. https://doi.org/10.3109/08958370903527908
Hautot D, Pankhurst QA, Khan N, Dobson J (2003) Preliminary evaluation of nanoscale biogenic magnetite in Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue. Proc Biol Sci B 270:62–64. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2003.0012
Hulskotte JHJ, Roskam GD, Denioer van der Gon HAC (2014) Elemental composition of current automotive braking materials and derived air emission factors. Atmos Environ 99:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.10.007
Jeleńska M, Górka-Kostrubiec B, Werner T, Kądziałko-Hofmokl M, Szczepaniak-Wnuk I, Gonet T, Szwarczewski P (2017) Evaluation of indoor/outdoor urban air pollution by magnetic, chemical and microscopic studies. Atmos Pollut Res 8:754–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.01.006
Khiroya H, Turner AM (2015) The role of iron in pulmonary pathology. Multidiscip Respir Med 10:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40248-015-0031-2
Kirschvink JL, Kobayashi-Kirscvink A, Woodford BJ (1992) Magnetite biomineralization in the human brain. PNAS 89:7683–7687. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.16.7683
Kukutschová J, Roubíček V, Malachová K, Pavlíčková Z, Holuša R, Kubačková J, Mička V, MacCrimmon D, Filip P (2009) Wear mechanism in automotive brake materials, wear debris and its potential environmental impact. Wear 267:807–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.01.034
Kukutschová J, Moravec P, Tomášek V, Matějka V, Smolík J, Schwarz J, Seidlerová J, Šafářová K, Filip P (2011) On airborne nano/micro-sized wear particles released from low-metallic automotive brakes. Environ Pollut 159:998–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.036
Lewinski N, Graczyk H, Riediker M (2013) Human inhalation exposure to iron oxide particles. BioNanoMaterials 14:5–23. https://doi.org/10.1515/bnm-2013-0007
Liati A, Pandurangi SS, Boulouchos K, Schreiber D, Arroyo Rojas Dasilva Y (2015) Metal nanoparticles in diesel exhaust derived by in-cylinder melting of detached engine fragments. Atmos Environ 101:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.11.014
Luňáček J, Životský O, Jirásková Y, Buršík J, Janoš P (2016) Thermally stimulated iron oxide transformations and magnetic behaviour of cerium dioxide/iron oxide reactive sorbents. Mater Charact 120:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.09.009
Lyu Y, Zhu Y, Olofsson U (2015) Wear between wheel and rail: a pin-on-disc study of environmental conditions and iron oxides. Wear 328-329:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.02.057
Maher BA, Ahmed IAM, Karloukovski V, MacLaren DA, Foulds PG, Allsop D, Mann DMA, Torres-Jardón R, Calderon-Garciduenas L (2016) Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. PNAS 113:10797–10801 https://10.1073/pnas.1605941113
Matějka V, Metinoz I, Wahlstrom J et al (2017) On the running-in of brake pads and discs for dyno bench tests. Tribol Int 115:424–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.06.008
Mitchell R, Maher BA (2009) Evaluation and application of biomagnetic monitoring of traffic-derived particulate pollution. Atmos Environ 43:2095–2103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.01.042
Moreno T, Querol X, Alastuey A et al (2008) Lanthanoid geochemistry of urban atmospheric particulate matter. Environ Sci Technol 42:6502–6507. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800786z
Moreno T, Martins V, Querol X, Jones T, BéruBé K, Minguillón MC, Amato F, Capdevila M, de Miguel E, Centelles S, Gibbons W (2015) A new look at inhalable metalliferous airborne particles on rail subway platforms. Sci Total Environ 505:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.013
Naboychenko SS, Murashova IB, Neikov OD (2005) Production of rare metal powders-Chapter 22: 485–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-85617-422-0.00022-7 in Neikov OD, Naboychenko SS, Murashova IV et al (2009) Handbook of non-ferrous metal powders ISBN 978-1-85617-422-0
Okagata Y (2013) Design technologies for railway wheels and future prospects. Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Technical Report 105:26–33 http://www.nssmc.com/en/tech/report/nssmc/pdf/105-06.pdf. Accessed 16 April 2018
Pankhurst Q, Hautot D, Khan N, Dobson J (2008) Increased levels of magnetic iron compounds in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 13:49–52. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2008-13105
Rajhelova H, Peikertová P, Čabanová K et al (2018) Determination of oxidative potential caused by brake wear debris in non-cellular systems. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.15866
Schultheiss-Grassi PP, Wessiken R, Dobson J (1999) TEM investigations of biogenic magnetite extracted from the human hippocampus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1426:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4165(98)00160-3
Statutory City of Ostrava (2015) Number of vehicles in the selected transport node in Czech Republic (city district Ostrava-Poruba in 2015). https://opendata.ostrava.cz/category/datove-sady/doprava/ [cited 2018-07-18]
Teculescu D, Albu A (1973) Pulmonary function in workers inhaling iron oxide dust. Internationales Archiv für Arbeitsmedizin 31:163–170
Thomas RJ (2013) Particle size and pathogenicity in the respiratory tract. Virulence 4:847–858. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.27172
Thorpe A, Harrison RM (2008) Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: a review. Sci Total Environ 400:270–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.007
US EPA - United States Environmental protection Agency (2018) Particulate matter (PM) pollution. Washington D.C., USA. https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics#PM [cited 2018-07-17]
Verma PC (2015) Determination of concentration of some heavy metals in roadside dust in Damaturu metropolis which causes environmental pollution. International Journal of Advances in Science Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2321-9009. http://www.iraj.in/journal/journal_file/journal_pdf/6-205-144921222787-92.pdf. Accessed 16 April 2018
Vossler T, Cernikovsky L, Novak J et al (2016) Source apportionment with uncertainty estimates of fine particulate matter in Ostrava, Czech Republic using Positive Matrix Factorization. Atmos Pollut Res 7:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2015.12.004
Wang K, Chiang K, Tsai C et al (2001) The effects of FeCl3 on the distribution of the heavy metals Cd, Cu, Cr, and Zn in a simulated multimetal incineration system. Environ Int 26:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(00)00115-X
Watanabe H, Nakajima F, Kasuga I, Furumai H (2011) Toxicity evaluation of road dust in the runoff process using a benthic ostracod Heterocypris incongruens. Sci Total Environ 409:2366–2372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.03.001
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Oldřich Motyka for statistical analysis of the experimental data and Mr. Chris Hopkinson for language corrections.
Funding
This study was supported by Project “Characterization and possible environmental risks of synthetic lanthanide oxides nanoparticles and particles from non-combustion processes in traffic” (number SP2018/81) funded by Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic, and by the Project “New Composite Materials for Environmental Applications” (number CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/17_048/0007399) funded by ERDF (European Regional Development Fund)/ESF (European Social Fund).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Čabanová, K., Hrabovská, K., Matějková, P. et al. Settled iron-based road dust and its characteristics and possible association with detection in human tissues. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 2950–2959 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3841-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3841-x