Abstract
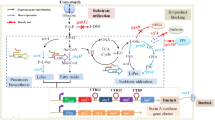
Cofactor supply is a rate-limiting step in the bioconversion of xylose to xylitol. Strain WZ04 was first constructed by a novel simultaneous deletion–insertion strategy, replacing ptsG, xylAB and ptsF in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110 with three mutated xylose reductase genes (xr) from Neurospora crassa. Then, the pfkA, pfkB, pgi and/or sthA genes were deleted and replaced by xr to investigate the influence of carbon flux toward the pentose phosphate pathway and/or transhydrogenase activity on NADPH generation. The deletion of pfkA/pfkB significantly improved NADPH supply, but minimally influenced cell growth. The effects of insertion position and copy number of xr were examined by a quantitative real-time PCR and a shake-flask fermentation experiment. In a fed-batch fermentation experiment with a 15-L bioreactor, strain WZ51 produced 131.6 g L−1 xylitol from hemicellulosic hydrolysate (xylitol productivity: 2.09 g L−1 h−1). This study provided a potential approach for industrial-scale production of xylitol from hemicellulosic hydrolysate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Shim WY, Jeon WY, Yoon BH, Kim JH (2012) Enhancement of xylitol production in Candida tropicalis by co-expression of two genes involved in pentose phosphate pathway. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:199–204
Bommareddy RR, Chen Z, Rappert S, Zeng AP (2014) A de novo NADPH generation pathway for improving lysine production of Corynebacterium glutamicum by rational design of the coenzyme specificity of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Metab Eng 25:30–37
Branco RDF, Santos JCD, Silva SSD (2011) A novel use for sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic fraction: xylitol enzymatic production. Biomass Bioenergy 35:3241–3246
Chen Q, Xue C, Zhang WM, Song WG, Wan LJ, Ma KS (2014) Green production of ultrahigh-basicity polyaluminum salts with maximum atomic economy by ultrafiltration and electrodialysis with bipolar membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:13467–13474
Chin JW, Cirino PC (2011) Improved NADPH supply for xylitol production by engineered Escherichia coli with glycolytic mutations. Biotechnol Progress 27:333–341
Chin JW, Khankal R, Monroe CA, Maranas CD, Cirino PC (2009) Analysis of NADPH supply during xylitol production by engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:209–220
Cirino PC, Chin JW, Ingram LO (2006) Engineering Escherichia coli for xylitol production from glucose–xylose mixtures. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:1167–1176
Iverson A, Garza E, Zhao J, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang J, Manow R, Zhou S (2013) Increasing reducing power output (NADH) of glucose catabolism for reduction of xylose to xylitol by genetically engineered Escherichia coli AI05. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1225–1232
Jiang Y, Chen B, Duan C, Sun B, Yang J, Yang S (2015) Multigene editing in the Escherichia coli genome via the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:2506–2514
Jin LQ, Wei X, Bo Y, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2018) Efficient biosynthesis of xylitol from xylose by coexpression of xylose reductase and glucose dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187:1143–1157
Khankal R, Chin JW, Cirino PC (2008) Role of xylose transporters in xylitol production from engineered Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 134:246–252
Ko B, Kim J, Kim J (2006) Production of xylitol from d-xylose by a xylitol dehydrogenase gene-disrupted mutant of Candida tropicalis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4207–4213
Kogje AB, Ghosalkar A (2017) Xylitol production by genetically modified industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae using glycerol as co-substrate. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:1–11
Lee WH, Park JB, Park K, Kim MD, Seo JH (2007) Enhanced production of ɛ-caprolactone by overexpression of NADPH-regenerating glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in recombinant Escherichia coli harboring cyclohexanone monooxygenase gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:329–338
Lim SJ, Jung YM, Shin HD, Lee YH (2002) Amplification of the NADPH-related genes zwf and gnd for the oddball biosynthesis of PHB in an E. coli transformant harboring a cloned phbCAB operon. J Biosci Bioeng 93:543–549
Nair NU, Zhao H (2010) Selective reduction of xylose to xylitol from a mixture of hemicellulosic sugars. Metab Eng 12:462
Oh YJ, Lee TH, Lee SH, Oh EJ, Ryu YW, Kim MD, Seo JH (2007) Dual modulation of glucose 6-phosphate metabolism to increase NADPH-dependent xylitol production in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Catal B Enzym 47:37–42
Pontrelli S, Chiu T-Y, Lan EI, Chen FYH, Chang P, Liao JC (2018) Escherichia coli as a host for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.04.008
Sauer U, Canonaco F, Heri S, Perrenoud A, Fischer E (2004) The soluble and membrane-bound transhydrogenases UdhA and PntAB have divergent functions in NADPH metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279:6613–6619
Su B, Wu M, Zhang Z, Lin J, Yang L (2015) Efficient production of xylitol from hemicellulosic hydrolysate using engineered Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 31:112–122
Su B, Zhang Z, Wu M, Lin J, Yang L (2016) Construction of plasmid-free Escherichia coli for the production of arabitol-free xylitol from corncob hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Sci Rep 6:26567
Zhang J, Zhang B, Wang D, Gao X, Hong J (2014) Xylitol production at high temperature by engineered Kluyveromyces marxianus. Bioresour Technol 152:192–201
Zhang J, Zhang B, Wang D, Gao X, Hong J (2015) Improving xylitol production at elevated temperature with engineered Kluyveromyces marxianus through over-expressing transporters. Bioresour Technol 175:642–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.150
Zhao H, Nair NU, Racine M, Woodyer R (2011) Production of xylitol from a mixture of hemicellulosic sugars. PCT/US2011/021277
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21376215), National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB710803) and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2012AA022302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, X., Wang, J., Lin, J. et al. Efficient production of xylitol by the integration of multiple copies of xylose reductase gene and the deletion of Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway-associated genes to enhance NADPH regeneration in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46, 1061–1069 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02169-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02169-3