Abstract
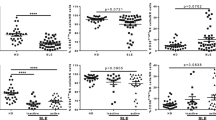
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the overall alterations of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). A total of 120 patients diagnosed with SLE and 64 health donors were enrolled. The lymphocyte subsets were detected using flow cytometry. Then the changes of lymphocyte subsets in patients and their correlation with disease activity were investigated. Compared with healthy controls, the counts of lymphocytes, T cells, B cells and NK cells in SLE patients were significantly decreased. Further analysis of T cells subpopulations revealed that the decrease in T cells counts in SLE patients was mainly attributed to a sharp decrease in CD4 + T cells counts. Meanwhile, there was a positive correlation between CD4 + T cells counts and serum complement 3 levels, and patients with lower CD4 + T cells counts had higher SLEDAI score. The counts of CD8 + T cells were comparable between SLE patients and controls, while the proportion of CD8 + T cells and cytotoxic T cells (CD8 + CD28 +) was prominently higher in SLE patients. Besides, the expression of HLA-DR on the surface of T and NK cells was significantly upregulated in SLE patients. Circulating lymphocyte subsets of SLE patients were seriously dysregulated, characterized by a decrease in CD4 + T cells and NK cells, as well as an increase in the proportion of activated T and NK cells. Reduction in CD4 + T cells in SLE patients was highly consistent with disease activity, indicating the crucial role of CD4 + T cells in the onset and progression of SLE.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(22):2110–21.
Fava A, Petri M. Systemic lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and clinical management. J Autoimmun. 2019;96:1–13.
Pons-Estel GJ, Alarcón GS, Scofield L, et al. Understanding the epidemiology and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39(4):257–68.
Fayyaz A, Igoe A, Kurien BT, et al. Haematological manifestations of lupus. Lupus Sci Med. 2015;2(1): e000078.
Rivero SJ, Díaz-Jouanen E, Alarcón-Segovia D. Lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical, diagnostic, and prognostic significance. Arthritis Rheum. 1978;21(3):295–305.
Rakebrandt N, Littringer K, Joller N. Regulatory T cells: balancing protection versus pathology. Swiss Med Wkly. 2016;146: w14343.
Ma K, Du W, Wang X, et al. Multiple functions of B cells in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6021.
Dema B, Charles N. Advances in mechanisms of systemic lupus erythematosus. Discov Med. 2014;17(95):247–55.
Mok CC. Current role of rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18(2):154–63.
Albert D, Dunham J, Khan S, et al. Variability in the biological response to anti-CD20 B cell depletion in systemic lupus erythaematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(12):1724–31.
Moulton VR, Tsokos GC. Abnormalities of T cell signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(2):207.
Crispín JC, Kyttaris VC, Juang YT, et al. How signaling and gene transcription aberrations dictate the systemic lupus erythematosus T cell phenotype. Trends Immunol. 2008;29(3):110–5.
Yang X, Wang W, Xu J, et al. Significant association of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells with clinical findings in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(5):93.
von Spee-Mayer C, Siegert E, Abdirama D, et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 selectively corrects regulatory T cell defects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(7):1407–15.
Gravano DM, Hoyer KK. Promotion and prevention of autoimmune disease by CD8+ T cells. J Autoimmun. 2013;45:68–79.
Minning S, Xiaofan Y, Anqi X, et al. Imbalance between CD8(+)CD28(+) and CD8(+)CD28(-) T-cell subsets and its clinical significance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2019;28(10):1214–23.
Zahran AM, Abdel-Rahim MH, Elsayh KI, et al. Natural killer and natural killer T cells in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus: relation to disease activity and progression. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019;67(3):161–9.
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcón GS, et al. Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2677–86.
Li C, Mu R, Lu XY, et al. Antilymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with disease activity and lymphopenia. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014: 672126.
Wofsy D, Seaman WE. Reversal of advanced murine lupus in NZB/NZW F1 mice by treatment with monoclonal antibody to L3T4. J Immunol. 1987;138(10):3247–53.
Rivero SJ, Llorente L, Díaz-Jouanen E, et al. T-lymphocyte subpopulation in untreated SLE. Variat Dis Act Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20(6):1169–73.
Tran DQ, Ramsey H, Shevach EM. Induction of FOXP3 expression in naive human CD4+FOXP3 T cells by T-cell receptor stimulation is transforming growth factor-beta dependent but does not confer a regulatory phenotype. Blood. 2007;110(8):2983–90.
Lyssuk EY, Torgashina AV, Soloviev SK, et al. Reduced number and function of CD4+CD25highFoxP3+ regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;601:113–9.
Alvarado-Sánchez B, Hernández-Castro B, Portales-Pérez D, et al. Regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2006;27(2):110–8.
Zhang B, Zhang X, Tang FL, et al. Clinical significance of increased CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(7):1037–40.
Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ. The B7-CD28 superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(2):116–26.
Fernández-Grande E, Cabrera CM, González B, et al. Enhanced HLA-DR expression on T-lymphocytes from patients in early stages of non-surgical sepsis. Med Clin (Barc). 2019;152(9):346–9.
Zhou H, Hu B, Huang N, et al. Aberrant T cell subsets and cytokines expression profile in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(9):2405–13.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Dr. Yu for her valuable assistance and all of the staff members of the Clinical Laboratory Centre. And I shall extend my thanks to my teacher Professor Jun He, who has helped me develop the fundamental and essential academic competence.
Funding
The authors have no funding to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZY and YL designed the project. ZY and WY conducted the experiment and analyzed the data. ZY drafted the manuscript and YL helped to revise the paper. YL approved the final version to be published. All the authors agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Qingdao Municipal Hospital Group, and the research was carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consents were obtained from all participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this research article and any accompanying images.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Yu, W. & Lu, Y. Circulating lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and their correlation with disease activity. Clin Exp Med 23, 4757–4763 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-01237-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-01237-4