Abstract
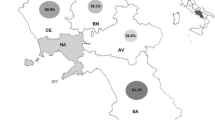
Yeast complexes in the fecal samples of wild (Dendrocopos major, Picus viridis) and partially synanthropic (Bombycilla garrulus, Garrulus glandarius, Pica pica, and Pyrrhula pyrrhula) birds were studied in a forest ecosystem during winter. A total of 18 yeast species were identified: 16 ascomycetes and two basidiomycetes belonging to five subphyla of fungi: Saccharomycotina (15), Pezizomycotina (1), Agaricomycotina (1), and Pucciniomycotina (1). Most yeast species were found in the fecal samples of P. pyrrhula (Candida parapsilosis, C. zeylanoides, Debaryomyces hansenii, Hanseniaspora uvarum, Metschnikowia pulcherrima, Meyerozyma carpophila, M. guilliermondii, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa); the lowest number of yeast species was observed in the feces of B. garrulus (C. parapsilosis, C. zeylanoides, Met. pulcherrima, and Rh. mucilaginosa). The opportunistic species of the genus Candida were found only in feces of partially synanthropic birds: C. parapsilosis was observed in the feces of B. garrulus, G. glandarius, P. pica, and P. pyrrhula; its relative abundance was 69.3%, 49.1%, 10.5%, and 1.1%, respectively; C. tropicalis was observed in the feces of P. pica and G. glandarius; its relative abundance was 54.6% and 7.1%, respectively. Strains of C. parapsilosis and C. tropicalis isolated from the feces of partially synanthropic birds were evaluated for their susceptibility to conventional antifungal agents (fluconazole, voriconazole, amphotericin B) and hydrolytic activity. A total of 160 strains were studied. Resistance to fluconazole was detected in 86.8% of C. parapsilosis strains and in 87% of C. tropicalis strains; resistance to voriconazole was detected in 71.7% of C. parapsilosis and in 66.7% of C. tropicalis strains, and the lowest percentage of resistant strains was detected to amphotericin B, 2.8% and 3.7% in C. parapsilosis and C. tropicalis strains, respectively. Multiresistance was detected in one strain of C. parapsilosis isolated from P. pica feces and in one strain of C. tropicalis isolated from G. glandarius feces. Phospholipase and hemolysin activities in the strains of C. parapsilosis were low (mean Pz values of 0.93 and 0.91, respectively); protease activity was moderate (mean Pz value of 0.53). The ability to produce hydrolytic enzymes was higher in the isolated strains of C. tropicalis. The mean Pz values of phospholipase and hemolysin activities were moderate (mean Pz values of 0.63 and 0.60, respectively), whereas protease activity was high (mean Pz value of 0.32). Thus, wild and partially synanthropic birds play an important role in disseminating of various yeast species. These yeasts can enter the topsoil via feces and contribute to the formation of allochthonous and uneven soil yeast diversity in natural ecosystems. In addition, partially synanthropic birds can be vectors of virulent strains of opportunistic Candida species from urban environments to natural biotopes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abi-Chacra EA, Souza LO, Cruz LP, Braga-Silva LA, Gonçalves DS, Sodre CL, Ribeiro MD, Seabra SH, Figueiredo-Carvalho MHG, Barbedo LS, Zancope-Oliveira RM, Ziccardi M, Santos AL (2013) Phenotypical properties associated with virulence from clinical isolates belonging to the Candida parapsilosis complex. FEMS Yeast Res 13(8):831–848. https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12092
Abulreesh HH, Organji SR, Elbanna K, Osman GE, Almalki MH, Abdel-Malek AY, Ghyathuddin AAK, Ahmad I (2019) Diversity, virulence factors, and antifungal susceptibility patterns of pathogenic and opportunistic yeast species in Rock Pigeon fecal droppings in Western Saudi Arabia. Pol J Microbiol 68(4):493–504. https://doi.org/10.33073/pjm-2019-049
Al-Seraih A, Flahaut C, Krier F, Cudennec B, Drider D (2015) Characterization of Candida famata isolated from poultry feces for possible probiotic applications. Probiotics & Antimicro Prot 7:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-015-9201-y
Al-Yasiri MH, Normand AC, Piarroux R, Ranque S, Mauffrey JF (2017) Gut yeast communities in Larus michahellis from various breeding colonies. Med Mycol 55(4):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myw088
Barry AL, Coyle MB, Thornsberry C, Gerlach EH, Hawkinson RW (1979) Methods of measuring zones of inhibition with the Bauer-Kirby disk susceptibility test. J Clin Microbiol 10(6):885–889
Branco J, Miranda IM, Rodrigues AG (2023) Candida parapsilosis virulence and antifungal resistance mechanisms: a comprehensive review of key determinants. J Fungi 9(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010080
Brilhante RSN, de Alencar LP, de Aguiar CR, Castelo DDSCM, Teixeira CEC, de Brito MR, de Oliveira MF (2013) Detection of Candida species resistant to azoles in the microbiota of rheas (Rhea americana): possible implications for human and animal health. J Med Microbiol 62(6):889–895. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.055566-0
Byzov BA, Thanh VN, Babjeva IP (1993) Yeasts associated with soil invertebrates. Biol Fertil Soils 16:183–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361405
Cafarchia C, Iatta R, Danesi P, Camarda A, Capelli G, Otranto D (2018) Yeasts isolated from cloacal swabs, feces, and eggs of laying hens. Med Mycol 57(3):340–345. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myy026
Cafarchia C, Romito D, Coccioli C, Camarda A, Otranto D (2008) Phospholipase activity of yeasts from wild birds and possible implications for human disease. Med Mycol 46(5):429–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780701885636
Cafarchia C, Romito D, Iatta R, Camarda A, Montagna MT, Otranto D (2006) Role of birds of prey as carriers and spreaders of Cryptococcus neoformans and other zoonotic yeasts. Med Mycol 44(6):485–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780600735452
Campana R, Fanelli F, Sisti M (2022) Role of melanin in the black yeast fungi Aureobasidium pullulans and Zalaria obscura in promoting tolerance to environmental stresses and to antimicrobial compounds. Fungal Biol 126(11-12):817–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2022.11.002
Carrasco M, Rozas JM, Barahona S, Alcaino J, Cifuentes V, Baeza M (2012) Diversity and extracellular enzymatic activities of yeasts isolated from King George Island, the sub-Antarctic region. BMC Microbiol 12:251. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-251
Ceylan Z, Gelen SU (2023) Identification of some yeast species in traditional Turkish fermented sausage with Vitek 2 compact system. Turkish J Vet Res 7(1):15–18. https://doi.org/10.47748/tjvr.1150543
Chai LYA, Denning DW, Warn P (2010) Candida tropicalis in human disease. Crit Rev Microbiol 36(4):282–298. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2010.489506
Chaves A, Trilles L, Alves GM, Figueiredo-Carvalho M, Brito-Santos F, Coelho RA, Martins IS, Almeida-Paes R (2021) A case-series of bloodstream infections caused by the Meyerozyma guilliermondii species complex at a reference center of oncology in Brazil. Med Mycol 59(3):235–243. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myaa044
Chen J, Tian S, Li F, Sun G, Yun K, Cheng S, Chu Y (2020) Clinical characteristics and outcomes of candidemia caused by Meyerozyma guilliermondii complex in cancer patients undergoing surgery. Mycopathologia 185:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-020-00485-2
Chryssanthou E, Wennberg H, Bonnedahl J, Olsen B (2011) Occurrence of yeasts in faecal samples from Antarctic and South American seabirds. Mycoses 54:e811–e815. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0507.2011.02031.x
CLSI (2018) Epidemiological cut-off values for antifungal susceptibility testing. M59, 2nd edn. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Costa AK, Sidrim JJ, Cordeiro RA, Brilhante RS, Monteiro AJ, Rocha MF (2010) Urban pigeons (Columba livia) as a potential source of pathogenic yeasts: a focus on antifungal susceptibility of Cryptococcus strains in Northeast Brazil. Mycopathologia 169:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-009-9245-1
Crous PW, Carnegie AJ, Wingfield MJ, Sharma R, Mughini G, Noordeloos ME, Santini A, Shouche YS, Bezerra JDP, Dima B, Guarnaccia V, Imrefi I, Jurjević Ž, Knapp DG, Kovács GM, Magistà D, Perrone G, Rämä T, Rebriev YA et al (2019) Fungal planet description sheets: 868-950. Persoonia 42:291–473. https://doi.org/10.3767/persoonia.2019.42.11
Czechowicz P, Nowicka J, Gościniak G (2022) Virulence factors of Candida spp. and host immune response important in the pathogenesis of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Int J Mol Sci 23(11):5895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23115895
de Oliveira SD, Hughes FM, Silveira MA, Evans JD, Pettis JS, Bastos EMAF, Rosa CA (2021) Microbial communities associated with honeybees in Brazil and in the United States. Braz J Microbiol 52:2097–2115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00539-7
Deorukhkar SC, Saini S, Mathew S (2014) Virulence factors contributing to pathogenicity of Candida tropicalis and its antifungal susceptibility profile. Int J Microbiol:456878. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/456878
Dulisz B, Dynowska M, Nowakowski JJ (2021) Body condition and colonization by fungi of house sparrows Passer domesticus in the urban and rural environment. Eur Zool J 88(1):152–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750263.2020.1857447
Fonseca A, Inácio J (2006) Phylloplane yeasts. In: In: biodiversity and ecophysiology of yeasts. Springer, Berlin. Heidelberg, pp 263–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-30985-3_13
Francesca N, Canale DE, Settanni L, Moschetti G (2012) Dissemination of wine-related yeasts by migratory birds. Environ Microbiol Rep 4(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-2229.2011.00310.x
Francesca N, Carvalho C, Almeida PM, Sannino C, Settanni L, Sampaio JP, Moschetti G (2013) Wickerhamomyces sylviae f.a., sp. nov., an ascomycetous yeast species isolated from migratory birds. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(Pt_12):4824–4830. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.056382-0
Francesca N, Carvalho C, Sannino C, Guerreiro MA, Almeida PM, Settanni L, Massa B, Sampaio JP, Moschetti G (2014) Yeasts vectored by migratory birds collected in the Mediterranean island of Ustica and description of Phaffomyces usticensis fa sp. nov., a new species related to the cactus ecoclade. FEMS Yeast Res 14(6):910–921. https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12179
Francesca N, Guerreiro MA, Carvalho C, Coelho M, Alfonzo A, Randazzo W, Sampaio JP, Moschetti G (2016) Jaminaea phylloscopi sp. nov. (Microstromatales), a basidiomycetous yeast isolated from migratory birds in the Mediterranean Basin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(2):824–829. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000801
Gai CS, Lacava PT, Maccheroni W Jr, Glienke C, Araujo WL, Miller TA, Azevedo JL (2009) Diversity of endophytic yeasts from sweet orange and their localization by scanning electron microscopy. J Basic Microbiol 49(5):441–451. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200800328
Glushakova A, Kachalkin A (2023) Yeasts associated with mines on tree leaves in the urban areas. Int Microbiol 26(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00370-0
Glushakova AM, Kachalkin AV (2017) Endophytic yeasts in Malus domestica and Pyrus communis fruits under anthropogenic impact. Microbiology 86:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716060102
Glushakova AM, Rodionova EN, Kachalkin AV (2021) Yeasts in feces of pigeons (Columba livia) in the city of Moscow. Curr Microbiol 78(1):238–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02251-5
Gouka L, Raaijmakers JM, Cordovez V (2022) Ecology and functional potential of phyllosphere yeasts. Trends Plant Sci 27(11):1109–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2022.06.007
Groenewald M, Lombard L, de Vries M, Lopez AG, Smith M, Crous PW (2018) Diversity of yeast species from Dutch garden soil and the description of six novel ascomycetes. FEMS Yeast Res 18(7):foy076. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foy076
GunTang W, Kamonvoradej N, Chomchat C, Suriyakan S, Sanit S, Wongwigkarn J, Lamlertthon S (2017) Prevalence and virulence factors of Candida spp. associated with blow flies. Asian Pac. J Trop Biomed 7(5):428–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.01.014
Hamer SA, Lehrer E, Magle SB (2012) Wild birds as sentinels for multiple zoonotic pathogens along an urban to rural gradient in greater Chicago, Illinois. Zoonoses Public Health 59(5):355–364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1863-2378.2012.01462.x
Hubálek Z (2004) An annotated checklist of pathogenic microorganisms associated with migratory birds. J Wildl Dis 40(4):639–659. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-40.4.639
Jang YH, Lee SJ, Lee JH, Chae HS, Kim SH, Choe NH (2011) Prevalence of yeast-like fungi and evaluation of several virulence factors from feral pigeons in Seoul, Korea. Lett Appl Microbiol 52(4):367–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2011.03009.x
Jarros IC, Veiga FF, Corrêa JL, Barros ILE, Gadelha MC, Voidaleski MF, Pieralisi N, Pedroso RB, Vicente VA, Negri M, Svidzinski TIE (2020) Microbiological and virulence aspects of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa. EXCLI J 19:687–704
Kachalkin AV, Glushakova AM, Venzhik AS (2021) Presence of clinically significant endophytic yeasts in agricultural crops: monitoring and ecological safety assessment IOP Conf Ser Earth. Environ Sci 723:042005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/723/4/042005
Kemler M, Witfeld F, Begerow D, Yurkov A (2017) Phylloplane yeasts in temperate climates. In: In yeasts in natural ecosystems: diversity. Springer, Cham, pp 171–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62683-3_6
Kielstein P, Hotzel H, Schmalreck A, Khaschabi D, Glawischnig W (2000) Occurrence of Cryptococcus spp. in excreta of pigeons and pet birds. Mycoses 43(1–2):7–15. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0507.2000.00534.x
Kregiel D, Nowacka M, Rygala A, Vadkertiová R (2022) Biological activity of pulcherrimin from the Meschnikowia pulcherrima Clade. Molecules 27(6):1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061855
Krzyczkowska J, Kozłowska M (2017) Effect of oils extracted from plant seeds on the growth and lipolytic activity of Yarrowia lipolytica yeast. J Am Oil Chem Soc 94:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-017-2975-1
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (2011) The yeasts: a taxonomic study. Elsevier, p 2080
Kwasna H, Szewczyk W, Baranowska M, Gallas E, Wisniewska M, Behnke-Borowczyk J (2021) Mycobiota associated with the vascular wilt of Poplar. Plants 10(5):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050892
Lord AT, Mohandas K, Somanath S, Ambu S (2010) Multidrug resistant yeasts in synanthropic wild birds. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 9(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-9-11
Luo G, Samaranayake LP, Yau JY (2001) Candida species exhibit differential in vitro hemolytic activities. J Clin Microbiol 39(8):2971–2974. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.39.8.2971-2974.2001
Mahboob N, Iqbal H, Ahmed M, Magnet MMH, Mamun KZ (2019) Disk diffusion method in enriched Mueller Hinton agar for determining susceptibility of Candida isolates from various clinical specimens. J Dhaka Med Coll 28(1):28–33. https://doi.org/10.3329/jdmc.v28i1.45753
Maksimova IA, Glushakova AM, Kachalkin AV, Chernov IY, Panteleeva SN, Reznikova ZI (2016) Yeast communities of Formica aquilonia colonies. Microbiology 85:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716010045
Mancianti F, Nardoni S, Ceccherelli R (2002) Occurrence of yeasts in psittacines droppings from captive birds in Italy. Mycopathologia 153(3):121–124. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014576304894
Mattsson R, Haemig PD, Olsen B (1999) Feral pigeons as carriers of Cryptococcus laurentii, Cryptococcus uniguttulatus and Debaryomyces hansenii. Med Mycol 37(5):367–369. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-280X.1999.00241.x
Medina IR, Fuentes LR, Arteaga MB, Valcárcel FR, Arbelo FA, Del Castillo DP, Suárez SD, Quintana OF, Gutiérrez BV, Sergent FS, Acosta-Hernández B (2017) Pigeons and their droppings as reservoirs of Candida and other zoonotic yeasts. Rev Iberoam Micol 34(4):211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riam.2017.03.001
Meissner W, Dynowska M, Goralska K, Rzyska H (2015) Mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) staying in urban environments have higher levels of microfungi biota diversity than do birds from nonurban areas. Fungal Ecol 17:164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.07.004
Mi R, Chen X, Xiong S, Qi B, Li J, Qiao X, Chen W, Qu C, Wang S (2021) Predominant yeasts in Chinese Dong fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) and their aroma-producing properties in fermented sausage condition. Food Sci Human Wellness 10(2):231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2021.02.013
Michán C, Martínez JL, Alvarez MC, Turk M, Sychrova H, Ramos J (2013) Salt and oxidative stress tolerance in Debaryomyces hansenii and Debaryomyces fabryi. FEMS Yeast Res 13(2):180–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12020
Moschetti G, Alfonzo A, Francesca N (2017) Yeasts in birds. In: Buzzini P, Lachance MA, Yurkov A (eds) Yeasts in natural ecosystems: diversity. Springer, Cham, pp 435–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62683-3_14
Naglik JR, Rodgers CA, Shirlaw PJ, Dobbie JL, Fernandes-Naglik LL, Greenspan D, Agabian N, Challacombe SJ (2003) Differential expression of Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinase and phospholipase B genes in humans correlates with active oral and vaginal infections. J Infect Dis 188(3):469–479. https://doi.org/10.1086/376536
Nakase T, Ninomiya S, Imanishi Y, Nakagiri A, Kawasaki H, Limtong S (2008) Ogataea paradorogensis sp. nov., a novel methylotrophic ascomycetous yeast species isolated from galleries of ambrosia beetles in Japan, with a close relation to Pichia dorogensis. J Gen Appl Microbiol 54(6):377–383. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.54.377
Nualmalang R, Thanomsridetchai N, Teethaisong Y, Sukphopetch P, Tangwattanachuleeporn M (2023) Identification of pathogenic and opportunistic yeasts in pigeon excreta by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and their prevalence in Chon Buri Province, Thailand. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20(4):3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043191
Péter G, Nagy ES, Dlauchy D (2019) Systematics, diversity and ecology of the genus Yarrowia and the methanol-assimilating yeasts. Non-conventional Yeasts: from Basic Res Appl:297–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21110-3_9
Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ, (2012) Progress in antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida spp. by use of clinical and laboratory standards institute broth microdilution methods, (2010) to 2012. J Clin Microbiol 50(9):2846–2856. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.00937-12
Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ, Turnidge JD, Castanheira M, Jones RN (2019) Twenty years of the SENTRY antifungal surveil-lance program: results for Candida species from 1997–2016. Open Forum Infect Dis 6:79–94. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofy358
Pinto LM, Neto FDAB, de Medeiros MAP, Alves DLZ, Chaves GM (2019) Candida species isolated from pigeon (Columbia livia) droppings may express virulence factors and resistance to azoles. Vet Microbiol 235:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.05.022
Price MF, Wilkinson ID, Gentry LO (1982) Plate method for detection of phospholipase activity in Candida albicans. Sabouraudia 20:7–14
Queiroz-Aaltonen IRDO, Melo Neto MFD, Fonseca LAVD, Silva DMW, Maranhão FCA (2022) Molecular detection of medically important Candida species from droppings of pigeons (Columbiformes) and captive birds (Passeriformes and Psittaciformes). Braz Arch Biol Technol 64:e21200763. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2021200763
Ramos-Moreno L, Ruiz-Pérez F, Rodríguez-Castro E, Ramos J (2021) Debaryomyces hansenii is a real tool to improve a diversity of characteristics in sausages and dry-meat products. Microorganisms 9(7):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071512
Reis EJ, Buscariolo F, Siqueira JP, Castilho EM, Almeida MT (2019) Agapornis sp. pet birds: source of dissemination of azole-resistant yeasts. Med Mycol 57(4):515–518. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myy061
Rhimi W, Aneke CI, Annoscia G, Camarda A, Mosca A, Cantacessi C, Otranto D, Cafarchia C (2021) Virulence and in vitro antifungal susceptibility of Candida albicans and Candida catenulata from laying hens. Int Microbiol 24:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-020-00141-1
Rossoni RD, Barbosa JO, Vilela SFG, dos Santos JD, Jorge AOC, Junqueira JC (2013) Correlation of phospholipase and proteinase production of Candida with in vivo pathogenicity in Galleria mellonella. Braz J Oral Sci 12(3):199–204 https://www.scielo.br/j/bjos/a/FmBTJgHW6px9CnLpwvkKCbB/#
Rüchel J, Tegeler R, Trost MA (1982) Comparison of secretory proteinases from different strains of Candida albicans. Sabouraudia 20:233–244
Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Huhndorf S, Robert V, Spouge JL, Levesque CA et al (2012) Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for Fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(16):6241–6246 https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1117018109
Sidrim JJC, de Souza Collares Maia DCB, RSN B, GDP S, Cordeiro RA, Monteiro AJ, MFG R (2010) Candida species isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of cockatiels (Nymphicus hollandicus): in vitro antifungal susceptibility profile and phospholipase activity. Vet Microbiol 145(3-4):324–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.04.006
Silva S, Negri M, Henriques M, Oliveira R, Williams DW, Azeredo J (2012) Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis: biology, epidemiology, pathogenicity and antifungal resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(2):288–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00278.x
Sipiczki M (2022) Taxonomic revision of the pulcherrima Clade of Metschnikowia (Fungi): merger of species. Taxonomy 2(1):107–123. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy2010009
Skarżyńska M, Zajac M, Bomba A, Bocian Ł, Kozdruń W, Polak M, Wia̧cek J, Wasyl D (2021) Antimicrobial resistance glides in the sky—free-living birds as a reservoir of resistant Escherichia coli with zoonotic potential. Front Microbiol 12:656223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.656223
Soltani M, Bayat M, Seyed J, Zia M, Pestechian N (2013) Isolation of Cryptococcus neoformans and other opportunistic fungi from pigeon droppings. J Res Med Sci 18(1):56–60
Sørensen T (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biol Skr k Dan Vidensk Selsk 5:1e34
Staniszewska M, Bondaryk M, Kowalska M, Magda U, Łuka M, Ochal Z, Kurzątkowski W (2014) Pathogenesis and treatment of fungal infections by Candida spp. Postep Mikrobiol 53(3):229–240
Subramanya SH, Baral BP, Sharan NK, Nayak N, Metok Y, Sathian B, Gokhale S (2017b) Antifungal susceptibility and phenotypic virulence markers of Candida species isolated from Nepal. BMC Res Notes 10:543. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2852-x
Subramanya SH, Sharan NK, Baral BP, Hamal D, Nayak N, Prakash PY, Sathian B, Bairy I, Gokhale S (2017a) Diversity, in-vitro virulence traits and antifungal susceptibility pattern of gastrointestinal yeast flora of healthy poultry, Gallus gallus domesticus. BMC Microbiol 17:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-017-1024-4
Suh SO, Zhou J (2010) Yeasts associated with the curculionid beetle Xyloterinus politus: Candida xyloterini sp. nov., Candida palmyrensis sp. nov. and three common ambrosia yeasts. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(7):1702–1708. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.016907-0
Tafer H, Sterflinger K, Lopandic K (2016) Draft genome of Debaryomyces fabryi CBS 789T, isolated from a human interdigital mycotic lesion. Genome Announc 4(1):e01580–e01515. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomea.01580-15
Teodoro VLI, Gullo FP, Sardi JDCO, Torres EM, Fusco-Almeida AM, Mendes-Giannini MJS (2013) Environmental isolation, biochemical identification, and antifungal drug susceptibility of Cryptococcus species. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 46(6):759–764. https://doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0025-2013
Tsiodras S, Kelesidis T, Kelesidis I, Bauchinger U, Falagas ME (2008) Human infections associated with wild birds. J Infect 56(2):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2007.11.001
Vadkertiová R, Molnárová J, Vránová D, Sláviková E (2012) Yeasts and yeast-like organisms associated with fruits and blossoms of different fruit trees. Can J Microbiol 58(12):1344–1352. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2012-0468
Vale HMM, Reis JBA, Oliveira M, Moreira GAM, Bomfim CA (2021) Yeasts in native fruits from Brazilian neotropical savannah: occurrence, diversity and enzymatic potential. Biota Neotropica 21(4):e20201184. https://doi.org/10.1590/1676-0611-BN-2020-1184
Vidal E, Medail F, Tatoni T (1998) Is the yellow-legged gull a super abundant bird species in the Mediterranean? Impact on fauna and flora, conservation measure sand research priorities. Biodivers Conserv 7:1013–1026. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008805030578
Vu D, Groenewald M, Szöke S, Cardinali G, Eberhardt U, Stielow B, de Vries M, Verkleij GJM, Crous PW, Boekhout T, Robert V (2016) DNA barcoding analysis of more than 9 000 yeast isolates contributes to quantitative thresholds for yeast species and genera delimitation. Stud Mycol 85(1):91–105 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28050055/
Vylkova S, Lorenz MC (2012) Encounters with mammalian cells: survival strategies of Candida species. In: In Candida and Candidiasis, pp 261–282. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555817176.ch17
WHO (2022) WHO fungal priority pathogens list to guide research, development and public health action. World Health Organization, Geneva Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Wu Y, Du P-C, Li W-G, Lu J-X (2012) Identification and molecular analysis of pathogenic yeasts in droppings of domestic pigeons in Beijing, China. Mycopathologia 174:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-012-9536-9
Ying S, Chunyang L (2012) Correlation between phospholipase of Candida albicans and resistance to fluconazole. Mycoses 55(1):50–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0507.2011.02024.x
Yurkov AM (2018) Yeasts of the soil–obscure but precious. Yeast 35(5):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3310
Yurkov AM, Kemler M, Begerow D (2012) Assessment of yeast diversity in soils under different management regimes. Fungal Ecol 5:24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2011.07.004
Zar JH (1996) Biostatistical analysis, third edn. Prentice-Hall, London, p 662
Zwillenberg LO (1966) Torulopsis anatomiae, a new yeast resistant against low concentrations of formalin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 32:135–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02097453
Acknowledgements
The study was carried out on the scientific equipment of the Collective Usage Center “I.I. Mechnikov NIIVS,” Moscow, Russia, with the finantial support of the project by the Russian Federation represented by the Ministry of Science of Russia (Agreement No. 075-15-2021-676 dated 28.07.2021).
Funding
The study was funded by the Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Agreement No. 075-15-2021-1051) and as a part of the Scientific Project of the State Order of the Goverment of Russian Federation to Lomonosov Moscow State University (No. 121040800174-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
А.V. Kachalkin: conceptualization; data curation; visualization; writing original draft; funding acquisition; supervision. А.М. Glushakova: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; methodology; visualization; writing original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Lomonosov Moscow State University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Glushakova, A., Kachalkin, A. Wild and partially synanthropic bird yeast diversity, in vitro virulence, and antifungal susceptibility of Candida parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis strains isolated from feces. Int Microbiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00437-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00437-y