Abstract
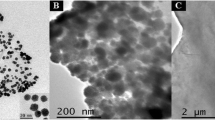
In this paper, an indicator-free electrochemical genosensing platform based on the self-signal changes of poly-xanthurenic acid (PXa) enhanced by Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide (Fe3O4/RGO) was constructed. The resulting nanocomposite (PXa-Fe3O4/RGO) was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The π–π* stacking and hydrogen bonding between the conjugated Fe3O4/GO and aromatic ring of xanthurenic acid monomer promoted the electropolymerization efficiency accompanied with an increased electrochemical response of PXa. The immobilization of the specific probe DNA was successfully realized via the noncovalent method due to the π–π* interaction between the conjugated nanostructure of PXa-Fe3O4/RGO and DNA bases. The hybridization between the probe DNA and target DNA induced the resulted double-stranded (ds)DNA to be released from the conjugated nanocomposite, accompanied with the self-signal regeneration of nanocomposite (“signal-on”). The self-signal changes could serve as a powerful tool for indicator-free and freely switchable detection of different target genes, and the synergistic effect of the integrated graphene-based nanocomposite effectively improved the sensitivity for the target DNA detection via EIS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sassolas A, Leca-Bouvier BD, Blum LJ (2008) DNA biosensors and microarrays. Chem Rev 108:109–139
Liu AL, Wang K, Weng SH, Lei Y, Lin LQ, Chen W, Lin XH, Chen YZ (2012) Development of electrochemical DNA biosensors. Trends Anal Chem 37:101–111
Hu YW, Li FH, Bai XX, Li D, Hua SC, Wang KK, Niu L (2011) Label-free electrochemical impedance sensing of DNA hybridization based on functionalized graphene sheets. Chem Commun 47:1743–1745
Li L, Wang S, Yang T, Huang SM, Wang JC (2012) Electrochemical growth of gold nanoparticles on horizontally aligned carbon nanotubes: a new platform for ultrasensitive DNA sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 33:279–283
Zhang W (2013) High-performance impedimetric genosensor based on biocompatible TiO2 nanoparticles supported carbon ionic liquid electrode. Sensors Actuators B 176:386–389
Hu YW, Yang T, Wang XX, Jiao K (2010) Highly sensitive indicator-free impedance sensing of DNA hybridization based on poly(m-aminobenzenesulfonic acid)/TiO2 nanosheet membranes with pulse potentiostatic method preparation. Chem Eur J 16:1992–1999
Peng H, Zhang LJ, Soeller C, Travas-Sejdic J (2009) Conducting polymers for electrochemical DNA sensing. Biomaterials 30:2132–2148
Bo Y, Yang HY, Hu Y, Yao TM, Huang SS (2011) A novel electrochemical DNA biosensor based on graphene and polyaniline nanowires. Electrochim Acta 56:2676–2681
Silva FAS, Lopes CB, Costa EO, Lima PR, Kubota LT, Goulart MOF (2010) Poly-xanthurenic acid as an efficient mediator for the electrocatalytic oxidation of NADH. Electrochem Commun 12:450–454
Lin KC, Li YS, Chen SM (2013) Electrochemical determination of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and hydrogen peroxide based on poly(xanthurenic acid), flavin adenine dinucleotide and functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sensors Actuators B 184:212–219
Weiss NO, Zhou HL, Liao L, Liu Y, Jiang S, Huang Y, Duan XF (2012) Graphene: an emerging electronic material. Adv Mater 24:5782–5825
Luo ZM, Ma XB, Yang DL, Yuwen LH, Zhu XR, Weng LX, Wang LH (2013) Synthesis of highly dispersed titanium dioxide nanoclusters on reduced graphene oxide for increased glucose sensing. Carbon 57:470–476
Nayak P, Anbarasan B, Ramaprabhu S (2013) Fabrication of organophosphorus biosensor using ZnO nanoparticle-decorated carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid composite prepared by a novel green technique. J Phys Chem C 117:13202–13209
Dong XC, Ma YW, Zhu GY, Huang YX, Wang J, Chan-Park MB, Wang LH, Huang W, Chen P (2012) Synthesis of grapheme-carbon nanotube hybrid foam and its use as a novel three-dimensional electrode for electrochemical sensing. J Mater Chem 22:17044–17048
Feng XM, Li RM, Ma YW, Chen RF, Shi NE, Fan QL, Huang W (2011) One-step electrochemical synthesis of graphene/polyaniline composite film and its applications. Adv Funct Mater 21:2989–2996
Yang T, Guan Q, Guo XH, Meng L, Du M, Jiao K (2013) Direct and freely switchable detection of target genes engineered by reduced graphene oxide-poly(m-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) nanocomposite via synchronous pulse electrosynthesis. Anal Chem 85:1358–1366
Yang T, Li QH, Li X, Wang XH, Du M, Jiao K (2013) Freely switchable impedimetric detection of target gene sequence based on synergistic effect of ERGNO/PANI nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 42:415–418
Bonanni A, Pumera M (2011) Graphene platform for hairpin-DNA-based impedimetric genosensing. ACS Nano 5:2356–2361
Jiang C, Yang T, Jiao K, Gao HW (2008) A DNA electrochemical sensor with poly-l-lysine/single-walled carbon nanotubes films and its application for the highly sensitive EIS detection of PAT gene fragment and PCR amplification of NOS gene. Electrochim Acta 53:2917–2924
Song YH, He ZF, Hou HQ, Wang XL, Wang L (2012) Architecture of Fe3O4-graphene oxide nanocomposite and its application as a platform for amino acid biosensing. Electrochim Acta 71:58–65
Haccoun J, Piro B, Tran LD, Dang LA, Pham MC (2004) Reagentless amperometric detection of l-lactate on an enzyme-modified conducting copolymer poly(5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone-co-5-hydroxy-3-thioacetic acid-1,4-naphthoquinone). Biosens Bioelectron 19:1325–1329
Zhang W, Yang T, Jiao K (2012) Ultrasensitive indicator-free and enhanced self-signal nanohybrid DNA sensing platform based on electrochemically grown poly-xanthurenic acid/Fe2O3 membranes. Biosens Bioelectron 31:182–189
Bonanni A, del Valle M (2010) Use of nanomaterials for impedimetric DNA sensors: a review. Anal Chim Acta 678:7–17
Hu YW, Wang KK, Zhang QX, Li FH, Wu TS, Niu L (2012) Decorated graphene sheets for label-free DNA impedance biosensing. Biomaterials 33:1097–1106
Wang L, Zhang YW, Tian JQ, Li HL, Sun XP (2011) Conjugation polymer nanobelts: a novel fluorescent sensing platform for nucleic acid detection. Nucleic Acids Res 39:e37
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21205057, 21101087, 21375057), Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2010BQ030), and the Doctoral Fund and Scientific Research Project of Linyi University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Wang, L. & Zheng, X. Indicator-free electrochemical genosensing originated from the self-signal of poly-xanthurenic acid enhanced by Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide. J Solid State Electrochem 18, 2367–2373 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2487-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2487-y