Abstract
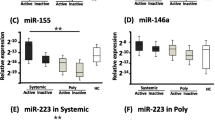
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is the most common chronic rheumatic disease of childhood, yet its etiology is unknown. It is known that microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) play a role in immunoregulation. We aimed to evaluate the plasma expression of some candidate miRNAs that are associated with the pathogenesis of autoimmunity. Thirty-one patients diagnosed with JIA and age-sex-matched 31 healthy children were enrolled for the study. The plasma levels of four candidate miRNAs (miRNA-16, miRNA-155, miRNA-204, and miRNA-451), which are known to be associated with autoimmunity, were examined in all the subjects. The plasma levels of miRNAs were measured with real-time PCR in the patients in active and inactive periods and in the healthy controls. The groups were compared with each other. The plasma miRNA-155 levels were found to increase in the JIA patients compared to the healthy controls, and it was statistically more significant in the inactive period. We found that the JIA patients had the higher levels of miRNA-16 and the lower levels of miRNA-204/miRNA-451 expressions compare with the control group, but there was no statistically significant difference. A statistically significant decrease in the plasma levels of miRNA-204 was found in the patients that were in inactive disease with only methotrexate therapy. The plasma miRNA expressions were compared in the JIA subtypes, and it was observed that miRNA-204 levels were higher in polyarticular JIA and miRNA-451 levels were higher in enthesitis-related arthritis without statistical significance. The significant alterations in the plasma expression of miRNA-155 and miRNA-204 suggest to us that these molecules may be related to the pathogenesis of JIA. More comprehensive and functional researches about the role of these molecules are needed in this regard.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cassidy JT, Petty RE (2011) Chronic arthritis in childhood. In: Cassidy JT, Petty RE, Laxer RM, Lindsley CB (eds) Textbook of pediatric rheumatology, 6th edn. Elsevier Inc, Philadelphia, pp 211–235
Jarvis JN, Jiang K, Frank MB, Knowlton N, Aggarwal A, Wallace CA, McKee R, Chaser B, Tung C, Smith LB, McGhee JL, Chen Y, Osban J, O’Neil KM, Centola M (2009) Gene expression profiling in neutrophils from children with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 60:1488–1495
Lin YT, Wang CT, Gershwin ME, Chiang BL (2011) The pathogenesis of oligoarticular/polyarticular vs systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 10:482–489
Kasapçopur Ö, Arısoy N (2003) Jüvenil idyopatik artrit. Türk Pediatri Arşivi 38:8–19
Tessitore A, Cicciarelli G, Del Vecchio F et al (2014) MicroRNAs in the DNA damage/repair network and cancer. Int J Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/820248
Raponi M, Dossey L, Jatkoe T, Wu X, Chen G, Fan H, Beer DG (2009) Micro RNA classifiers for predicting prognosis of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 69:5776–5783
Yu SL, Chen HY, Chang GC, Chen CY, Chen HW, Singh S, Cheng CL, Yu CJ, Lee YC, Chen HS, Su TJ, Chiang CC, Li HN, Hong QS, Su HY, Chen CC, Chen WJ, Liu CC, Chan WK, Chen WJ, Li KC, Chen JJW, Yang PC (2008) MicroRNA signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer Cell 13:48–57
Ventura A, Jacks T (2009) MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell 136:586–591
Ceribelli A, Yao B, Dominguez-Gutierrez PR et al (2011) MicroRNAs in systemic rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 13:229
Contreras J, Rao DS (2012) MicroRNAs in inflammation and immune responses. Leukemia 26:404–413
Carissimi C, Fulci V, Macino G (2009) MicroRNAs: novel regulators of immunity. Autoimmun Rev 8:520–524
Singh RP, Massachi I, Manickavel S, Singh S, Rao NP, Hasan S, Mc Curdy DK, Sharma S, Wong D, Hahn BH, Rehimi H (2013) The role of miRNA in inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 12:1160–1165
Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL et al (2008) Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 10:101
Hu Z, Jiang K, Frank MB, Chen Y, Jarvis JN (2016) Complexity and specificity of the neutrophil transcriptomes in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Sci Rep 6:27453
Stanczyk J, Pedrioli DM, Brentano F et al (2008) Altered expression of MicroRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:1001–1009
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S, Ballantine LE, Asquith DL, Millar NL, Gilchrist DS, Reilly J, Ierna M, Fraser AR, Stolarski B, McSharry C, Hueber AJ, Baxter D, Hunter J, Gay S, Liew FY, McInnes IB (2011) MicroRNA-155 as a proinflammatory regulator in clinical and experimental arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:11193–11198
Naraparaju K, Kolla V, Zhuang T, Higashi M, Iyer R, Kolla S, Okawa ER, Blobel GA, Brodeur GM (2016) Role of microRNAs in epigenetic silencing of the CHD5 tumor suppressor gene in neuroblastomas. Oncotarget 7:15977–15985
Butrym A, Rybka J, Baczyńska D, Tukiendorf A, Kuliczkowski K, Mazur G (2015) Low expression of microRNA-204 (miR-204) is associated with poor clinical outcome of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 34:68
Ma L, Deng X, Wu M, Zhang G, Huang J (2014) Down-regulation of miRNA-204 by LMP-1enhances CDC42 activity and facilitates invasion of EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett 588:1562–1570
Li K, Xyu Q, Liu X, Liu Q, Wang M (2015) Growth inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma by miRNA-204 via down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Sirt1 expression. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 31:168–172
Béres NJ, Kiss Z, Sztupinszki Z, Lendvai G, Arató A, Sziksz E, Vannay Á, Szabó AJ, Müller KE, Cseh Á, Boros K, Veres G (2017) Altered mucosal expression of microRNAs in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Liver Dis 49:378–387
Lai NS, Yu HC, Tung CH, Huang KY, Huang HB, Lu MC (2017) The role of aberrant expression of T cell miRNAs affected by TNF-α in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 19:261
Rosenberger CM, Podyminogin RL, Navarro G, Zhao GW, Askovich PS, Weiss MJ, Aderem A (2012) miR-451 regulates dendritic cell cytokine responses to influenza infection. J Immunol 189:5965–5975
Lucherini OM, Obici L, Ferracin M et al (2013) First report of circulating microRNAs in tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). PLoS One 8:73443
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN, Goldenberg J, He X, Maldonado-Cocco J, Orozco-Alcala J, Prieur AM, Suarez-Almazor ME, Woo P, International League of Associations for Rheumatology (2004) International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
Wallace CA, Giannini EH, Huang B, Itert L, Ruperto N, Childhood Arthritis Rheumatology Research Alliance, Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group, Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation (2011) American College of Rheumatology provisional criteria for defining clinical inactive disease in select categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:929–936
Sun J, Feng M, Wu F, Ma X, Lu J, Kang M, Liu Z (2016) Plasma miR-26a as a diagnostic biomarker regulates cytokine expression in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 43:1607–1614
Ma X, Wu F, Xin L et al (2015) Differential plasma microRNAs expression in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 20:1–9
Kamiya Y, Kawada J, Kawano Y, Torii Y, Kawabe S, Iwata N, Ito Y (2015) Serum microRNAs as potential biomarkers of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34:1705–1712
Li D, Duan M, Feng Y, Geng L, Li X, Zhang W (2016) MiR-146a modulates macrophage polarization in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis by targeting INHBA. Mol Immunol 77:205–212
Murata K, Yoshitomi H, Tanida S, Ishikawa M, Nishitani K, Ito H, Nakamura T (2010) Plasma and synovial fluid microRNAs as potential biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R86. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3013
Li X, Tian F, Wang F (2013) Rheumatoid arthritis-associated MicroRNA-155 targets SOCS1 and upregulates TNF-α and IL-1β in PBMCs. Int J Mol Sci 14:23910–23921
Ravelli A, Martini A (2007) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 369:767–778
Filkova M, Aradi B, Senolt L et al (2014) Association of circulating miR-223 and miR-16 with disease activity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1898–1904
Xia Z, Liu F, Zhang J et al (2015) Decreased expression of MiRNA-204-5p contributes to glioma progression and promotes glioma cell growth, migration and invasion. PLoS One 10:132399
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all participating children and their families.
Funding
This work is financially supported by Scientific Research Committee of the Karadeniz Technical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was carried out by Department of Pediatric Rheumatology and Department of Medical Genetics in Karadeniz Technical University, Faculty of Medicine. The protocol of the study was approved by the local ethics committee of the same university (Approval No.: 2015/198). All the participants and their legal guardians were informed, and their written consent was obtained.
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, F., Çebi, A.H. & Kalyoncu, M. Evaluation of plasma microRNA expressions in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 37, 3255–3262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4277-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4277-x