Abstract
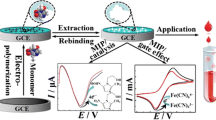
A novel electrochemical sensor based on dual-template molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) with nanoporous gold leaf (NPGL) was established for the simultaneous determination of dopamine (DA) and uric acid (UA). NPGL acts as an enlarged loading platform to enhance sensing capacity, and the MIP layer was synthesized in situ in the presence of monomer and dual templates (DA and UA) to provide specific recognition. Under the optimal conditions, the sensor shows a good linear range of 2.0~180 μM for DA at a working potential of 0.15 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) and 5.0~160 μM for UA at 0.35 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), with the respective detection limit of 0.3 μM and 0.4 μM (S/N = 3). Good selectivity of the sensor to its dual templates was confirmed as the sensing signals are significantly different between templates and interfering species. The responses maintained higher than 96% of the initial values after 30-day storage, and the day-to-day relative standard deviation is less than 3.0%. Real sample simultaneous determination of DA and UA was conducted with bovine serum, and the results were in good agreement with those from high-performance liquid chromatography. It can be concluded that this work offers a reliable, facile, fast, and cost-effective method of simultaneous quantification of two or more chem-/bio-molecules.

Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wightman RM, Amatore C, Engstrom RC, Hale PD, Kristensen EW, Kuhr WG, May LJ (1988) Real-time characterization of dopamine overflow and uptake in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 25:513–523
Xu T, Zhang Q, Zheng J, Lv Z, Wei J, Wang A, Feng J (2014) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using Pt nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide. Electrochim Acta 115:109–115
Mo JW, Ogorevc B (2001) Simultaneous measurement of dopamine and ascorbate at their physiological levels using voltammetric microprobe based on overoxidized poly(1,2-phenylenediamine)-coated carbon fiber. Anal Chem 73:1196–1202
Perreault ML, Hasbi A, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2014) Heteromeric dopamine receptor signaling complexes: emerging neurobiology and disease relevance. Neuropsychopharmacol 39:156–168
Erkal A, Aşık İ, Yavuz S, Kariper A, Üstündağ Z (2016) Biosensor application of carbonaceous nanocoil material: preparation, characterization, and determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. J Electrochem Soc 163:H269–H277
Huang J, Liu Y, Hou H, You T (2008) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid using palladium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24:632–637
Yu S, Luo C, Wang L, Peng H, Zhu Z (2013) Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-modified Ni/silicon microchannel plate electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Analyst 138:1149–1155
Lakshmi D, Whitcombe MJ, Davis F, Sharma PS, Prasad BB (2011) Electrochemical detection of uric acid in mixed and clinical samples: a review. Electroanal 23:305–320
Szantai E, Szilagyi A, Guttman A, Sasvari-Szekely M, Ronai Z (2004) Genotyping and haplotyping of the dopamine D4 receptor gene by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1053:241–245
Gui R, Jin H, Guo H, Wang Z (2018) Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 100:56–70
Creery M, Richard L (2008) Advanced carbon electrode materials for molecular electrochemistry. Chem Rev 108:2646–2687
Ronkainen NJ, Halsall HB, Heineman WR (2010) Electrochemical biosensors. Chem Soc Rev 39:1747–1763
Zhu C, Yang G, Li H, Du D, Lin Y (2014) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal Chem 87:230–249
Li Y, Song H, Zhang L, Zuo P, Ye B, Yao J, Chen W (2016) Supportless electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer modified nanoporous microrod for determination of dopamine at trace level. Biosens Bioelectron 78:308–314
Liu Y, Liu J, Liu J, Gan W, Ye B, Li Y (2017) Highly sensitive and selective voltammetric determination of dopamine using a gold electrode modified with a molecularly imprinted polymeric film immobilized on flaked hollow nickel nanospheres. Microchim Acta 184:1285–1294
Zheng C, Zhang X, Liu W, Liu B, Yang H, Lin Z, Chen G (2013) A selective artificial enzyme inhibitor based on nanoparticle-enzyme interactions and molecular imprinting. Adv Mater 25:5922–5927
Suryanarayanan V, Wu C, Ho K (2010) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors. Electroanal 22:1795–1811
Fatma S, Prasad BB, Jaiswal S, Singh R, Singh K (2019) Electrochemical simultaneous analysis of dopamine and epinephrine using double imprinted one monomer acryloylated graphene oxide-carbon black composite polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 135:36–44
Afkhami A, Ghaedi H, Madrakian T, Ahmadi M, Mahmood-Kashani H (2013) Fabrication of a new electrochemical sensor based on a new nano-molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective and sensitive determination of tramadol in human urine samples. Biosens Bioelectron 44:34–40
Bali Prasad B, Jauhari D, Tiwari MP (2013) A dual-template imprinted polymer-modified carbon ceramic electrode for ultra trace simultaneous analysis of ascorbic acid and dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 50:19–27
Lu Z, Li Y, Liu T, Wang G, Sun M, Jiang Y, He H, Wang Y, Zou P, Wang X, Zhao Q, Rao H (2020) A dual-template imprinted polymer electrochemical sensor based on AuNPs and nitrogen-doped graphene oxide quantum dots coated on NiS2/biomass carbon for simultaneous determination of dopamine and chlorpromazine. Chem Eng J 389:124417
Rezaei B, Rahmanian O (2011) Nanolayer treatment to realize suitable configuration for electrochemical allopurinol sensor based on molecular imprinting recognition sites on multiwall carbon nanotube surface. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 160:99–104
Li Y, Liu Y, Liu J, Liu J, Tang H, Cao C, Zhao D, Ding Y (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer decorated nanoporous gold for highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensors. Sci Rep 5:7699
Liu Y, Liu J, Tang H, Liu J, Xu B, Yu F, Li Y (2015) Fabrication of highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor by using optimized molecularly imprinted polymers on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for metronidazole measurement. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 206:647–652
Motia S, Tudor IA, Madalina Popescu L, Piticescu RM, Bouchikhi B, El Bari N (2018) Development of a novel electrochemical sensor based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer for selective detection of sodium lauryl sulfate in environmental waters and cosmetic products. J Electroanal Chem 823:553–562
Rong L, Yang C, Qian Q, Xia X (2007) Study of the nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes. Talanta 72:819–824
Nantaphol S, Chailapakul O, Siangproh W (2015) Sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor using silver nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of cholesterol in bovine serum. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 207:193–198
AaAmadio BT, Amako K, Coutinho YA, Amelung C, Grosse-Knetter J (2016) Search for invisible decays of a Higgs boson using vector-boson fusion in pp collisions at root s=8 TeV with the ATLAS detector. J High Energy Phys
Li Y, Zhang L, Liu J, Zhou S, Al-Ghanim KA, Mahboob S, Ye B, Zhang X (2016) A novel sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on a nanoporous gold leaf modified electrode for warfarin sodium determination. RSC Adv 6:43724–43731
Scanlon MD, Salaj-Kosla U, Belochapkine S, MacAodha D, Leech D, Ding Y, Magner E (2011) Characterization of nanoporous gold electrodes for bioelectrochemical applications. Langmuir 28:2251–2261
Li Y, Liu J, Yu F, Tang H, Zhao F, Ye B, Chen W, Lv X (2015) Electrochemical determination of trace lead(II) with enhanced sensitivity and selectivity by three-dimensional nanoporous gold leaf and self-assembled homocysteine monolayer. J Electroanal Chem 758:78–84
Zhang L, Liu C, Wang Q, Wang X, Wang S (2020) Electrochemical sensor based on an electrode modified with porous graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets (C3N4) embedded in graphene oxide for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 187:149
Wang Z, Yue H, Huang S, Yu Z, Gao X, Chen H, Wang W, Song S, Guan E, Zhang H (2019) Gold nanoparticles anchored onto three-dimensional graphene: simultaneous voltammetric determination of dopamine and uric acid. Mikrochim Acta 186:573
Chen Y, Zhang X, Wang A, Zhang Q, Huang H, Feng J (2019) Ultrafine Fe3C nanoparticles embedded in N-doped graphitic carbon sheets for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and xanthine. Microchim Acta 186:660
Chen A, Chatterjee S (2013) Nanomaterials based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 42:5425–5438
Posha B, Kuttoth H, Sandhyarani N (2019) 1-Pyrene carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube-gold nanoparticle nanocomposite for electrochemical sensing of dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 186:672
Krishnan S, Tong L, Liu S, Xing R (2020) A mesoporous silver-doped TiO2-SnO2 nanocomposite on g-C3N4 nanosheets and decorated with a hierarchical core-shell metal-organic framework for simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Mikrochim Acta 187:82
Madhuvilakku R, Piraman S (2019) One-dimensional NiFe2O4 nanorods modified with sulfur-rich spherical carbon nanoparticles for simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 186:434
Cheng M, Zhang X, Wang M, Huang H, Ma J (2017) A facile electrochemical sensor based on well-dispersed graphene-molybdenum disulfide modified electrode for highly sensitive detection of dopamine. J Electroanal Chem 786:1–7
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by Shenzhen science and technology research and development fund (JCYJ20180305180609083), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (KQJSCX20180328165437711, KQTD20170810105439418), the project on the key technique improvement of Xinjiang Licorice planting and quality control of Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps (2018AB012), Innovative team and talent training project of Shihezi (2018TD02), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773680, 81973280).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2.16 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Nan, C., Mei, X. et al. Electrochemical sensor based on dual-template molecularly imprinted polymer and nanoporous gold leaf modified electrode for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 187, 496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04413-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04413-5