Abstract
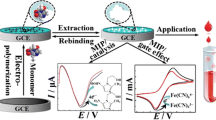
A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles immobilized on amine-multi-walled carbon nanotubes by the strong chemisorption had been developed for detecting dipyridamole (DIP) in human serum using precipitation polymerization method. DIP can be detected by this electrochemical sensor through the response current change before and after binding DIP with the formation of hydrogen bonds. The experimental binding data for this study was modeled with the Freundlich isotherm (FI) equation, demonstrating the high imprinting efficiency. The molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on Fe3O4@Au-MWCNT nanocomposite amplifies the response current in differential pulse voltammetry measurement, allowing the detection limit reaching 0.03 ng mL−1 in a wide linear range from 0.5 to 1900 ng mL−1, which is remarkably better than those of currently used methods and the previous reports. Moreover, this molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor has first been developed for the detection of DIP based on the Fe3O4@Au-MWCNT composite, which has a promising potential in the detection of DIP in human serum which enables low-cost, effective, and sensitive determination.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iuliano L, Pratico D, Ghiselli A, Bonavita MS, Violi F (1992) Reaction of dipyridamole with the hydroxyl radical. Lipids 27(5):349–353
Zhen YS, Taniki T, Weber G (1992) Azidothymidine and dipyridamole as biochemical response modifiers: synergism with methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil in human colon and pancreatic carcinoma cells. Oncol Res 4(2):73–78
Pulgarín JAM, Molina AA, López PF (1997) Direct determination of dipyridamole in serum. Anal Biochem 245(1):8–16
Salinas-Castillo A, Carretero AS, Fernández-Gutiérrez A (2003) Sensitive and simple determination of the vasodilator agent dipyridamole in pharmaceutical preparations by phosphorimetry. Anal Bioanal Chem 376(7):1111–1114
El-Ragehy NA, Hassan NY, Tantawy MA, Abdelkawy M (2016) Simultaneous determination of aspirin, dipyridamole and two of their related impurities in capsules by validated TLC-densitometric and HPLC methods. J Chromatogr Sci 54(7):1120–1128
Reddy DV, Sreelatha P, Devi BR (2015) A rapid novel RP-HPLC stability indicating assay method devel-opment and validation of dipyridamole in dipyridamole extended release capsules. Anal Chem 15(4):140–150
Abdel-Ghany M, Hussien L, Rahman MA (2016) Determination of dipyridamole in the presence of its degradation products and in the presence of aspirin. Anal Chem 16(8):344–361
Zhu G, Ju H, Zheng H (2004) Fluorescence spectroscopic determination of dipyridamole binding on pancreas-1 tumor cell membrane. Clin Chim Acta 348(1–2):101–106
Puram S, Batheja R, Vivekanand PA, Nallamekala SRB, Kubal A, Kalaivani RA (2016) Evaluation of aspirin and dipyridamole using low concentration potassium fluoride as a stabilizer in human plasma by LC-MS/MS mode. Asian J Chem 28(11):2403–2406
Oshrine B, Malinin A, Pokov A, Dragan A, Hanley D, Serebruany V (2005) Criticality of pH for accurate fluorometric measurements of dipyridamole levels in biological fluids. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 27(2):95–100
Ruiz-Medina A, Fernández-de Córdova ML, Molina-Díaz A (2001) A flow-through optosensing device with fluorimetric transduction for rapid and sensitive determination of dipyridamole in pharmaceuticals and human plasma. Eur J Pharm Sci 13(4):385–391
Wang L, Zhang Z (2008) Chemiluminescence imaging assay dipyridamole based on molecular imprinted polymer as recognition material. Sensors Actuators B Chem 133(1):40–45
Li C (2007) Electrochemical determination of dipyridamole at a carbon paste electrode using cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide as enhancing element. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 55(1):77–83
Li Y, Wen T, Xue C, Han Q, Wang Y, Hong J, Zhou X, Jiang H (2013) RGO LBL modified biomimetic electrochemical sensor for detection of Sildenafil in herbal sexual health products. Biosens Bioelectron 42:287–292
Xue C, Han Q, Wang Y, Wu J, Wen T, Wang R, Hong J, Zhou X, Jiang H (2013) Amperometric detection of dopamine in human serumby electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles doped molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens Bioelectron 49:199–203
Javanbakht M, Fathollahi F, Divsar F, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2013) A selective and sensitive voltammetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for the determination of dipyridamole in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids. Sensors Actuators B Chem 182:362–367
Xue X, Wei Q, Wu D, Li H, Zhang Y, Feng R, Du B (2014) Determination of methyl parathion by a molecularly imprinted sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene sheets. Electrochim Acta 116:366–371
Xing X, Liu S, Yu J, Lian W, Huang J (2012) Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted film at polypyrrole-sulfonated graphene/hyaluronic acid-multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for determination of tryptamine. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):277–283
Song H, Ni Y, Kokot S (2013) A novel electrochemical biosensor based on the hemin-graphene nano-sheets and gold nano-particles hybrid film for the analysis of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chim Acta 788:24–31
Liu HD, Zhang JL, Xu DD, Huang LH, Tan SZ, Mai WJ (2015) Easy one-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/iron oxide hybrid as efficient supercapacitor material. J Solid State Electrochem 19(1):135–144
Wang Y, Zhang H, Yao D, Pu J, Zhang Y, Gao X, Sun Y (2013) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin on graphene/Fe3O4 nanocomposite-modified glass carbon electrode and its sensitive detection for hydrogen peroxide. J Solid State Electrochem 17(3):881–887
Liu B, Tang D, Zhang B, Que X, Yang H, Chen G (2013) Au(III)-promoted magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres for electrochemical determination of streptomycin residues in food. Biosens Bioelectron 41:551–556
Liu M, Chen Q, Lai C, Zhang Y, Deng J, Li H, Yao S (2013) A double signal amplification platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen based on a nanocomposite of ferrocene thiolate stabilized Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles with graphene sheet. Biosens Bioelectron 48:75–81
Arvand M, Hassannezhad M (2014) Magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2/MWCNT nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode for amplified electrochemical sensing of uric acid. Mater Sci Eng C 36:160–167
Tang L, Tong Y, Zheng R, Liu W, Gu Y, Li C, Chen R, Zhang Z (2014) Ag nanoparticles and electrospun CeO2-Au composite nanofibers modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of levofloxacin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 203:95–101
Wang Y, Xie J, Tao L, Tian H, Wang S, Ding H (2014) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of epirubicin and methotrexate in human blood using a disposable electrode modified with nano-Au/MWNTs-ZnO composites. Sensors Actuators B Chem 204:360–367
Wang D, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang T (2012) Nanostructured Fe2O3–graphene composite as a novel electrode material for supercapacitors. J Solid State Electrochem 16(6):2095–2102
Zhang W, Wang L, Zheng X (2014) Indicator-free electrochemical genosensing originated from the self-signal of poly-xanthurenic acid enhanced by Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide. J Solid State Electrochem 18(9):2367–2373
Bian C-L, Zeng Q-X, Yang L-J, Xiong H-Y, Zhang X-H, Wang S-F (2011) Voltammetric studies of the interaction of rutin with DNA and its analytical applications on the MWNTs–COOH/Fe3O4 modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 156(2):615–620
Li Y, Zhao X, Li P, Huang Y, Wang J, Zhang J (2015) Highly sensitive Fe(3)O(4) nanobeads/graphene-based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for 17beta-estradiol in water. Anal Chim Acta 884:106–113
Raoof JB, Ojani R, Baghayeri M, Amiri-Aref M (2012) Application of a glassy carbon electrode modified with functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a sensor device for simultaneous determination of acetaminophen and tyramine. Anal Methods 4(6):1579–1587
Xuan S, Wang F, Wang Y-X J, Yu JC, Leung KC-F (2010) Facile synthesis of size-controllable monodispersed ferrite nanospheres. J Mater Chem 20(24):5086–5094
Liang R-P, Yao G-H, Fan L-X, Qiu J-D (2012) Magnetic Fe3O4@Au composite-enhanced surface plasmon resonance for ultrasensitive detection of magnetic nanoparticle-enriched α-fetoprotein. Anal Chim Acta 737:22–28
Baghayeri M, Veisi H (2015) Fabrication of a facile electrochemical biosensor for hydrogen peroxide using efficient catalysis of hemoglobin on the porous Pd@Fe3O4-MWCNT nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 74:190–198
Haghshenas E, Madrakian T, Afkhami A (2015) A novel electrochemical sensor based on magneto Au nanoparticles/carbon paste electrode for voltammetric determination of acetaminophen in real samples. Mater Sci Eng C 57:205–214
Kassaee MZ, Masrouri H, Movahedi F (2011) Sulfamic acid-functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an efficient and reusable catalyst for one-pot synthesis of α-amino nitriles in water. Appl Catal A Gen 395(1–2):28–33
Zhou H, Gan N, Li T, Cao Y, Zeng S, Zheng L, Guo Z (2012) The sandwich-type electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for α-fetoprotein based on enrichment by Fe3O4-Au magnetic nano probes and signal amplification by CdS-Au composite nanoparticles labeled anti-AFP. Anal Chim Acta 746:107–113
Han F, Ma L, Sun Q, Lei C, Lu A (2014) Rationally designed carbon-coated Fe3O4 coaxial nanotubes with hierarchical porosity as high-rate anodes for lithium ion batteries. Nano Res 7(11):1706–1717
Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Chi M, Yang Z, Nie G, Lu X, Wang C (2016) Fabrication of Au nanoparticles supported on CoFe2O4 nanotubes by polyaniline assisted self-assembly strategy and their magnetically recoverable catalytic properties. Appl Surf Sci 363:578–585
Wang S, Wang R, Wu X, Wang Y, Xue C, Wu J, Hong J, Liu J, Zhou X (2012) Magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based on dendritic-grafting modification for determination of estrogens in plasma samples. J Chromatogr B 905:105–112
Hu S, Wu K, Yi H, Cui D (2002) Voltammetric behavior and determination of estrogens at Nafion-modified glassy carbon electrode in the presence of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Anal Chim Acta 464(2):209–216
Motaharian A, Motaharian F, Abnous K, Hosseini MRM, Hassanzadeh-Khayyat M (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based electrochemical sensor for determination of diazinon pesticide in well water and apple fruit samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(24):6769–6779
Rezaei B, Foroughi-Dehnavi S, Ensafi AA (2015) Fabrication of electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and nanoparticles for determination trace amounts of morphine. Ionics 21(10):2969–2980
Liu Y, Liu J, Liu J, Gan W, B-c Y, Li Y (2017) Highly sensitive and selective voltammetric determination of dopamine using a gold electrode modified with a molecularly imprinted polymeric film immobilized on flaked hollow nickel nanospheres. Microchim Acta 184(5):1285–1294
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Two-Way Support Programs of Sichuan Agricultural University (Proect No. 03570113), the Education Department of Sichuan Provincial, PR China (Grant No.16ZA0039). We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6210 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhong, J., Rao, H. et al. Electrochemical dipyridamole sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on electrode modified with Fe3O4@Au/amine-multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Solid State Electrochem 21, 3071–3082 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3650-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3650-z