Abstract
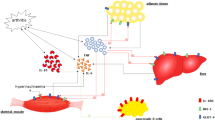
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by persistent synovial inflammation and irreversible cartilage and bone damage. Despite its predominant osteoarticular and periarticular manifestations, RA is also a systematic disease associated with organ-specific extra-articular manifestation. Increasing evidence indicates that RA patients are susceptible to diabetes mellitus (DM), and RA aggravates metabolic disordered in DM, indicating the close association between RA and DM. Many factors involved in RA stimulate insulin resistance and DM development. These factors include proinflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β), RA autoantibodies (such as rheumatoid factor, cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies), excess RA related adipokines (such as leptin, resistin, ANGPTL4), C-creative protein, and other protein (such as TXNDC5, NLRP3, RBP4). Furthermore, commonly used RA drugs, such as conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), and glucocorticoids, provide potential benefits in improving insulin resistance and inhibiting DM development. This review discusses the mechanistic and therapeutic links between RA and DM, aiming to provide valuable information for the prevention and treatment of DM in RA patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACPA:
-
Cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
- AGEs:
-
Advanced glycation end products
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- ANGPTL4:
-
Angiopoientin-like protein 4
- bDMARDs:
-
Biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
- CPRD:
-
Clinical Practice Research Datalink
- CRP:
-
C-creative protein
- csDMARDs:
-
Conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4
- DAS:
-
Disease activity score
- DKD:
-
Diabetic kidney disease
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- Fas:
-
Factor associated suicide
- FasL:
-
Factor associated suicide ligand
- FLS:
-
Fibroblast-like synoviocyte
- GLUT4:
-
Glucose transporter 4
- GSK-3:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3
- HbA1c:
-
Glycated hemoglobin
- HCQ:
-
Hydroxychloroquine
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance
- HR:
-
Harzard ratio
- hs-CRP:
-
High-sensitivity CRP
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like growth factors-1
- IGFBP1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein
- IGF-IR:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IRS-1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate-1
- IRS-2:
-
Insulin receptor substrate-2
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase
- JAK2:
-
Janus Kinases 2
- JAKi:
-
Inhibitors of JAKs
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LepRb:
-
Leptin receptor
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- MTX:
-
Methotrexate
- NDB:
-
National Data Bank
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-B
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-like receptor protein 3
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- PGE2:
-
Prostaglandin E2
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- PTP-1B:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- RF:
-
Rheumatoid factor
- RANKL:
-
Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κ B Ligand
- RBP4:
-
Retinol-binding protein 4
- SOCS3:
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α antagonists
- TNFR:
-
TNF receptors
- TXNDC5:
-
Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Hoy D, Smith E, Bettampadi D, Mansournia MA, et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(11):1463–71.
Prete M, Racanelli V, Digiglio L, Vacca A, Dammacco F, Perosa F. Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: an update. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;11(2):123–31.
Hresko A, Lin TC, Solomon DH. Medical care costs associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the US: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018;70(10):1431–8.
Hu H, Luan L, Yang K, Li SC. Burden of rheumatoid arthritis from a societal perspective: a prevalence-based study on cost of this illness for patients in China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(8):1572–80.
Sakran N, Graham Y, Pintar T, Yang W, Kassir R, Willigendael EM, et al. The many faces of diabetes. Is there a need for re-classification? A narrative review. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):9.
Malone JI, Hansen BC. Does obesity cause type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)? Or is it the opposite? Pediatr Diabetes. 2019;20(1):5–9.
Sampath Kumar A, Maiya AG, Shastry BA, Vaishali K, Ravishankar N, Hazari A, et al. Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2019;62(2):98–103.
Choi CHJ, Cohen P. Epigenetics: How does obesity lead to insulin resistance? Elife. 2017;6:e33298.
Pi H, Zhou H, Jin H, Ning Y, Wang Y. Abnormal glucose metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9670434.
Radovanović-Dinić B, Tešić-Rajković S, Zivkovic V, Grgov S. Clinical connection between rheumatoid arthritis and liver damage. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(5):715–24.
Tejera-Segura B, López-Mejías R, Domínguez-Luis MJ, de Vera-González AM, González-Delgado A, Ubilla B, et al. Incretins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):229.
Jiang P, Li H, Li X. Diabetes mellitus risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33(1):115–21.
Baker JF, England BR, George M, Cannon G, Sauer B, Ogdie A, et al. Disease activity, cytokines, chemokines and the risk of incident diabetes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(5):566–72.
Ruscitti P, Ursini F, Cipriani P, Ciccia F, Liakouli V, Carubbi F, et al. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis: results from a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(34):e7896.
Jin Y, Chen SK, Liu J, Kim SC. Risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(9):1248–56.
Liu XZ, Gao Y, Fan J, Xu X, Zhang J, Gao J, et al. Metabolic abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis patients with comorbid diabetes mellitus. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(1):219–26.
Ruscitti P, Ursini F, Cipriani P, Liakouli V, Carubbi F, Berardicurti O, et al. Poor clinical response in rheumatoid arthritis is the main risk factor for diabetes development in the short-term: A 1-year, single-centre, longitudinal study. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(7):e0181203.
Xie B, He J, Liu Y, Liu T, Liu C. A meta-analysis of HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and concentration in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1):18.
Pierini FS, Botta E, Soriano ER, Martin M, Boero L, Meroño T, et al. Effect of tocilizumab on LDL and HDL characteristics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. an observational study. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(2):803–15.
Arias de la Rosa I, Escudero-Contreras A, Rodríguez-Cuenca S, Ruiz-Ponce M, Jiménez-Gómez Y, Ruiz-Limón P, et al. Defective glucose and lipid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis is determined by chronic inflammation in metabolic tissues. J Intern Med. 2018;284(1):61–77.
Al-Mansoori L, Al-Jaber H, Prince MS, Elrayess MA. Role of inflammatory cytokines, growth factors and adipokines in adipogenesis and insulin resistance. Inflammation. 2021;45(1):31–44.
Masuko K. Angiopoietin-like 4: A molecular link between insulin resistance and rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(5):939–43.
Ursini F, Russo E, D’Angelo S, Arturi F, Hribal ML, D’Antona L, et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes in rheumatoid arthritis: an OGTT study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(7):e2552.
Costa NT, Veiga Iriyoda TM, Kallaur AP, Delongui F, Alfieri DF, Lozovoy MA, et al. Influence of insulin resistance and TNF-α on the inflammatory process, oxidative stress, and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:8962763.
Yao Z, Getting SJ, Locke IC. Regulation of TNF-induced osteoclast differentiation. Cells. 2021;11(1):132.
Sethi JK, Hotamisligil GS. Metabolic messengers: tumour necrosis factor. Nat Metab. 2021;3(10):1302–12.
Tse MCL, Herlea-Pana O, Brobst D, Yang X, Wood J, Hu X, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α promotes phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhancer A and AMP-activated protein kinase interaction to suppress lipid oxidation in skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 2017;66(7):1858–70.
Copps KD, White MF. Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia. 2012;55(10):2565–82.
Liang Y, Xu WD, Peng H, Pan HF, Ye DQ. SOCS signaling in autoimmune diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44(5):1265–75.
Stagakis I, Bertsias G, Karvounaris S, Kavousanaki M, Virla D, Raptopoulou A, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy improves insulin resistance, beta cell function and insulin signaling in active rheumatoid arthritis patients with high insulin resistance. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(3):R141.
van den Oever IAM, Baniaamam M, Simsek S, Raterman HG, van Denderen JC, van Eijk IC, et al. The effect of anti-TNF treatment on body composition and insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(2):319–28.
Atzeni F, Nucera V, Masala IF, Sarzi-Puttini P, Bonitta G. Il-6 Involvement in pain, fatigue and mood disorders in rheumatoid arthritis and the effects of Il-6 inhibitor sarilumab. Pharmacol Res. 2019;149:104402.
Millrine D, Jenkins RH, Hughes STO, and Jones SA. Making sense of IL-6 signalling cues in pathophysiology. FEBS Lett. 2021.
McElvaney OJ, Curley GF, Rose-John S, McElvaney NG. Interleukin-6: obstacles to targeting a complex cytokine in critical illness. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(6):643–54.
Rehman K, Akash MSH, Liaqat A, Kamal S, Qadir MI, Rasul A. Role of interleukin-6 in development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2017;27(3):229–36.
Jansen K, Cevhertas L, Ma S, Satitsuksanoa P, Akdis M, van de Veen W. Regulatory B cells A to Z. Allergy. 2021;76(9):2699–715.
Akbari M, Hassan-Zadeh V. IL-6 signalling pathways and the development of type 2 diabetes. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(3):685–98.
Giacomelli R, Ruscitti P, Alvaro S, Ciccia F, Liakouli V, Di Benedetto P, et al. IL-1β at the crossroad between rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes: may we kill two birds with one stone? Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016;12(8):849–55.
Amarasekara DS, Yun H, Kim S, Lee N, Kim H, Rho J. Regulation of osteoclast differentiation by cytokine networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8.
Aye IL, Jansson T, Powell TL. Interleukin-1β inhibits insulin signaling and prevents insulin-stimulated system A amino acid transport in primary human trophoblasts. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;381(1–2):46–55.
Kang T, Huang H, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Larsen MR. Divalent metal transporter 1 knock-down modulates IL-1β mediated pancreatic beta-cell pro-apoptotic signaling pathways through the autophagic machinery. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8013.
Liu C, Feng X, Li Q, Wang Y, Li Q, Hua M. Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine. 2016;86:100–9.
Ruscitti P, Masedu F, Alvaro S, Airò P, Battafarano N, Cantarini L, et al. Anti-interleukin-1 treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes (TRACK): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2019;16(9):e1002901.
Sokolove J, Johnson DS, Lahey LJ, Wagner CA, Cheng D, Thiele GM, et al. Rheumatoid factor as a potentiator of anti-citrullinated protein antibody-mediated inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):813–21.
Laurent L, Anquetil F, Clavel C, Ndongo-Thiam N, Offer G, Miossec P, et al. IgM rheumatoid factor amplifies the inflammatory response of macrophages induced by the rheumatoid arthritis-specific immune complexes containing anticitrullinated protein antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(7):1425–31.
Takeuchi T, Miyasaka N, Inui T, Yano T, Yoshinari T, Abe T, et al. High titers of both rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies at baseline in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are associated with increased circulating baseline TNF level, low drug levels, and reduced clinical responses: a post hoc analysis of the RISING study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):194.
Derksen V, Huizinga TWJ, van der Woude D. The role of autoantibodies in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39(4):437–46.
Umeda N, Matsumoto I, Sumida T. The pathogenic role of ACPA in rheumatoid arthritis. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2017;40(6):391–5.
Dong X, Zheng Z, Lin P, Fu X, Li F, Jiang J, et al. ACPAs promote IL-1beta production in rheumatoid arthritis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17(3):261–71.
Dong X, Zheng Z, Lin P, Fu X, Li F, Jiang J, et al. ACPAs promote IL-1β production in rheumatoid arthritis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17(3):261–71.
Recinella L, Orlando G, Ferrante C, Chiavaroli A, Brunetti L, Leone S. Adipokines: new potential therapeutic target for obesity and metabolic, rheumatic, and cardiovascular diseases. Front Physiol. 2020;11:578966.
Rho YH, Chung CP, Solus JF, Raggi P, Oeser A, Gebretsadik T, et al. Adipocytokines, insulin resistance, and coronary atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(5):1259–64.
Steinz MM, Santos-Alves E, Lanner JT. Skeletal muscle redox signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020;134(21):2835–50.
Corrado A, Colia R, Rotondo C, Sanpaolo E, Cantatore FP. Changes in serum adipokines profile and insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-α. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019;35(12):2197–205.
Kang Y, Park HJ, Kang MI, Lee HS, Lee SW, Lee SK, et al. Adipokines, inflammation, insulin resistance, and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R194.
Olama SM, Senna MK, Elarman M. Synovial/serum leptin ratio in rheumatoid arthritis: the association with activity and erosion. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(3):683–90.
Hivert MF, Sullivan LM, Fox CS, Nathan DM, D’Agostino RB Sr, Wilson PW, et al. Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(8):3165–72.
Han H, Zhou W. Leptin and its derivatives: a potential target for autoimmune diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(15):1563–71.
Evans MC, Lord RA, Anderson GM. Multiple leptin signalling pathways in the control of metabolism and fertility: a means to different ends? Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9210.
El Jammal T, Sève P, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Jamilloux Y. State of the art: approved and emerging JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(2):205–18.
Favoino E, Prete M, Catacchio G, Ruscitti P, Navarini L, Giacomelli R, et al. Working and safety profiles of JAK/STAT signaling inhibitors Are these small molecules also smart? Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(3):102750.
Boström EA, Svensson M, Andersson S, Jonsson IM, Ekwall AK, Eisler T, et al. Resistin and insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):2894–904.
Saeedi Borujeni MJ, Esfandiary E, Taheripak G, Codoñer-Franch P, Alonso-Iglesias E, Mirzaei H. Molecular aspects of diabetes mellitus: resistin, microRNA, and exosome. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(2):1257–72.
Engin A. The pathogenesis of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:221–45.
Makoveichuk E, Ruge T, Nilsson S, Södergren A, Olivecrona G. High concentrations of angiopoietin-like protein 4 detected in serum from patients with rheumatoid arthritis can be explained by non-specific antibody reactivity. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(1):e0168922.
Knowles HJ. Multiple roles of angiopoietin-like 4 in osteolytic disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017;8:80.
Swales C, Athanasou NA, Knowles HJ. Angiopoietin-like 4 is over-expressed in rheumatoid arthritis patients: association with pathological bone resorption. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(10):e109524.
Gusarova V, O’Dushlaine C, Teslovich TM, Benotti PN, Mirshahi T, Gottesman O, et al. Genetic inactivation of ANGPTL4 improves glucose homeostasis and is associated with reduced risk of diabetes. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2252.
Guo L, Li SY, Ji FY, Zhao YF, Zhong Y, Lv XJ, et al. Role of Angptl4 in vascular permeability and inflammation. Inflamm Res. 2014;63(1):13–22.
Shapiro SC. Biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis. Cureus. 2021;13(5):e15063.
Pope JE, Choy EH. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51(1):219–29.
Mugabo Y, Li L, Renier G. The connection between C-reactive protein (CRP) and diabetic vasculopathy. Focus on preclinical findings. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2010;6(1):27–34.
Neale EP, Batterham MJ, Tapsell LC. Consumption of a healthy dietary pattern results in significant reductions in C-reactive protein levels in adults: a meta-analysis. Nutr Res. 2016;36(5):391–401.
Xu JW, Morita I, Ikeda K, Miki T, Yamori Y. C-reactive protein suppresses insulin signaling in endothelial cells: role of spleen tyrosine kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(2):564–73.
Horna-Terrón E, Pradilla-Dieste A, Sánchez-de-Diego C, Osada J. TXNDC5, a newly discovered disulfide isomerase with a key role in cell physiology and pathology. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(12):23501–18.
Li J, Xu B, Wu C, Yan X, Zhang L, Chang X. TXNDC5 contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by down-regulating IGFBP1 expression. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;192(1):82–94.
Chawsheen HA, Ying Q, Jiang H, Wei Q. A critical role of the thioredoxin domain containing protein 5 (TXNDC5) in redox homeostasis and cancer development. Genes Dis. 2018;5(4):312–22.
Guo C, Fu R, Wang S, Huang Y, Li X, Zhou M, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(2):231–43.
Shen HH, Yang YX, Meng X, Luo XY, Li XM, Shuai ZW, et al. NLRP3: A promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(7):694–702.
Tannahill GM, O’Neill LA. The emerging role of metabolic regulation in the functioning of Toll-like receptors and the NOD-like receptor Nlrp3. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(11):1568–72.
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011;17(2):179–88.
Stienstra R, van Diepen JA, Tack CJ, Zaki MH, van de Veerdonk FL, Perera D, et al. Inflammasome is a central player in the induction of obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(37):15324–9.
Ferraz-Amaro I, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Diaz-Gonzalez F. Retinol-binding protein 4 in rheumatoid arthritis-related insulin resistance and beta-cell function. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(4):658–65.
Mun S, Lee J, Park M, Shin J, Lim MK, Kang HG. Serum biomarker panel for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):31.
Wei Y, Xia N, Zhang W, Huang J, Ren Z, Zhu L, et al. Serum retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with insulin resistance in patients with early and untreated rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2019;86(3):335–41.
Boaghi A, Pop RM, Vasilache SL, Banescu C, Hutanu A, Marginean OC, et al. Plasma RBP4 level in association with body composition, metabolic profile, STRA6 and RBP4 gene polymorphisms in obese romanian children. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:4643–50.
Norseen J, Hosooka T, Hammarstedt A, Yore MM, Kant S, Aryal P, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 inhibits insulin signaling in adipocytes by inducing proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and toll-like receptor 4-dependent and retinol-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(10):2010–9.
Ursini F, Salvatore DA, Russo E, Ammerata G, Abenavoli L, Mauro D, et al. Serum complement C3 and type 2 diabetes in rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2018;13(3):215–21.
Ursini F, D’Angelo S, Russo E, Arturi F, D’Antona L, Bruno C, et al. Serum complement C3 strongly correlates with whole-body insulin sensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(1):18–23.
Al Haj Ahmad RM, Al-Domi HA. Complement 3 serum levels as a pro-inflammatory biomarker for insulin resistance in obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017;11(Suppl 1):S229–32.
Solomon DH, Massarotti E, Garg R, Liu J, Canning C, Schneeweiss S. Association between disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. JAMA. 2011;305(24):2525–31.
Lin C, Ji H, Cai X, Yang W, Lv F, Ji L. The association between the biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and the incidence of diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res. 2020;161:105216.
Xie W, Yang X, Ji L, Zhang Z. Incident diabetes associated with hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, biologics and glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020;50(4):598–607.
Li HZ, Xu XH, Lin N, Lu HD. Metabolic and cardiovascular benefits of hydroxychloroquine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(3):e21.
Ozen G, Pedro S, Holmqvist ME, Avery M, Wolfe F, Michaud K. Risk of diabetes mellitus associated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and statins in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(5):848–54.
Lillegraven S, Greenberg JD, Reed GW, Saunders K, Curtis JR, Harrold L, et al. Immunosuppressive treatment and the risk of diabetes in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(1):e0210459.
Perdan-Pirkmajer K, Pirkmajer S, Thevis M, Thomas A, Praprotnik S, Hočevar A, et al. Methotrexate reduces HbA1c concentration but does not produce chronic accumulation of ZMP in patients with rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2016;45(5):347–55.
Baghdadi LR. Effect of methotrexate use on the development of type 2 diabetes in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(7):e0235637.
Mantravadi S, George M, Brensinger C, Du M, Baker JF, Ogdie A. Impact of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and methotrexate on diabetes mellitus among patients with inflammatory arthritis. BMC Rheumatol. 2020;4:39.
Thornton CC, Al-Rashed F, Calay D, Birdsey GM, Bauer A, Mylroie H, et al. Methotrexate-mediated activation of an AMPK-CREB-dependent pathway: a novel mechanism for vascular protection in chronic systemic inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(2):439–48.
Antohe JL, Bili A, Sartorius JA, Kirchner HL, Morris SJ, Dancea S, et al. Diabetes mellitus risk in rheumatoid arthritis: reduced incidence with anti-tumor necrosis factor α therapy. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(2):215–21.
Wang CR, Tsai HW. Anti- and non-tumor necrosis factor-α-targeted therapies effects on insulin resistance in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. World J Diabetes. 2021;12(3):238–60.
Otsuka Y, Kiyohara C, Kashiwado Y, Sawabe T, Nagano S, Kimoto Y, et al. Effects of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and tocilizumab on the glycosylated hemoglobin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; an observational study. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(4):e0196368.
Romano C, Del Mastro A, Sellitto A, Solaro E, Esposito S, Cuomo G. Tocilizumab reduces complement C3 and C4 serum levels in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(6):1695–700.
Schultz O, Oberhauser F, Saech J, Rubbert-Roth A, Hahn M, Krone W, et al. Effects of inhibition of interleukin-6 signalling on insulin sensitivity and lipoprotein (a) levels in human subjects with rheumatoid diseases. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(12):e14328.
Castañeda S, Remuzgo-Martínez S, López-Mejías R, Genre F, Calvo-Alén J, Llorente I, et al. Rapid beneficial effect of the IL-6 receptor blockade on insulin resistance and insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(3):465–73.
Tournadre A, Pereira B, Dutheil F, Giraud C, Courteix D, Sapin V, et al. Changes in body composition and metabolic profile during interleukin 6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(4):639–46.
Yip RML, Yim CW. Role of interleukin 6 inhibitors in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021;27(8):e516–24.
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Vølund A, Ehses JA, Seifert B, et al. Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(15):1517–26.
Genovese MC, Burmester GR, Hagino O, Thangavelu K, Iglesias-Rodriguez M, John GS, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor blockade or TNFα inhibition for reducing glycaemia in patients with RA and diabetes: post hoc analyses of three randomised, controlled trials. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):206.
Ruscitti P, Ursini F, Cipriani P, Greco M, Alvaro S, Vasiliki L, et al. IL-1 inhibition improves insulin resistance and adipokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes: An observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(7):e14587.
Esser N, Paquot N, Scheen AJ. Anti-inflammatory agents to treat or prevent type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(3):283–307.
Angelini J, Talotta R, Roncato R, Fornasier G, Barbiero G, Dal Cin L, et al. JAK-inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a focus on the present and an outlook on the future. Biomolecules. 2020;10(7):1002.
Witte T. Janus kinase inhibitors. Z Rheumatol. 2021.
Chen J, Yue J, Liu Y, Liu J, Jiao K, Teng M, et al. Blocking of STAT-3/SREBP1-mediated glucose-lipid metabolism is involved in dietary phytoestrogen-inhibited ovariectomized-induced body weight gain in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;61:17–23.
Barclay JL, Nelson CN, Ishikawa M, Murray LA, Kerr LM, McPhee TR, et al. GH-dependent STAT5 signaling plays an important role in hepatic lipid metabolism. Endocrinology. 2011;152(1):181–92.
Richard AJ, Stephens JM. The role of JAK-STAT signaling in adipose tissue function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842(3):431–9.
Gurzov EN, Stanley WJ, Pappas EG, Thomas HE, Gough DJ. The JAK/STAT pathway in obesity and diabetes. Febs J. 2016;283(16):3002–15.
Brosius FC, Tuttle KR, Kretzler M. JAK inhibition in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia. 2016;59(8):1624–7.
Burrell JA, Boudreau A, Stephens JM. Latest advances in STAT signaling and function in adipocytes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020;134(6):629–39.
Menshawey R, Menshawey E, Alserr AHK, Abdelmassih AF. JAK out of the Box; The Rationale behind Janus Kinase Inhibitors in the COVID-19 setting, and their potential in obese and diabetic populations. Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2021;10(2):80–8.
Kim S, Kim HS, Chung KW, Oh SH, Yun JW, Im SH, et al. Essential role for signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 in pancreatic beta-cell death and autoimmune type 1 diabetes of nonobese diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2007;56(10):2561–8.
LiverTox: Clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury. Bethesda (MD); 2012.
Liu M, Yu Y, Hu S. A review on applications of abatacept in systemic rheumatic diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96:107612.
Sarmiento-Monroy JC, Parada-Arias L, Rodríguez-López M, Rodríguez-Jiménez M, Molano-González N, Rojas-Villarraga A, et al. Subcutaneous abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis: A real-life experience. J Transl Autoimmun. 2019;2:100016.
Scherholz ML, Schlesinger N, Androulakis IP. Chronopharmacology of glucocorticoids. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;151–152:245–61.
Wilson JC, Sarsour K, Gale S, Pethö-Schramm A, Jick SS, Meier CR. Incidence and risk of glucocorticoid-associated adverse effects in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71(4):498–511.
Wu J, Mackie SL, Pujades-Rodriguez M. Glucocorticoid dose-dependent risk of type 2 diabetes in six immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: a population-based cohort analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(1):e001220.
Movahedi M, Beauchamp ME, Abrahamowicz M, Ray DW, Michaud K, Pedro S, et al. Risk of Incident Diabetes Mellitus Associated With the Dosage and Duration of Oral Glucocorticoid Therapy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(5):1089–98.
Vandewalle J, Luypaert A, De Bosscher K, Libert C. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(1):42–54.
Hoes JN, van der Goes MC, van Raalte DH, van der Zijl NJ, den Uyl D, Lems WF, et al. Glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with or without low-to-medium dose glucocorticoids. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(11):1887–94.
Strehl C, Bijlsma JW, de Wit M, Boers M, Caeyers N, Cutolo M, et al. Defining conditions where long-term glucocorticoid treatment has an acceptably low level of harm to facilitate implementation of existing recommendations: viewpoints from an EULAR task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):952–7.
Inamo J, Kochi Y, Takeuchi T. Is type 2 diabetes mellitus an inverse risk factor for the development of rheumatoid arthritis? J Hum Genet. 2021;66(2):219–23.
Tentolouris A, Thanopoulou A, Tentolouris N, Eleftheriadou I, Voulgari C, Andrianakos A, et al. Low prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis among patients with pre-existing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(20):399.
Semb AG, Rollefstad S, Ikdahl E, Wibetoe G, Sexton J, Crowson C, et al. Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an international audit. RMD Open. 2021;7(2).
Lu MC, Yan ST, Yin WY, Koo M, Lai NS. Risk of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based case-control study. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(7):e101528.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81972133, 82172482, 81670806), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. xzy012019094), and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (No. 2020JM-365).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Chen, Y., Liu, Q. et al. Mechanistic and therapeutic links between rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus. Clin Exp Med 23, 287–299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00816-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-022-00816-1